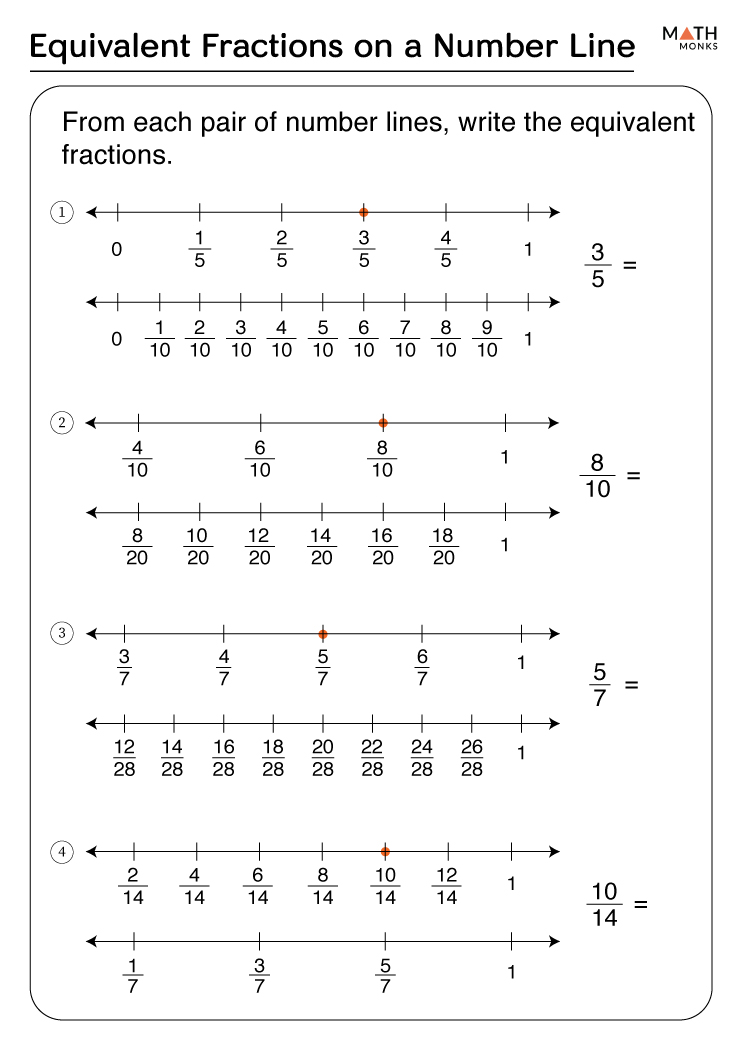
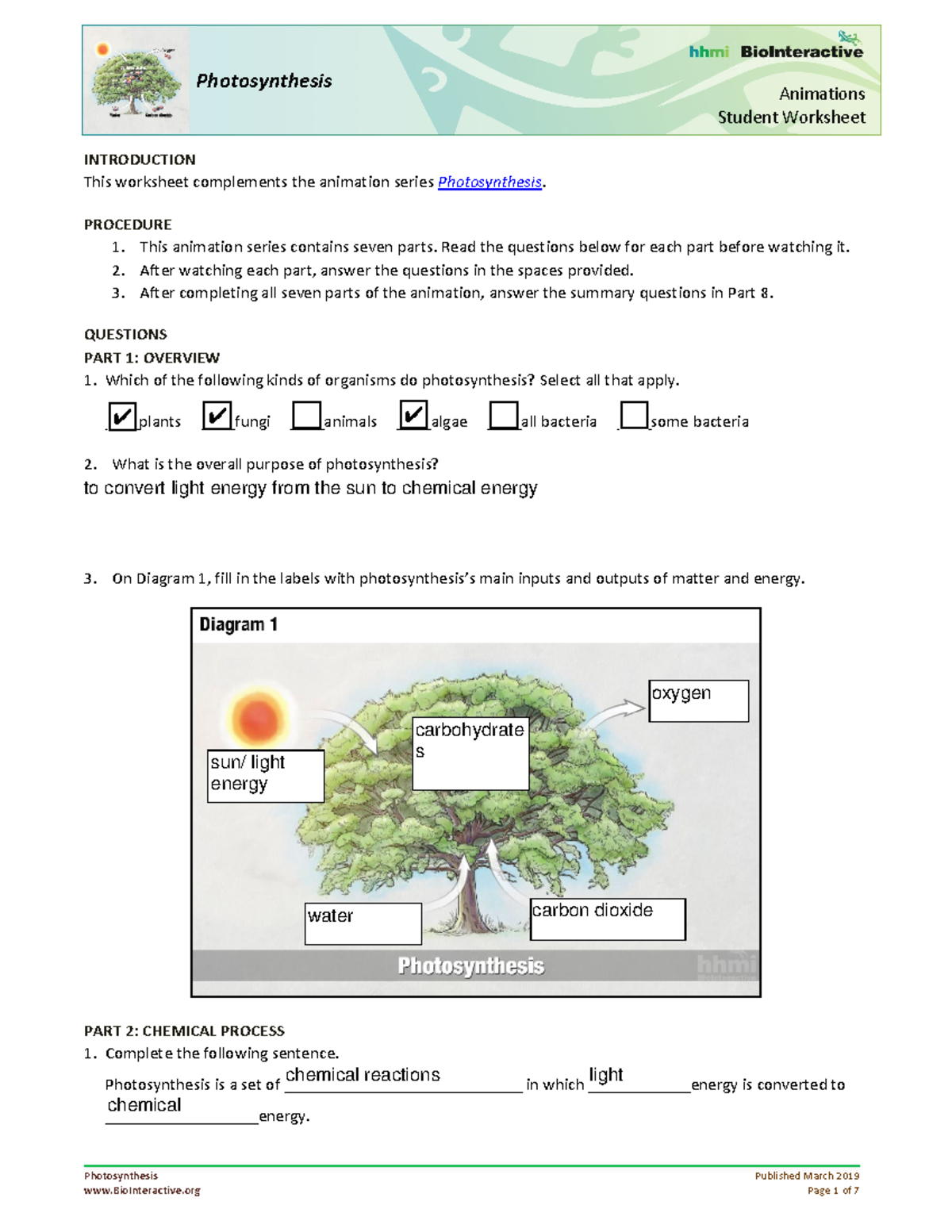
5 Essential Pharmacy Math Practice Worksheets for Students

