8 Ways to Understand the Electromagnetic Spectrum for Students

In the fascinating realm of physics, the electromagnetic spectrum is a key concept that not only shapes our understanding of light and energy but also has profound applications in technology, communication, and even health sciences. For students, grasping this spectrum can be somewhat daunting, but it's an essential part of learning how our world works. Here, we explore eight effective strategies to help students understand and appreciate the electromagnetic spectrum:
1. Start with Fundamentals: What is Electromagnetic Radiation?


Begin by introducing the concept of electromagnetic (EM) radiation:
- Explain that EM radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it moves from a source. This radiation comprises both electric and magnetic fields oscillating in sync with each other.
- Highlight that these waves can travel through space or matter, making them unique in their ability to reach us from distant stars or the other side of the Earth.
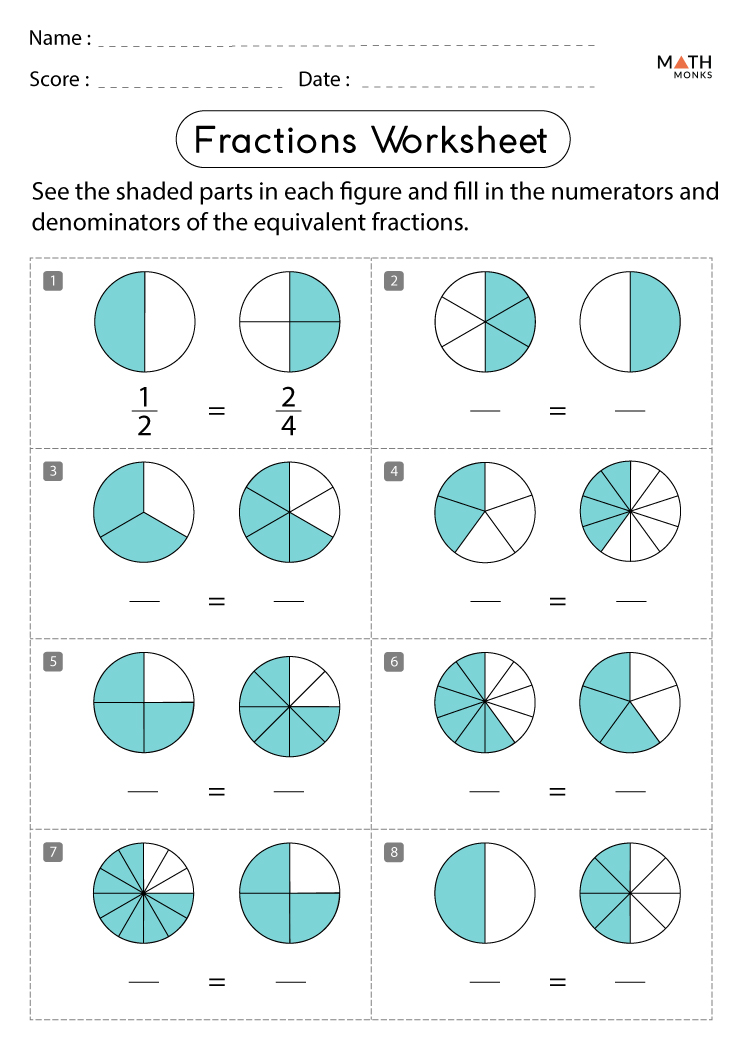
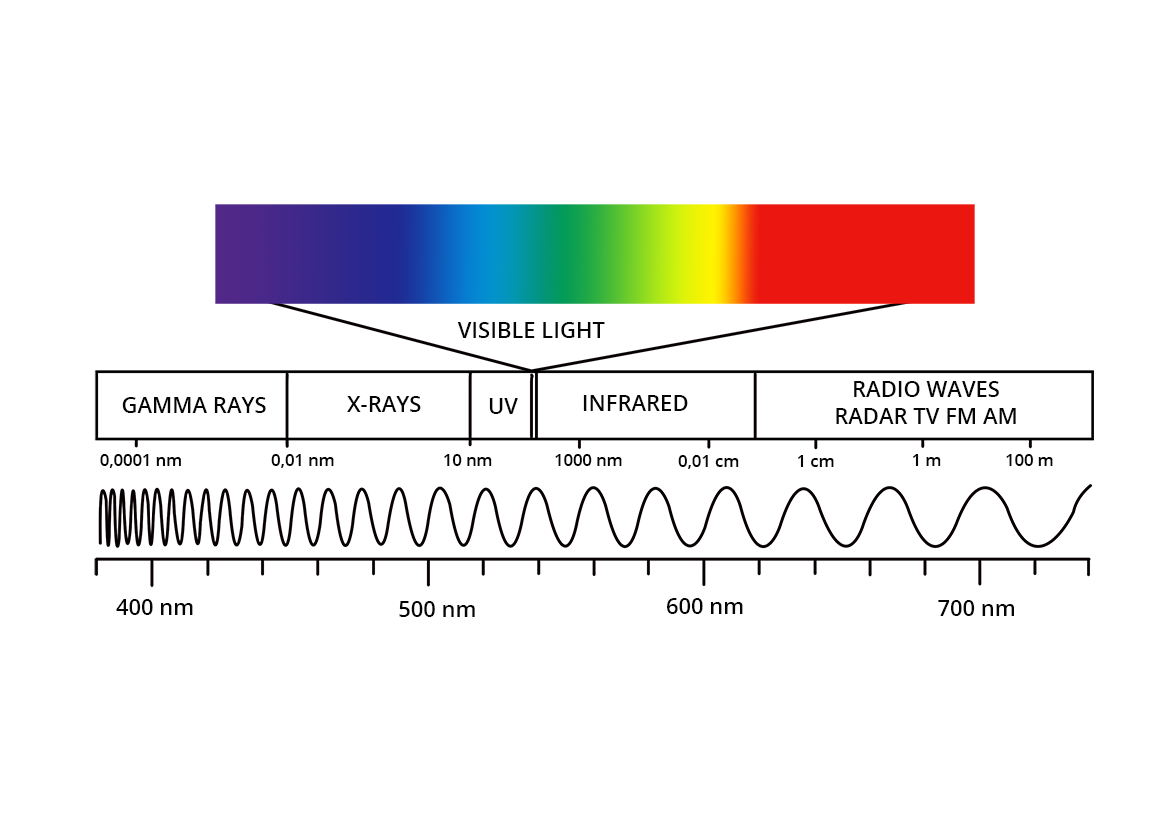
2. Use Visual Aids to Depict the Spectrum

