7 Ways to Solve 2 Step Equations Easily
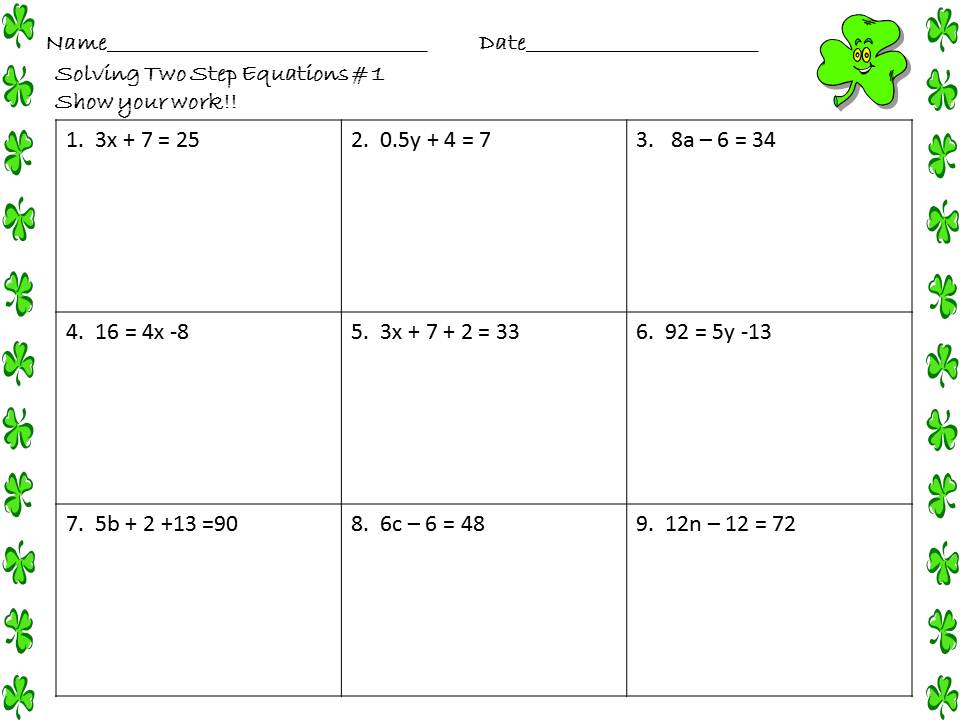
Understanding the Basics of 2-Step Equations

When dealing with 2-step equations, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of the basics. A 2-step equation is a linear equation that requires two operations to solve for the variable. These equations are typically represented in the form of ax + b = c, where a, b, and c are constants. To solve 2-step equations, you’ll need to perform two inverse operations to isolate the variable.
Breaking Down the Problem
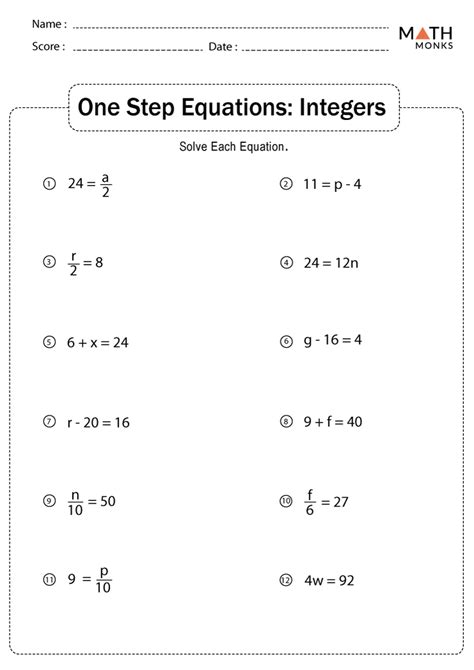
Before diving into the solution, take a moment to analyze the equation. Identify the variable and the constants. Look for any patterns or relationships between the numbers. This will help you determine the best approach to solve the equation.
Step 1: Simplify the Equation (If Necessary)
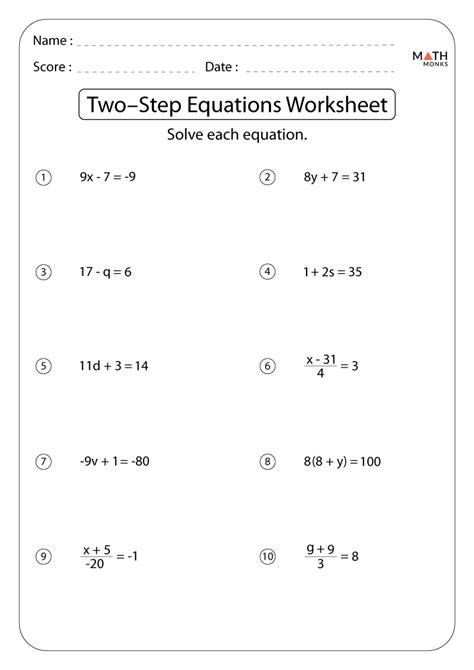
Sometimes, 2-step equations can be simplified by combining like terms or eliminating any unnecessary symbols. For example, if the equation is 2x + 3 + 2 = 7, you can combine the constants by adding 3 and 2, resulting in 2x + 5 = 7.
7 Strategies to Solve 2-Step Equations Easily
Here are seven strategies to help you solve 2-step equations with ease:
1. Add or Subtract the Same Value to Both Sides
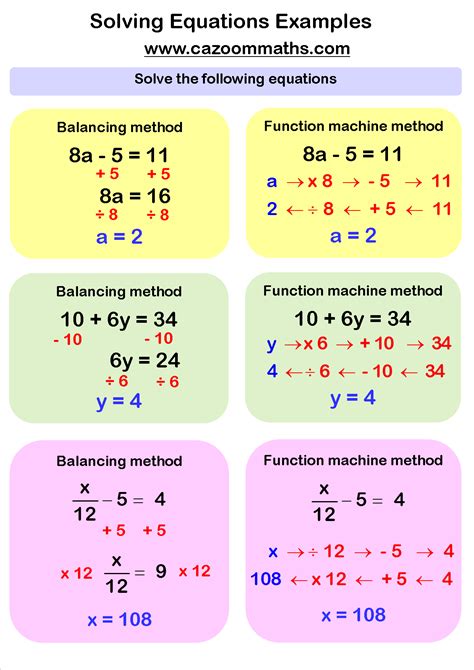
This strategy involves adding or subtracting the same value to both sides of the equation to eliminate the constant. For example, if the equation is x + 3 = 5, you can subtract 3 from both sides, resulting in x = 2.
2. Multiply or Divide Both Sides by the Same Value

