Unlock Photosynthesis and Respiration Secrets: Worksheet Answers

Understanding Photosynthesis and Respiration

Photosynthesis and respiration are two of the most fundamental biological processes that underpin life on Earth. They are complementary processes where photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, while cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release energy, using oxygen, and produces carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. Here, we delve into the intricacies of these processes, providing insights through a structured worksheet that highlights key stages, reactants, and products involved.
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into organic compounds (usually glucose) and oxygen. This process occurs in two main stages:
Light-dependent reactions: These take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. Here’s what happens:
- Water (H2O) is split through photolysis, releasing oxygen (O2) as a byproduct.
- Light energy is captured by pigments like chlorophyll, exciting electrons which move through the electron transport chain.
- ATP and NADPH, the energy carriers, are produced.
Light-independent reactions or Calvin Cycle: This happens in the stroma of chloroplasts:
- ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to fix carbon dioxide (CO2) into a sugar molecule (G3P), eventually forming glucose (C6H12O6).
- CO2 is reduced, and ATP is hydrolyzed to regenerate the starting material (RuBP).
Cellular Respiration

Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert the chemical energy stored in glucose into ATP, the universal energy currency of cells. It involves several steps:
Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm, it involves:
- Breaking down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Producing a small amount of ATP and NADH.
The Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): Occurs in the mitochondria’s matrix:
- Pyruvate is further broken down to produce ATP, NADH, FADH2, and CO2.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation: These steps happen in the inner mitochondrial membrane:
- Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed down the chain, leading to the creation of a proton gradient.
- ATP is synthesized from ADP through chemiosmosis as protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix.
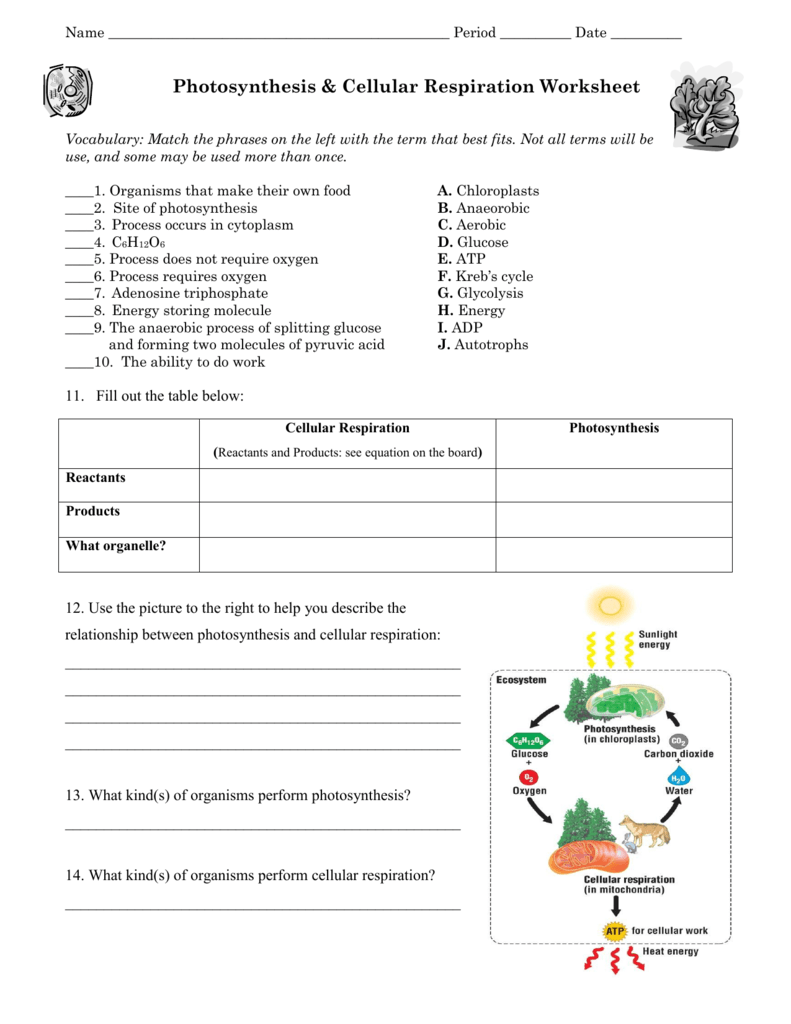
Interconnections Between Photosynthesis and Respiration

Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected in a beautiful cycle of life:
- The oxygen produced in photosynthesis is used by organisms for respiration.
- The CO2 produced in respiration is used by plants for photosynthesis.
This relationship ensures a sustainable exchange of gases vital for life.
Worksheet Answers

Below is a sample worksheet to help students understand the processes better:
| Process | Key Stages | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis |
|
|
|
| Respiration |
|
|
|

🌱 Note: While the above table provides a simplified overview, photosynthesis can also occur in cyanobacteria and certain algae, which have different structural setups than plant chloroplasts.
To summarize, the intertwining of photosynthesis and respiration creates a balanced ecosystem where energy from the sun is captured, stored, and then released to support life. By understanding these processes, we appreciate the delicate balance of nature and the importance of preserving these cycles for our survival.
What happens if there’s too much or too little light for photosynthesis?
+
Too much light can cause photoinhibition, which can damage the photosystem II reaction center, reducing photosynthesis efficiency. Conversely, too little light limits the energy available for photosynthesis, slowing the rate of the process.
How do plants use the glucose produced by photosynthesis?

+
Glucose serves as a building block for other molecules like cellulose for cell walls, starch for energy storage, or directly as a source of energy through cellular respiration. It can also be converted into other substances like lipids and amino acids.
Why is oxygen considered a byproduct in photosynthesis?

+
Oxygen is released during the light-dependent reactions when water is split. While it’s essential for life, in terms of the photosynthetic process, oxygen is not the primary product; it’s the glucose that the plant needs for growth and energy.