Visual aids are incredibly effective for learning:
- Create or use existing diagrams of the electromagnetic spectrum showing various types of EM radiation from gamma rays to radio waves. Color-code them to illustrate their wavelength and frequency differences.
- Display real-life examples of each type of radiation in action (e.g., X-rays in medical imaging, infrared in thermal imaging).
3. Make it Interactive with Practical Demonstrations

Engage students with hands-on activities:
- Show UV beads that change color under UV light to demonstrate the existence of UV radiation.
- Use heat-sensitive materials to demonstrate infrared radiation.
- Conduct simple experiments with radio waves, like using an AM/FM radio to explore different frequencies.
4. Connect to Real-World Applications

Link theoretical knowledge to real-life scenarios:
- Discuss how radio waves are used in communication technologies like Wi-Fi, television, and mobile networks.
- Explain medical uses like MRI which utilizes radiofrequency pulses in combination with magnetic fields to produce detailed images.
- Explore the importance of UV radiation in vitamin D synthesis in our skin.
🔍 Note: Understanding real-world applications not only makes the topic more relatable but also highlights its significance in daily life.
5. Use Technology and Digital Resources

Modern technology can make abstract concepts concrete:
- Employ simulations to illustrate how waves travel, their interaction with matter, and how they can be modified or used.
- Use apps that let students visualize different wavelengths and see the effects of EM radiation, like infrared thermography apps.
6. Address Common Misconceptions

Clarify misunderstandings students might have:
- Discuss that all forms of EM radiation travel at the same speed in a vacuum (speed of light) but differ in energy, wavelength, and frequency.
- Explain why visible light is just a small part of the spectrum and why we only see this portion.
7. Incorporate Historical Context
History can enrich understanding:
- Talk about the discovery of the spectrum by James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz’s experiments demonstrating the existence of radio waves.
- Discuss the evolution of technology through understanding of EM radiation, from Marconi’s first radio transmission to modern-day applications.
8. Encourage Project-Based Learning

Projects help solidify understanding:
- Assign projects where students can choose a part of the spectrum to explore in depth, like UV light’s effects on materials or the science behind microwave ovens.
- Have them present their findings, incorporating their projects into a class-wide symposium on electromagnetic phenomena.
In summary, understanding the electromagnetic spectrum can transform from a complex subject into a fascinating journey through the invisible forces that govern our world. By using a blend of visual, practical, and contextual learning methods, students can not only grasp the theoretical aspects but also see how these waves are the foundation of technologies they use daily. Engaging with this fundamental physics concept can ignite a passion for science, open doors to innovative thinking, and provide a deeper appreciation for the invisible yet omnipresent world of electromagnetic waves.
What is the most harmful type of electromagnetic radiation?

+
Gamma rays and X-rays are the most harmful due to their high energy levels, which can ionize atoms and molecules, potentially damaging living tissues. Protection from these is crucial, especially for those working with or around sources like medical equipment or nuclear reactors.
How do electromagnetic waves affect our health?
+
EM waves, particularly at the ionizing end of the spectrum, can have both beneficial and harmful effects. They are used in medical diagnostics and treatments but overexposure can lead to health issues like radiation sickness or cancer. Non-ionizing radiation, while less damaging, can still affect health in conditions like microwave exposure leading to burns or heat-related issues.
Why can’t we see all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum?

+
Our eyes have evolved to detect a small range of EM radiation called visible light. This is because the energy levels of visible light photons match the energy required to trigger photoreceptor cells in our eyes, which convert light into signals sent to our brain for image processing.
Can humans produce electromagnetic radiation?

+
Yes, humans do emit electromagnetic radiation in the form of body heat, which is infrared radiation. Additionally, biological processes like nerve impulses create small electrical fields, although not strong enough to be considered significant radiation.