This strategy involves multiplying or dividing both sides of the equation by the same value to eliminate the coefficient. For example, if the equation is 2x = 6, you can divide both sides by 2, resulting in x = 3.
3. Use the Inverse Operation to Isolate the Variable

This strategy involves using the inverse operation to isolate the variable. For example, if the equation is x - 2 = 3, you can add 2 to both sides, resulting in x = 5.
4. Use Parentheses to Simplify the Equation

Sometimes, 2-step equations can be simplified by using parentheses to group like terms. For example, if the equation is 2(x + 3) = 12, you can distribute the 2 and then solve for x.
5. Use the Order of Operations to Evaluate the Equation

This strategy involves using the order of operations (PEMDAS) to evaluate the equation. For example, if the equation is 2x + 3^2 = 11, you can evaluate the exponent first, resulting in 2x + 9 = 11.
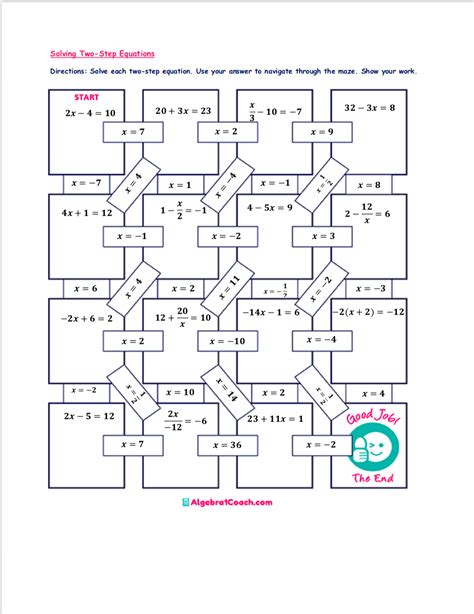
6. Check Your Solution by Plugging It Back into the Original Equation

Once you’ve solved the equation, plug your solution back into the original equation to ensure it’s correct. For example, if the equation is x + 2 = 5 and you think the solution is x = 3, plug x = 3 back into the equation to get 3 + 2 = 5, which is true.
7. Use Real-World Applications to Make the Equation More Meaningful

Finally, try to use real-world applications to make the equation more meaningful. For example, if the equation is 2x + 5 = 11 and you’re trying to find the cost of x number of items that cost $5 each, you can use this context to make the equation more relatable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When solving 2-step equations, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
💡 Note: Make sure to perform the inverse operation to isolate the variable. For example, if the equation is x + 2 = 5, you need to subtract 2 from both sides, not add 2.
📝 Note: Check your solution by plugging it back into the original equation. This ensures that your solution is correct and helps you avoid errors.
🤔 Note: Be careful when using parentheses to group like terms. Make sure to distribute any coefficients outside the parentheses to the terms inside.
Conclusion
Solving 2-step equations can seem daunting at first, but with practice and persistence, it becomes easier. By breaking down the problem, using the seven strategies outlined above, and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll become a pro at solving 2-step equations in no time. Remember to always check your solution and use real-world applications to make the equation more meaningful.
What is a 2-step equation?

+
A 2-step equation is a linear equation that requires two operations to solve for the variable.
How do I simplify a 2-step equation?
+
You can simplify a 2-step equation by combining like terms, eliminating any unnecessary symbols, or using parentheses to group like terms.
What is the inverse operation?
+The inverse operation is the opposite operation used to isolate the variable. For example, if the equation is x + 2 = 5, the inverse operation is subtracting 2 from both sides.
How do I check my solution?
+You can check your solution by plugging it back into the original equation to ensure it’s correct.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when solving 2-step equations?
+Some common mistakes to avoid include not performing the inverse operation, not checking your solution, and not using parentheses correctly.
Related Terms:
- Multi Step Equations Worksheet
- One step Equations Worksheet



