Simple Machines Worksheet: Answer Key Revealed

Simple Machines Worksheet: Answer Key Revealed

Understanding simple machines is essential for grasping basic physics concepts. These fundamental mechanisms make our lives easier by allowing us to use less force to do work. This blog post provides a comprehensive answer key for our Simple Machines Worksheet, ensuring you can check your answers or find more in-depth explanations of these fascinating devices.
Types of Simple Machines

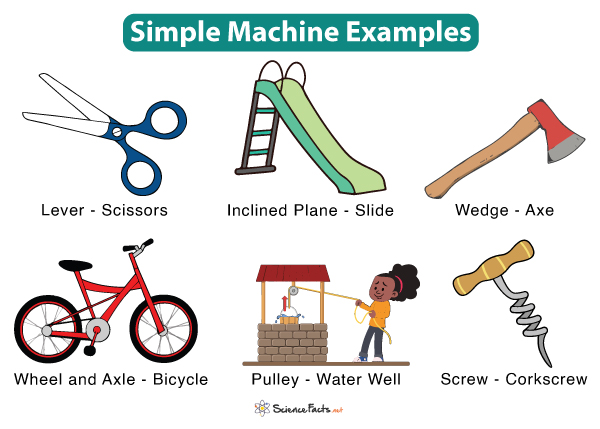
There are six classical types of simple machines. Here’s a quick overview:
- Lever: A rigid object that rotates around a pivot point, called the fulcrum.
- Wheel and Axle: A wheel attached to a shaft that rotates together.
- Pulley: A wheel with a groove around its circumference, used to change the direction or multiply force.
- Inclined Plane: A slanted surface used to move objects up or down with less effort.
- Wedge: A triangular shape often used to separate, lift, or hold objects in place.
- Screw: An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.
Worksheet Questions & Answers

Question 1: Identify the Simple Machine

Identify which type of simple machine is depicted in the following images:
 |
A lever |
 |
A pulley |
 |
A screw |

🔧 Note: The images provided were designed to clearly represent each type of simple machine for ease of identification.
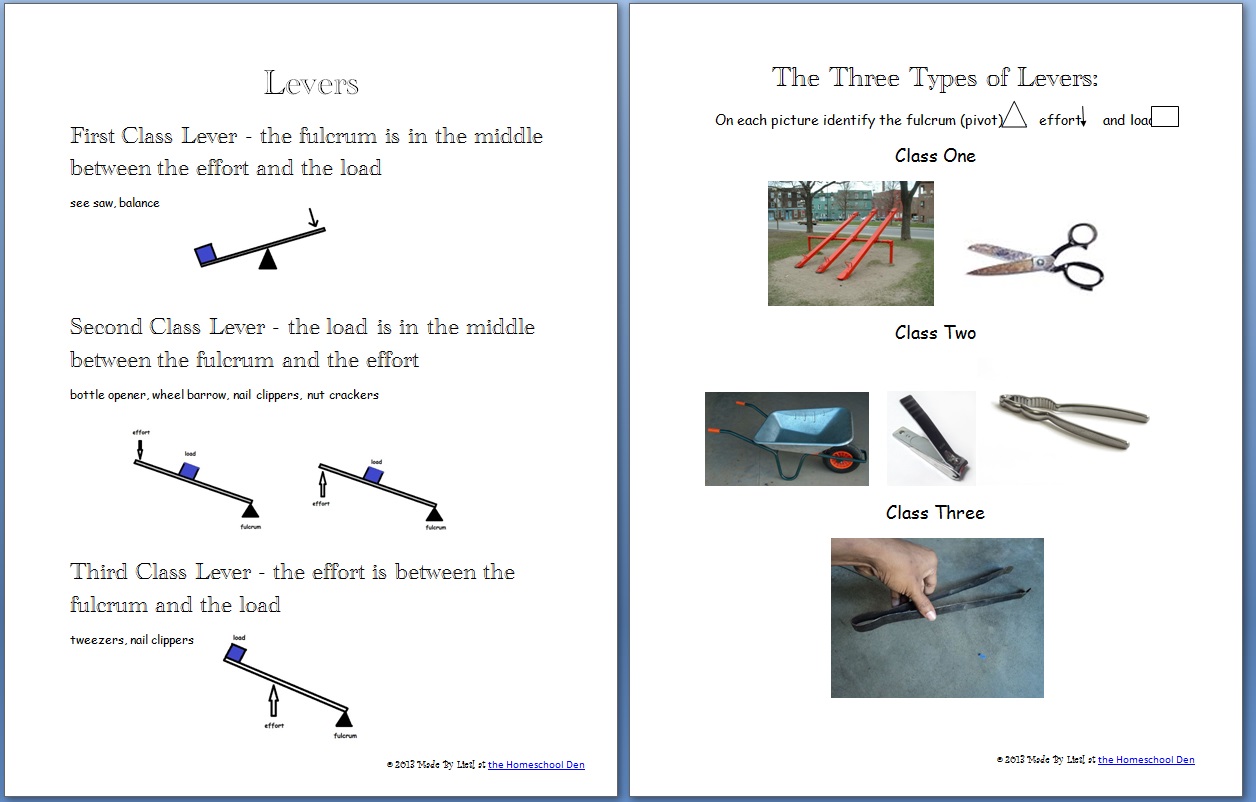
Question 2: Lever Classification

