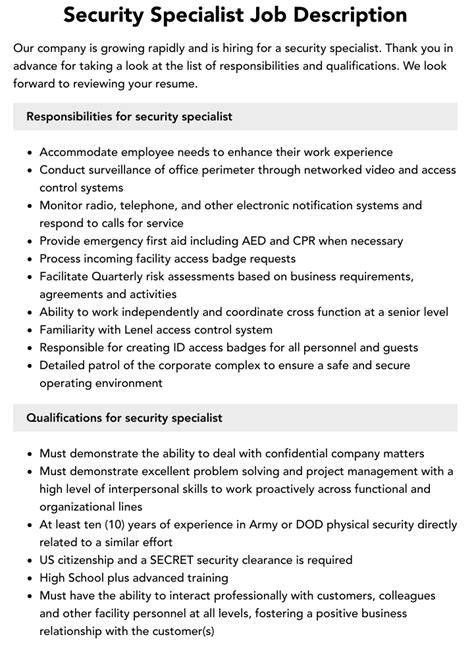
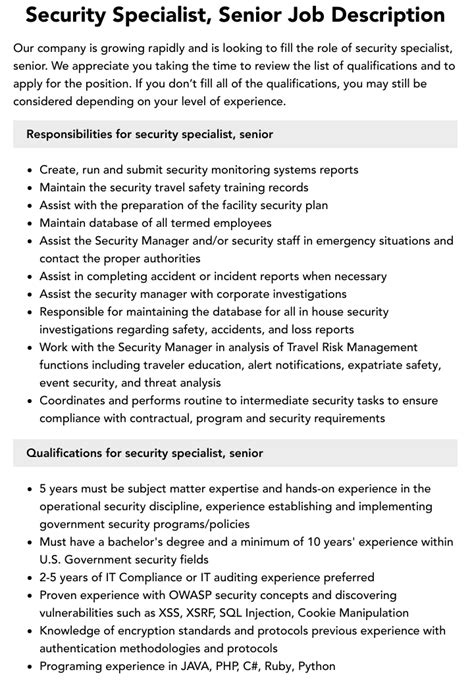
5 Key Responsibilities of a Security Specialist
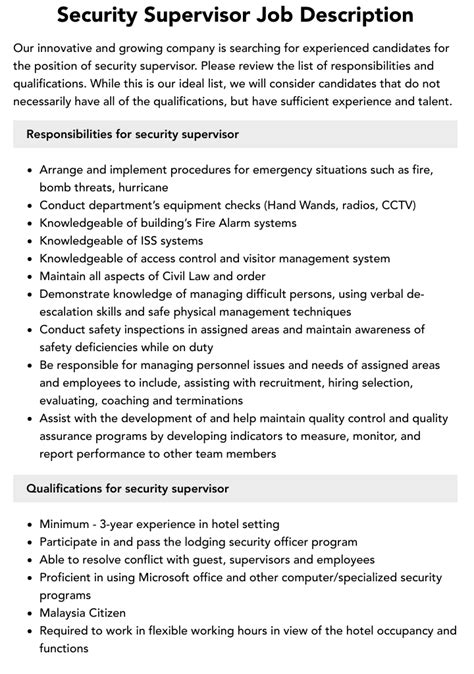
Protecting the Digital Realm: The Crucial Role of a Security Specialist

In today’s interconnected world, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As technology advances and more businesses move online, the threat of cyberattacks and data breaches grows exponentially. This is where the security specialist comes in – a guardian of the digital realm, tasked with protecting networks, systems, and data from malicious actors. But what exactly does this critical role entail?
Key Responsibilities of a Security Specialist

A security specialist’s primary objective is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s digital assets. To achieve this, they must perform a range of critical tasks, including:
1. Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Management
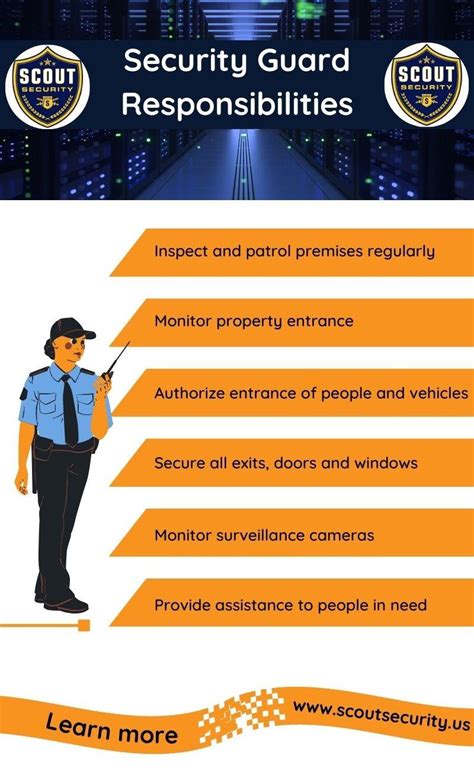
Security specialists must identify potential vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and networks, assessing the likelihood and potential impact of a cyberattack. This involves:
- Conducting regular risk assessments and penetration testing
- Identifying vulnerabilities and prioritizing remediation efforts
- Developing and implementing patch management strategies
- Collaborating with development teams to ensure secure coding practices
2. Incident Response and Management

In the event of a security breach, a security specialist must respond quickly and effectively to contain the damage. This includes:
- Developing and implementing incident response plans
- Conducting forensic analysis to determine the scope and cause of the breach
- Coordinating with stakeholders to respond to and resolve the incident
- Documenting lessons learned and implementing improvements to prevent future breaches
3. Security Architecture and Design

Security specialists must design and implement secure architectures for an organization’s systems and networks. This involves:
- Developing security policies and procedures
- Designing secure network architectures and configurations
- Implementing encryption and access controls
- Conducting security testing and validation
4. Compliance and Regulatory Management

Security specialists must ensure that an organization’s security practices comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes:
- Conducting regular compliance audits and risk assessments
- Developing and implementing compliance policies and procedures
- Collaborating with stakeholders to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements
- Staying up-to-date with changing regulatory requirements and industry standards
5. Security Awareness and Training

Security specialists must educate employees on security best practices and promote a culture of security awareness within the organization. This includes:
- Developing and delivering security awareness training programs
- Conducting phishing simulations and other security exercises
- Collaborating with stakeholders to promote security awareness and best practices
- Developing and maintaining security policies and procedures
🚨 Note: The specific responsibilities of a security specialist may vary depending on the organization, industry, and specific job requirements.
Additional Skills and Qualifications

While the key responsibilities outlined above provide a foundation for the role of a security specialist, there are additional skills and qualifications that are highly valued in this profession. These include:
- Technical skills: Proficiency in security technologies such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption
- Analytical skills: Ability to analyze complex security data and identify potential threats
- Communication skills: Ability to communicate technical information to non-technical stakeholders
- Certifications: Relevant certifications such as CompTIA Security+, CISSP, or CEH
Conclusion

In conclusion, the role of a security specialist is critical in today’s digital landscape. By understanding the key responsibilities of this profession, organizations can better protect themselves against cyber threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their digital assets.
What is the primary objective of a security specialist?
+
The primary objective of a security specialist is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s digital assets.
What are some common certifications for security specialists?
+
Relevant certifications for security specialists include CompTIA Security+, CISSP, and CEH.
What is incident response and management in cybersecurity?

+
Incident response and management refers to the process of responding to and managing a cybersecurity incident, such as a security breach or malware outbreak.