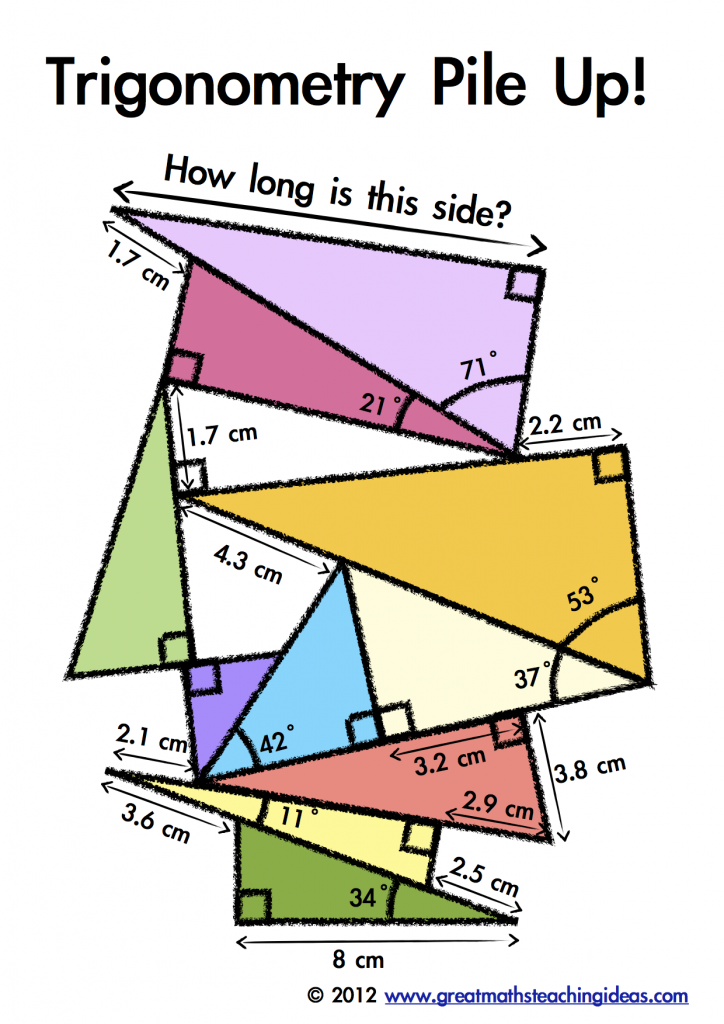
Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet Answer Key: 5 Essential Insights

Understanding photosynthesis is fundamental for students learning about plant biology, environmental science, or ecology. By engaging with a photosynthesis diagram worksheet, learners not only get to visualize the process but also grasp the intricacies involved in energy conversion from sunlight to chemical energy. This blog post will provide you with the Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet Answer Key and delve into five essential insights that enhance comprehension of this pivotal biological process.
The Basic Mechanism of Photosynthesis


Photosynthesis is essentially the process through which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. The simplified equation can be represented as:
[ CO_2 + H_2O + \text{light energy} \rightarrow C6H{12}O_6 + O_2 ]
- Light Dependent Reactions: Occurring in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast, these reactions capture solar energy, splitting water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): Utilizes the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into sugars via the Calvin cycle in the stroma.
Key Players in Photosynthesis

The mechanism of photosynthesis involves several crucial molecular components:
- Chlorophyll: This pigment captures light energy, critical for the whole process.
- Photosystems: These are groups of pigments and proteins that use light to transfer electrons through an electron transport chain.
- ATP Synthase: An enzyme involved in generating ATP by utilizing the proton gradient created across the thylakoid membrane.
Variations in Photosynthesis

While the basic mechanism of photosynthesis is conserved across plants and other photosynthetic organisms, there are significant variations:
- C3 Photosynthesis: Most plants use this pathway; it involves ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) for carbon fixation.
- C4 Photosynthesis: Primarily found in tropical plants, this pathway helps to reduce photorespiration by concentrating CO2 near RuBisCO.
- CAM Photosynthesis: Typically seen in succulents, CAM plants open their stomata at night to take in CO2, reducing water loss in arid environments.
The Limiting Factors

