5 Essential Tips for Solubility Worksheet Answers Chemistry

Solubility, a fundamental concept in chemistry, underpins numerous applications from pharmaceuticals to environmental science. Understanding solubility isn't just about memorizing solubility charts; it involves comprehending the interactions at a molecular level. Here are 5 essential tips for accurately completing solubility worksheet answers, which will enhance your understanding of this complex yet fascinating topic.
1. Understand the Basics of Solubility


Solubility is defined as the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature. To master solubility worksheets:
- Memorize the Solubility Rules: Learn the solubility rules which dictate when salts are soluble or insoluble. Common ions that form soluble salts include sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and nitrate (NO3-).
- Understand Intermolecular Forces: Solubility often depends on the type of intermolecular forces between solute and solvent. Like dissolves like; polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents and vice versa.
🌟 Note: Knowing the temperature-dependence of solubility can be crucial for experimental chemistry, where temperature changes can significantly alter solubility.
2. Apply the Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)

| Salt | Ksp |
|---|---|
| AgCl | 1.8 × 10^-10 |
| Ca(OH)2 | 4.7 × 10^-6 |

The Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) is a quantitative measure of the solubility of an ionic compound. Here are the steps to use it:
- Write the Equilibrium Expression: For a salt like AgCl, the dissociation equilibrium is AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq), and Ksp = [Ag+][Cl-].
- Understand the Concept: A larger Ksp value indicates higher solubility. However, Ksp doesn’t tell you how much of the solute will dissolve but rather the equilibrium concentrations when dissolved.
🔍 Note: Ksp can also help in predicting precipitation reactions when ion concentrations exceed the Ksp value.
3. Recognize Solubility Exceptions
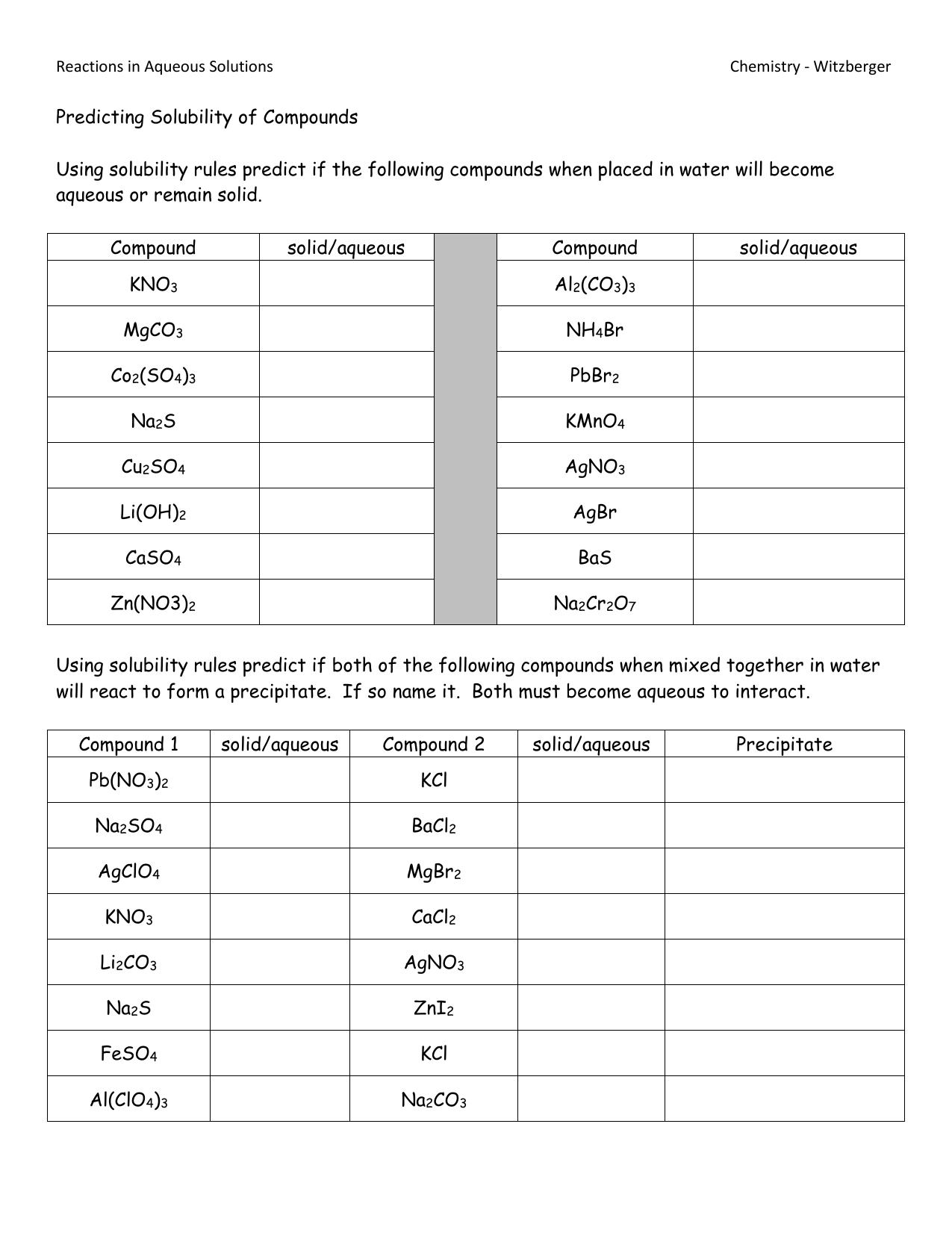
Not all ions follow the basic solubility rules, and exceptions can be key in solving complex solubility problems:
- Exceptions to Solubility Rules: Some common exceptions include:
- Carbonates and phosphates of Group 1 metals are soluble, despite the general rule for carbonates and phosphates.
- Sulphates of Pb2+, Ag+, Hg22+, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ are insoluble despite the general solubility of sulphates.
- Understand Why Exceptions Exist: These exceptions often relate to the energetics involved in the formation of the precipitate or the hydration energy of the ions.
4. Use Temperature and Pressure Effects

