Solubility Rules Worksheet: Boost Your Chemistry Skills

Whether you're navigating through high school chemistry or delving into advanced topics in college, mastering solubility rules is fundamental to understanding chemical reactions and solutions. This detailed guide will walk you through solubility rules, their application, and why they're crucial in both theoretical and practical chemistry.
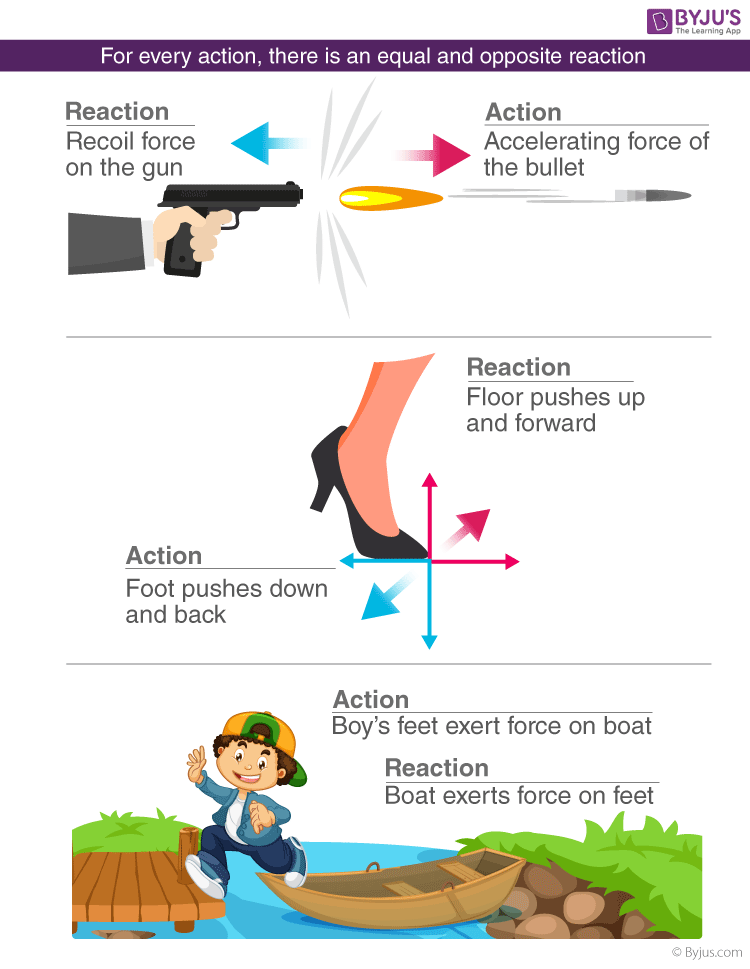
What Are Solubility Rules?


Solubility rules are a set of guidelines to predict whether a substance will dissolve in water or another solvent. These rules are especially useful in determining the products of precipitation reactions where one or more compounds form an insoluble solid.
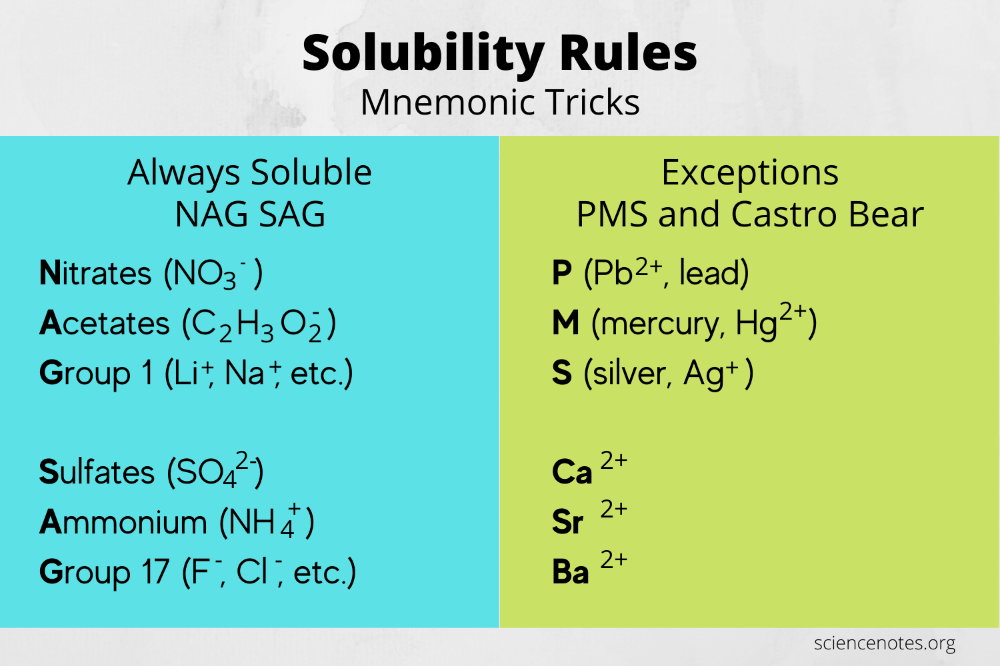
- All group IA (alkali metals) and ammonium salts are soluble.
- All nitrates (NO3-), acetates (CH3COO-), and chlorates (ClO3-) are soluble.
- Most chlorides (Cl-) are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg, and Pb.
- Bromides (Br-) and iodides (I-) follow similar solubility rules as chlorides.
- All sulfates (SO42-) are soluble, except those of Ba, Sr, Ca, Ag, and Hg.
Why Solubility Matters?

