7 Simple Tips for Mastering Present Tense Verbs

Mastering present tense verbs is crucial for anyone learning English or improving their language skills. Whether you're writing an academic paper, crafting a social media post, or engaging in everyday conversation, using the present tense correctly enhances clarity, precision, and engagement. Here are seven simple tips to help you master the use of present tense verbs:
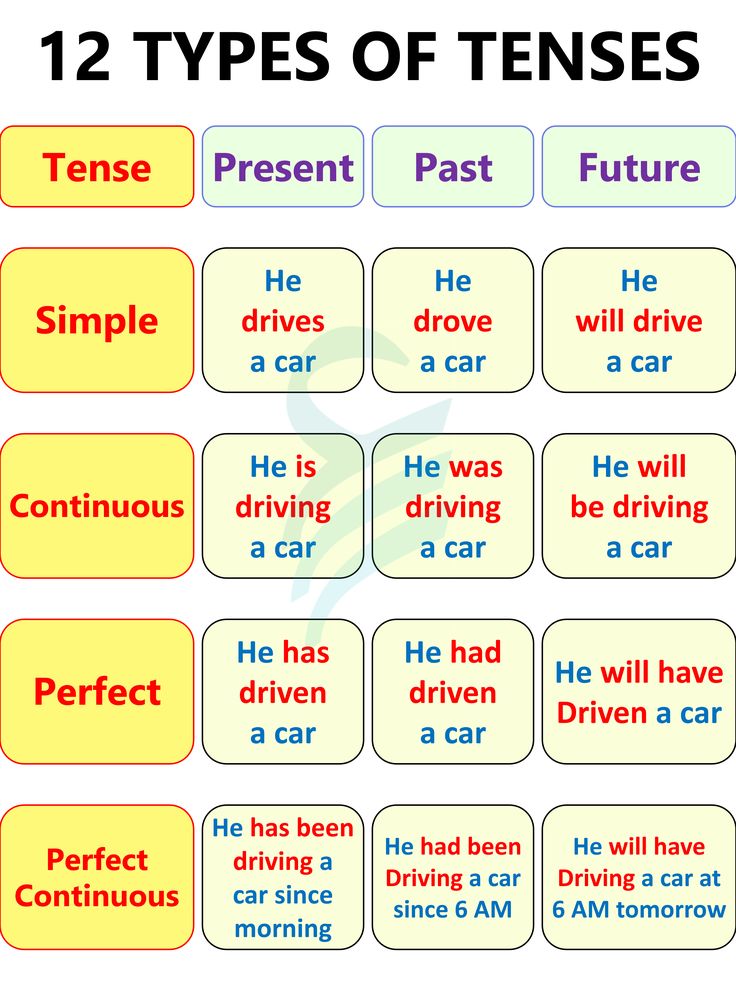
1. Understand the Three Forms of Present Tense

The present tense in English has three main forms:
- Simple Present: Used for actions that are habitual or generally true. For example, "He eats breakfast at 7 AM."
- Present Continuous: Used for actions that are happening now or around the current period of time. For example, "She is reading a book right now."
- Present Perfect: Indicates actions completed at the time of speaking or at some unspecified time in the past with a connection to the present. For example, "I have seen that movie."
🧠 Note: While these are the core forms, there are nuances and exceptions in English, particularly with the auxiliary verbs like 'do', 'have', and 'be'.
2. Know When to Use Each Form

Choosing the right form of the present tense depends on the context:
- Use Simple Present for routines, facts, and general truths.
- Example: "The sun rises in the east."
- Use Present Continuous for actions happening at the moment or temporary situations.
- Example: "They are playing soccer on the field."
- Use Present Perfect for experiences, changes, or accomplishments with an effect on the present.
- Example: "She has just arrived at the station."
3. Master Verb Conjugation

English verbs conjugate differently in the present tense depending on the subject:
| Subject | Simple Present | Present Continuous | Present Perfect |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | eat | am eating | have eaten |
| You/We/They | eat | are eating | have eaten |
| He/She/It | eats | is eating | has eaten |

📝 Note: Pay attention to the third person singular where most verbs end in -s or -es.
4. Practice with Contextual Examples

Using real-life examples or scenarios can significantly help in mastering present tense usage. Here are a few exercises:
- Write a diary entry about your daily routine using simple present tense.
- Describe what someone is currently doing in your household using present continuous.
- Explain a personal achievement or recent event using the present perfect tense.
5. Pay Attention to Time Expressions

Time expressions can help guide you in using the correct present tense:
- Now, at the moment: Present Continuous (She is calling the customer service now.)
- Every day, always, often: Simple Present (He always eats breakfast at 7 AM.)
- Since, yet, already: Present Perfect (I have not eaten since morning.)
6. Use Visual Aids and Mnemonics

Visualizing the tense forms or creating mnemonic devices can aid in learning:
- Use charts or timelines to visualize when each tense should be used.
- Create phrases or songs that help remember verb forms (e.g., "He eats, she eats, it eats - adding 's' makes all neat!")
7. Read and Listen Actively

Immersion in English through reading books, watching movies, or listening to native speakers can:
- Give you context on how native speakers use present tense verbs.
- Help you understand subtle differences between tenses through natural exposure.
🎧 Note: Active listening involves paying attention to verb usage in real-life scenarios, which can be more educational than passive listening.
In summary, mastering present tense verbs involves understanding the different forms, knowing when to use each form, correctly conjugating verbs, practicing in context, recognizing time expressions, using aids for learning, and engaging with the language. By following these tips and applying them consistently, you'll find your proficiency in using present tense verbs significantly improved, leading to clearer and more effective communication.
What is the difference between the simple present and present continuous tenses?
+
The simple present is used for actions that are habitual or generally true (e.g., “He eats breakfast”). The present continuous indicates an action happening right now or a temporary state (e.g., “He is eating breakfast”).
When should I use the present perfect tense?

+
Use the present perfect when referring to an action or experience that has occurred at an unspecified time before now or when there’s a link to the present (e.g., “I have seen that movie” means I’ve seen it at some point in the past, and it’s relevant now).
How can I remember verb conjugation for present tense?
+
To remember verb conjugation, practice regularly. Use mnemonic devices, create songs or rhymes, or refer to conjugation tables. The rule for third person singular in simple present is often remembered as adding ’s’ or ‘es’ to the base form (e.g., “He reads,” “She goes”).