Solubility changes with alterations in temperature and, to a lesser extent, pressure:
- Effect of Temperature: For most ionic compounds, solubility increases with temperature. However, for substances like sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), solubility decreases with an increase in temperature.
- Pressure and Gases: Gases are more soluble in liquids at lower temperatures and higher pressures. Henry’s law describes this behavior.
🌡️ Note: Be aware of the anomalies in solubility-temperature relationships, especially when dealing with exothermic dissolution processes.
5. Work with Practice Problems and Real-World Examples

Applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios is vital for mastering solubility:
- Solve Real-World Problems: Consider pharmaceutical applications where solubility affects drug formulation, or environmental scenarios where solubility plays a role in pollution remediation.
- Use Practice Worksheets: Engage in solubility problem-solving exercises, focusing on the application of rules, Ksp calculations, and temperature effects.
In summary, mastering solubility involves understanding the fundamental principles of solute-solvent interactions, applying solubility rules and exceptions, recognizing the impact of temperature and pressure, and continually practicing with real-world scenarios. By incorporating these five essential tips, students and chemists can enhance their ability to predict and analyze solubility behaviors, crucial for many chemical processes and applications.
What is the importance of solubility in everyday life?

+
Solubility affects many aspects of daily life, from the taste of beverages due to sugar solubility to the effectiveness of medicines. Understanding solubility helps in cooking, environmental cleanup, and even in industrial processes where solubility impacts efficiency.
Can solubility rules ever change?

+
While the basic solubility rules remain consistent, certain conditions like temperature, pressure, and pH can change the solubility of a substance. Also, the rules might not apply in unusual solvents or under extreme conditions.
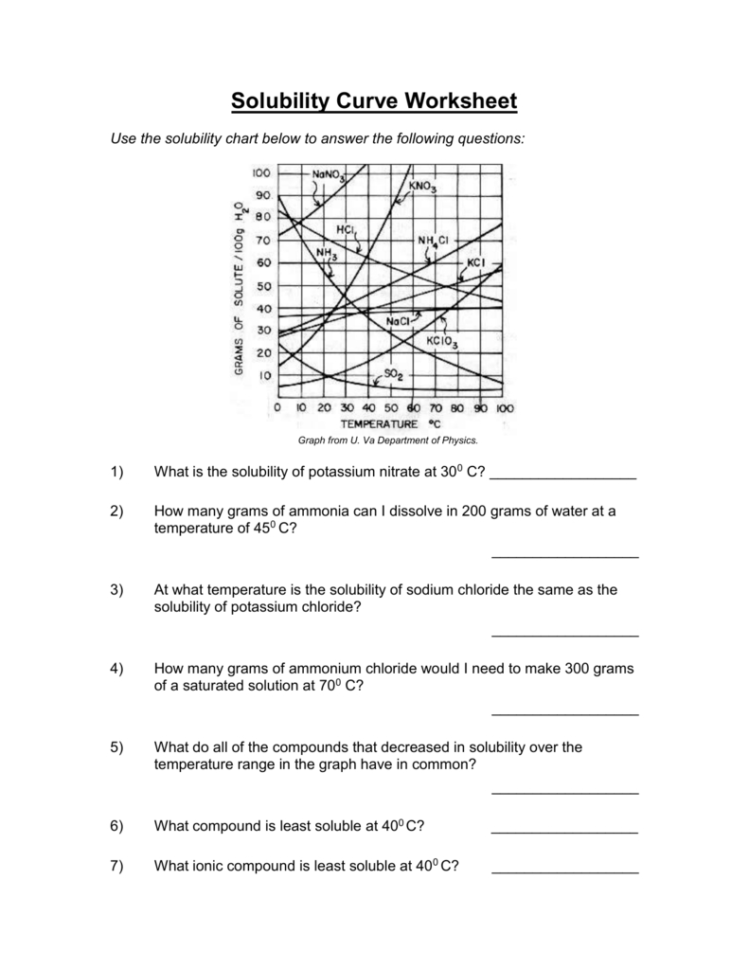
Why does temperature affect solubility?
+
Temperature affects solubility because it changes the kinetic energy of the particles. Higher temperatures typically increase the solubility of solids by allowing the solvent molecules to break down solute more effectively. For gases, increasing temperature usually decreases solubility as gas molecules escape more readily from the solution.