Photosynthesis efficiency can be influenced by several factors:
- Light Intensity: Up to a certain point, higher light intensity increases photosynthesis rate. Beyond that point, it levels off or decreases due to photoinhibition.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Increased CO2 initially leads to higher rates of photosynthesis but can saturate.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis has an optimal temperature range; above or below this, the rate decreases.
🌿 Note: Understanding these limiting factors can help in optimizing plant growth conditions.
Importance of Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis plays multiple critical roles in our ecosystem:
- Energy Source: It is the primary source of energy for almost all life forms on Earth, either directly or indirectly through the food chain.
- Atmospheric Balance: It helps maintain the level of CO2 and O2 in the atmosphere, crucial for the biosphere's balance.
- Climate Regulation: Photosynthesis absorbs CO2, a greenhouse gas, mitigating climate change.
Steps for Using the Answer Key

| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Components | Locate and label the key components like chlorophyll, thylakoids, and stroma in the diagram. |
| 2. Follow the Flow | Trace the path of water, CO2, and energy through light-dependent and light-independent reactions. |
| 3. Answer Key Validation | Use the answer key to verify your labels and the steps in the process. |
| 4. Review | Ensure you understand the significance of each step in the photosynthesis process. |
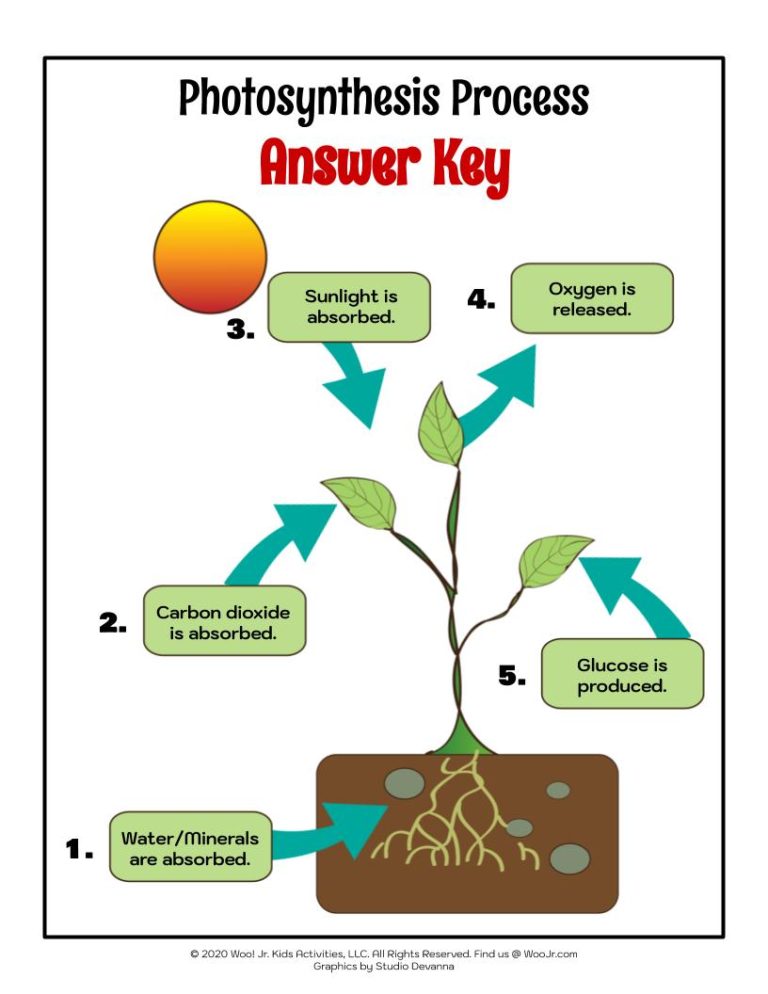
In wrapping up, understanding photosynthesis through a detailed Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet and its Answer Key provides not only an academic benefit but also real-world applications. This process is at the heart of life on Earth, influencing global ecosystems, climate, and human activities. From optimizing crop yields to mitigating climate change, the implications of photosynthesis extend far beyond the classroom. Reflecting on these five essential insights, we encourage you to explore further, experiment, and perhaps discover new ways to harness this magnificent natural process.
Why is the light reaction considered important in photosynthesis?

+
The light reaction is crucial because it captures sunlight to generate ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the subsequent Calvin cycle, where sugar is produced.
What is the difference between C3 and C4 plants?

+
C3 plants use a pathway that does not have a specific mechanism to concentrate CO2 around RuBisCO, while C4 plants have an additional step where CO2 is concentrated before entering the Calvin cycle, thus minimizing photorespiration.
How does temperature affect photosynthesis?

+
Enzymes involved in photosynthesis have an optimal temperature range. Above or below this, the rate of photosynthesis decreases due to either the enzymes working slower or getting damaged by high temperatures.