Describe the three types of levers and provide an example for each:
- First-Class Lever: Fulcrum in the middle, load and effort on opposite ends (e.g., see-saw).
- Second-Class Lever: Fulcrum at one end, load in the middle, and effort at the other end (e.g., wheelbarrow).
- Third-Class Lever: Effort is applied between the fulcrum and the load (e.g., fishing rod).
Remember, the mechanical advantage varies with the placement of the fulcrum, load, and effort.
Question 3: Mechanical Advantage Calculation

Calculate the mechanical advantage for a pulley system where there are three ropes supporting the load:
Mechanical Advantage = Number of Ropes Supporting Load = 3
Question 4: Real-World Applications

Give two examples of where you might find each type of simple machine in everyday life:
- Lever: A crowbar used to pry things open, a bottle opener.
- Wheel and Axle: The steering wheel in a car, a door knob.
- Pulley: Blinds on a window, a flagpole rope system.
- Inclined Plane: A ramp for accessibility, stairs.
- Wedge: A knife slicing through food, a shovel separating soil.
- Screw: Jar lids, screws and nails in construction.
📚 Note: Understanding where simple machines are in daily life can help in recognizing their utility and efficiency.
Simple Machines in Modern Technology

Simple machines are not just remnants of the past; they are foundational to many modern technologies:
- Robotics: Servo motors often include gears, which are a form of wheel and axle, for precise movements.
- Construction Machinery: Cranes use pulleys, levers, and screws to lift and move heavy objects with less human effort.
- Transportation: Cars, planes, and even bicycles use variations of simple machines in their design for efficient movement and control.
Summing Up the Lesson

In this deep dive into simple machines, we explored their types, identified them visually, classified levers, calculated mechanical advantages, and saw their applications in our daily lives. Simple machines provide an advantage by enabling us to amplify force, increase the distance over which force is applied, or change the direction of an applied force. By understanding how simple machines work, we gain a better understanding of the world around us, and we can appreciate the ingenious ways they help us overcome physical challenges with efficiency.
What is the mechanical advantage of a simple machine?
+
Mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force. In simple machines, it describes how the machine makes work easier by either reducing the effort needed to do the same work or by allowing the work to be done over a longer distance with less force.
Can simple machines change the direction of force?

+
Yes, some simple machines like pulleys can change the direction of the force applied. For example, when you pull down on a pulley, the force can lift the object upwards.
Why are screws considered inclined planes?

+
A screw is essentially an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder, allowing for the force applied to be spread over a longer distance, thus requiring less effort to move or tighten something.
How do compound machines relate to simple machines?

+
Compound machines combine two or more simple machines to perform complex tasks with increased mechanical advantage. For example, a bicycle uses levers (handlebars), wheels and axles (wheels), and screws (adjustable seat and brakes).
Where can I learn more about simple machines?
+
There are many resources available including educational websites, textbooks on physics, and hands-on kits for those who prefer interactive learning. Workshops and science museums often have exhibits or demonstrations of simple machines.