Understanding solubility can help you:
- Predict the formation of precipitates: Knowing which compounds are soluble helps in predicting which chemical reactions will result in a visible precipitate.
- Design industrial processes: Many industries, including pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and material science, depend on solubility rules to develop and optimize processes.
- Environmental impact assessments: Solubility data helps in assessing how pollutants might spread in water bodies.
Applying Solubility Rules
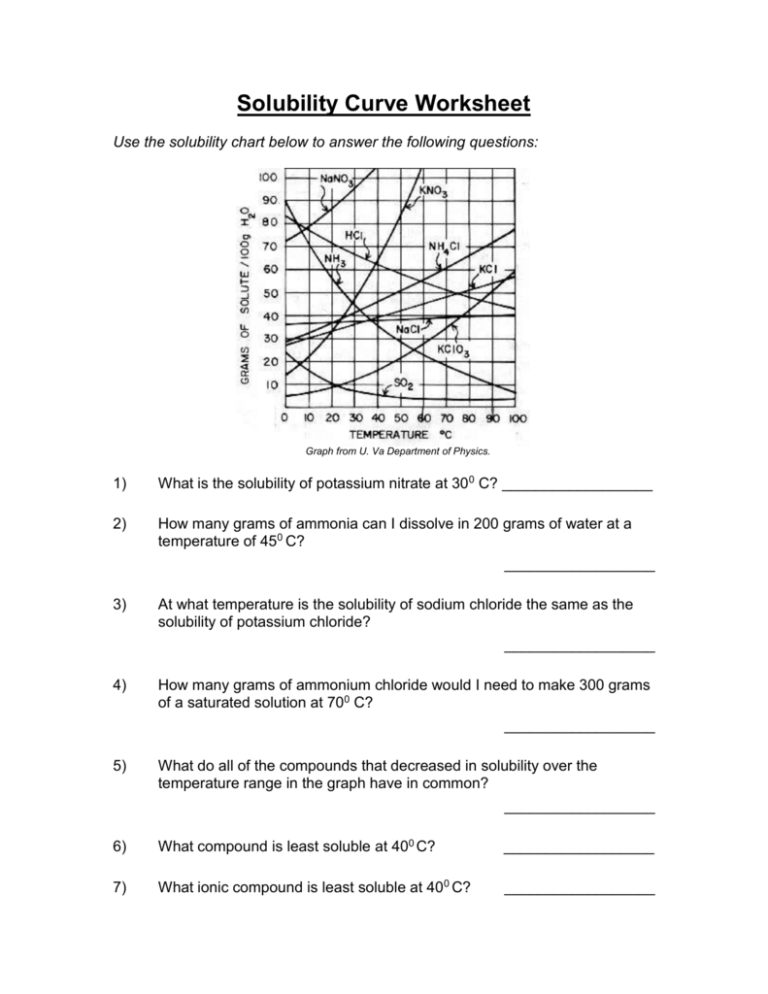
Here’s how you can use these rules in a practical setting:
- Identify the ions present in the compounds: Determine the metal or ammonium ion and the anion.
- Refer to the solubility rules: Look at the list and determine the solubility of each compound formed.
- Analyze solubility exceptions: Some ions might have exceptions; check these against the rules.
🌟 Note: Always start with the general rules, then look for exceptions to ensure accuracy in predictions.
Interactive Solubility Worksheet
To cement your understanding, here is an interactive worksheet:
| Compound | Ions | Solubility (Yes/No) |
|---|---|---|
| NaOH | Na+, OH- | Yes |
| AgCl | Ag+, Cl- | No |
| CaSO4 | Ca2+, SO42- | Yes |
| BaSO4 | Ba2+, SO42- | No |

💡 Note: This worksheet is meant to be interactive. Print it or use an editable document to fill in and practice.
Advanced Tips and Tricks

Here are some advanced insights into solubility:
- Complexation: Some ions can form complex ions, altering their solubility.
- Temperature Effect: Solubility changes with temperature. Many salts increase solubility with increasing temperature.
- pH Influence: The pH of a solution can alter solubility, especially for salts where one of the ions can react with H+ or OH-.
In conclusion

In this comprehensive guide on solubility rules, we’ve explored how these fundamental principles can be applied in various chemistry contexts. From predicting precipitation reactions to aiding in environmental assessments, solubility rules provide a foundational understanding necessary for both students and professionals in chemistry-related fields. Whether you’re conducting experiments, analyzing chemical behavior, or simply trying to understand the basics of chemical solubility, these rules serve as a valuable tool in demystifying the behavior of substances in solution.
Why do we study solubility rules?

+
Solubility rules allow chemists to predict the outcomes of precipitation reactions, understand the behavior of compounds in aqueous solutions, and design processes in industry and research.
Can solubility rules predict all solubility?

+
While solubility rules give a good baseline prediction, other factors like temperature, pH, and the presence of other solutes can significantly alter solubility.
What are some common exceptions to solubility rules?

+
Common exceptions include silver halides (AgCl, AgBr, AgI) and lead iodide, which are insoluble despite general solubility trends.