5 Key Differences: Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration
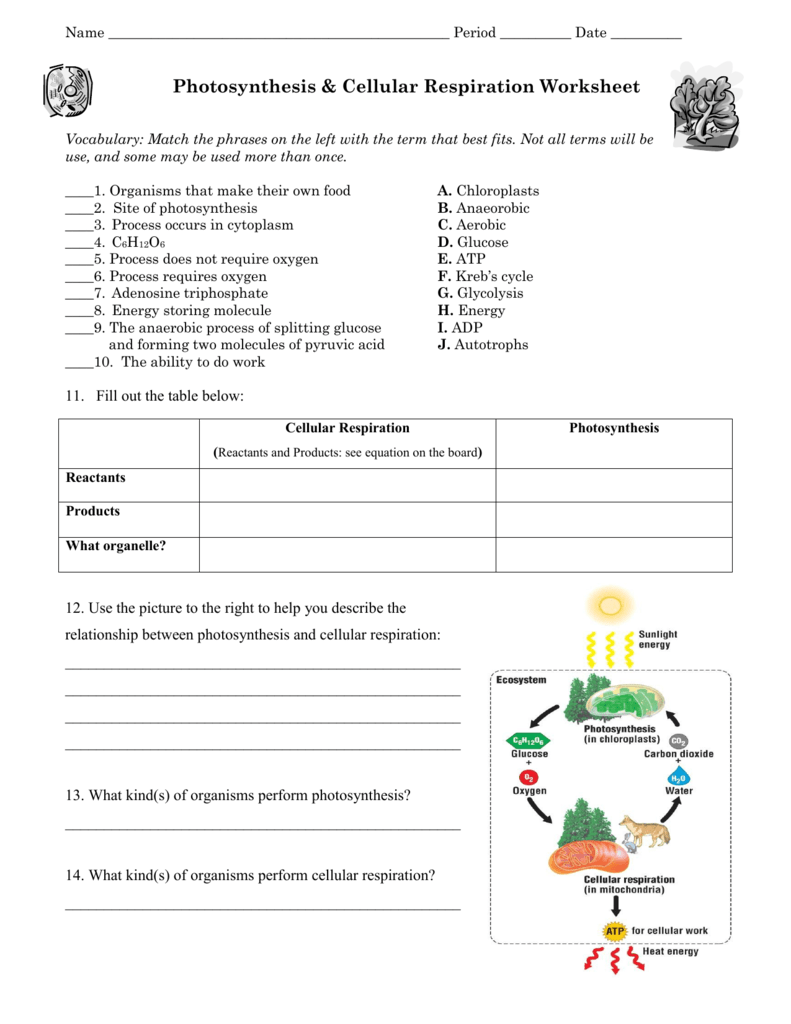
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental biochemical processes that are intricately linked in maintaining life on Earth. While both involve energy conversion, they occur in distinct organisms and settings, playing different roles in the energy cycle of life. Understanding these processes illuminates the interconnected nature of ecosystems. Here, we'll delve into five key differences between these life-sustaining activities.
Energy Flow Direction

- Photosynthesis: This process captures solar energy from the sun and transforms it into chemical energy, specifically in the form of glucose (a type of sugar). The energy flow in photosynthesis can be thought of as an energy input from the environment.
- Cellular Respiration: Here, energy is released from glucose and other organic molecules, converting it into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of the cell. This represents an energy output for the cell.
The direction of energy flow is a critical distinction, as photosynthesis builds up energy stores, while cellular respiration uses this stored energy.
Raw Materials and Products

| Process | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Water, Carbon Dioxide, Light Energy | Glucose, Oxygen |
| Cellular Respiration | Glucose, Oxygen | Water, Carbon Dioxide, ATP |

- Photosynthesis: Utilizes water, carbon dioxide, and light energy to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Cellular Respiration: Breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen to yield water, carbon dioxide, and ATP.
These differences highlight how photosynthesis acts as an anabolic process (building up), while cellular respiration is catabolic (breaking down).
Location in the Cell

Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically within the thylakoid membranes where the chlorophyll captures light energy, and the stroma where glucose synthesis takes place. In contrast, cellular respiration happens in the:
- Cytoplasm for glycolysis.
- Mitochondria for the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and the electron transport chain.
🍃 Note: Although cellular respiration starts in the cytoplasm, the majority of ATP production occurs within the mitochondria.
Light Dependency

- Photosynthesis: Is directly dependent on light. The process cannot occur without the presence of light because light energy drives the conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Cellular Respiration: Does not require light and happens continuously, day and night, in cells that require energy.
This difference underscores how photosynthesis contributes to the biosphere’s energy input, while cellular respiration is an internal energy utilization process.
Organisms Involved

Photosynthesis is carried out by:
- Plants
- Algae
- Some bacteria
Whereas cellular respiration occurs in:
- All living cells, including plants, animals, fungi, and prokaryotes.
🧬 Note: Photosynthesis allows plants to synthesize their own food, making them autotrophs, while cellular respiration is the energy-producing process for both autotrophs and heterotrophs, which rely on consuming other organisms for energy.
In summary, photosynthesis and cellular respiration stand as counterparts in the cycle of life, where energy is captured, stored, and utilized in different forms. Photosynthesis is the cornerstone of energy input, converting sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Cellular respiration then completes the cycle by breaking down these energy-rich molecules to fuel cellular activities. Their distinct locations, dependencies, and the organisms involved highlight their complementary roles in sustaining life. The balance between these processes supports the continuity of life, with photosynthesis providing the energy source for cellular respiration to extract and use, creating an interconnected web of life-supporting activities.
Can photosynthesis occur at night?

+
No, photosynthesis cannot occur at night because it relies on sunlight to provide the energy needed to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
What happens to the oxygen produced during photosynthesis?

+
The oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct, which is then used by animals and other organisms for cellular respiration.
Why do plants need both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?

+
Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis for energy storage. They also need cellular respiration to break down this glucose to produce ATP for growth, maintenance, and other life processes.