Mathematics is a fundamental skill required in every field of healthcare, with pharmacy being no exception. For pharmacy students, grasping mathematical concepts is crucial to avoid errors that could compromise patient safety. From calculating doses to understanding drug ratios, pharmacy math is both an art and a science. In this detailed guide, we explore five essential pharmacy math practice worksheets designed to help students build their competence in this critical area.
1. Drug Concentration and Dilution

One of the foundational skills in pharmacy practice is the ability to calculate drug concentrations and perform dilutions accurately. Here are some examples to hone these skills:
- Drug Concentration Problems: These problems require you to calculate the concentration of a drug in a given solution or determine the amount of active ingredient in a dosage.
- Dilution Calculations: Understanding how to dilute stock solutions to prepare patient medications or prepare medications for specific therapeutic needs.
Here's an example for drug concentration:
| Active Ingredient (mg) | Total Solution (mL) | Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 50 | 10 |
| 750 | 250 | 3 |

For dilution, consider this scenario: A stock solution of 15 mg/mL needs to be diluted to 2 mg/mL for a pediatric dose. Use the provided formula and calculate the necessary volumes of stock solution and diluent.
💡 Note: Always double-check your calculations to prevent errors. Use the C1V1 = C2V2 formula where C = concentration and V = volume.
2. Dimensional Analysis

Dimensional analysis, or factor-label method, is a powerful technique used to solve conversion problems in pharmacy. It's crucial for pharmacy students as it helps in converting from one unit of measurement to another accurately.
- Converting Between Units: Problems such as converting micrograms to milligrams or liters to fluid ounces.
- Dosage Conversion: Calculating dosages based on body weight or surface area using dimensional analysis.
Worksheet examples include:
- Convert 0.5 grams to milligrams using dimensional analysis.
- Calculate the dosage for a patient weighing 60 kg if the dose is 10 mg/kg.
🛑 Note: Pay attention to the units. A single misplaced decimal can lead to significant errors in medication administration.
3. Infusion Rate Calculations

Accurate infusion rate calculations are essential for delivering medications intravenously. These worksheets focus on:
- Basic Infusion Rate: Determining the rate at which an IV should run to administer a specific dose over a period.
- Titration Rates: Adjusting the IV rate based on patient response or changing medical conditions.
Example questions include:
- Calculate the infusion rate in mL/hour for a 500 mL bag to run over 8 hours.
- Adjust the infusion rate if the medication dosage needs to be increased by 10%.
4. Percentages, Ratios, and Proportions

Pharmacy students must also understand how to work with percentages, ratios, and proportions for accurate compounding, drug concentrations, and dosage calculations.
- Percentage Calculations: Solving for the weight-to-volume (w/v) or volume-to-volume (v/v) percentages in solutions.
- Ratio and Proportion: Using ratios to solve for quantities or to set up IVs with specific concentrations.
Example exercises:
- Find the amount of a solute needed for a 1% solution of 100 mL.
- Given a solution with a 5:1 ratio of drug A to drug B, calculate the amount of drug B required if 20 mg of drug A is needed.
5. Algebraic Equations

In some cases, more complex calculations involving algebraic equations are required to solve pharmacy problems. These worksheets are designed to:
- Set Up and Solve Equations: Create equations to solve for unknown values in pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic calculations.
- Linear and Exponential Equations: Understand how to apply algebraic concepts to drug delivery and elimination.
Sample questions might include:
- Using the equation Vd = Dose / Plasma Concentration, find Vd if the dose is 200 mg and the plasma concentration is 0.5 mg/L.
- Calculate the time for half the concentration of a drug to be reached if its elimination rate constant (Kel) is 0.15 per hour.
⚗️ Note: Practice setting up equations regularly to improve your speed and accuracy in real-life scenarios.
The journey through pharmacy math can be challenging, but these five worksheets provide a comprehensive approach to mastering the subject. They cater to both the initial learning phase and the need for ongoing practice to reinforce and expand your mathematical skills. Remember, pharmacy involves exact sciences where every digit counts. Through diligent practice with these worksheets, you'll be well on your way to becoming a proficient and error-free pharmacy professional.
Why is pharmacy math important?

+
Pharmacy math is critical because errors in calculations can lead to incorrect dosages, potentially endangering patient safety. Understanding math ensures pharmacists can accurately prepare, dispense, and administer medications.
How can I improve my skills in pharmacy math?

+
Consistent practice using worksheets, understanding the underlying principles of each calculation, and seeking guidance from experienced pharmacists or tutors can significantly improve your math skills.
Can I use online resources for pharmacy math practice?

+
Yes, many online platforms offer interactive tools, quizzes, and worksheets tailored for pharmacy students. These can complement traditional study methods by providing instant feedback and diverse problems.
What are common mistakes in pharmacy math calculations?

+
Common mistakes include misreading units, decimal errors, incorrect factor conversion, overlooking the patient’s weight in dose calculation, and neglecting to double-check complex calculations.
How do I know if I’m ready for real pharmacy calculations?

+
Assess your readiness by consistently solving problems with high accuracy under timed conditions, understanding the reasoning behind each calculation, and applying math to real-world scenarios under supervision.