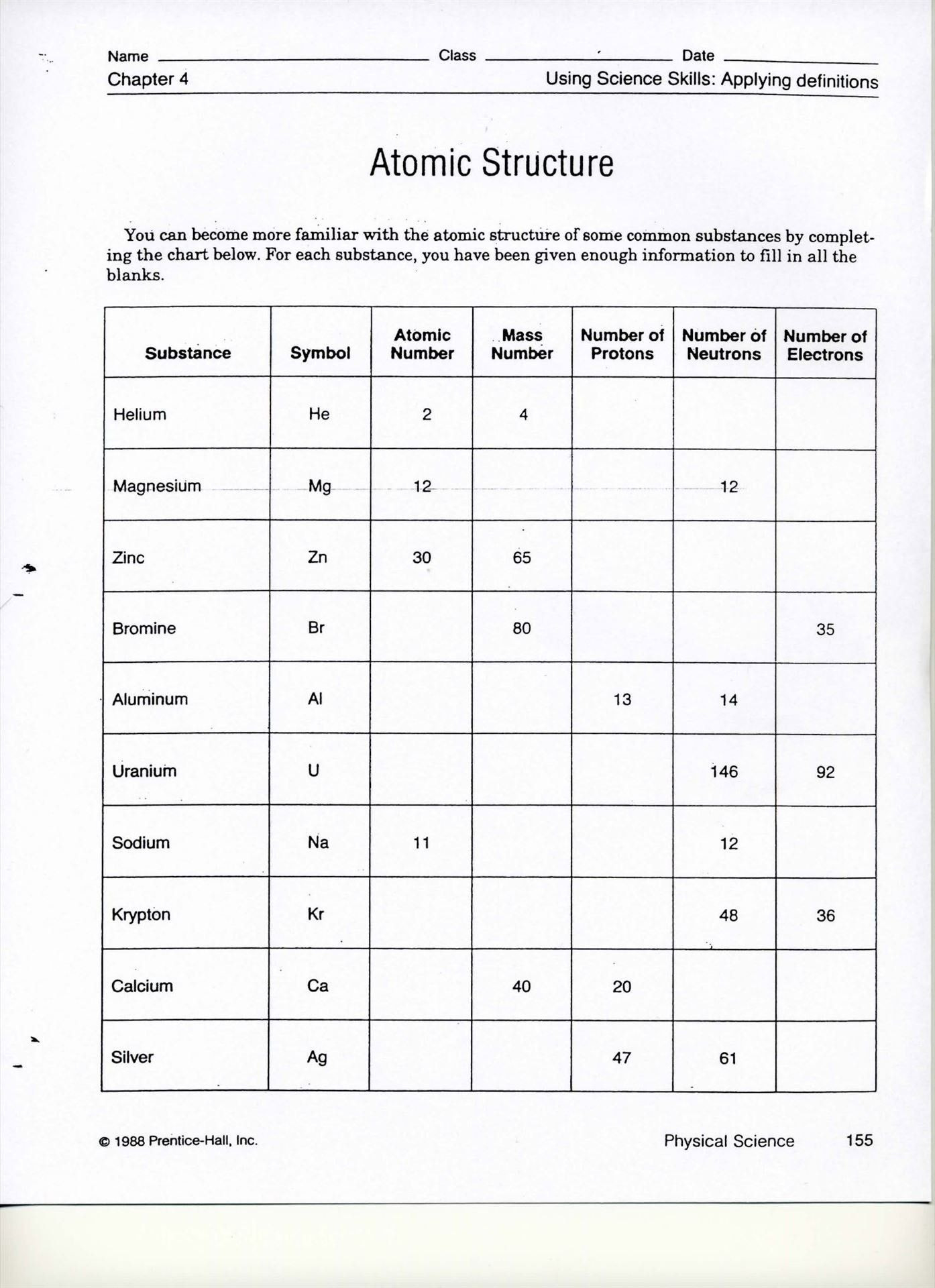
Mastering pH Practice: A Fun Worksheet Guide

Understanding the principles of pH is fundamental in both science and everyday life, whether you're brewing the perfect cup of coffee, managing a home aquarium, or conducting experiments in a chemistry lab. This blog post delves deep into the practice of measuring and understanding pH, offering a fun and educational journey through the acidic and basic realms of chemistry. We'll explore the significance of pH, how to measure it, practical applications, and even provide interactive worksheets for a hands-on learning experience.
Why pH Matters

pH, which stands for “power of hydrogen,” measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It’s a logarithmic scale from 0 to 14, where:
- 0 to 6.9 indicates acidity
- 7 is neutral
- 7.1 to 14 indicates alkalinity
Here’s why pH matters:
- Environmental Health: pH levels affect aquatic life, soil condition, and air quality.
- Biological Systems: The human body maintains a strict pH for optimal functioning, with blood pH staying close to 7.4.
- Industrial Processes: From brewing to wastewater treatment, controlling pH is crucial for efficiency and safety.
Measuring pH

There are several methods to measure pH, each suited for different applications:
1. pH Meter
- Electrically measures pH with high precision using a pH electrode.
- Best for laboratories and industrial settings where accuracy is paramount.
2. pH Indicator Papers

- They change color to indicate pH when dipped into a solution.
- Best for quick field tests or educational purposes.
3. pH Test Strips

- Similar to indicator papers but easier to read with a color scale.
- Best for home use like aquariums, pools, or soil testing.
🔬 Note: Always calibrate your pH meter before use for accurate readings.
Interactive pH Worksheets

Learning can be fun, especially when it involves interactive activities. Here are some worksheet ideas to practice pH:
Practical pH Experiments

Design experiments where students:
- Test household substances for pH and categorize them.
- Compare natural vs. artificial pH indicators.
- Investigate how pH changes with the addition of acids or bases.
pH Scale Coloring Activity

Provide a pH scale where students color in different pH ranges with specific colors to understand the scale visually:
| pH | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0-6.9 | Red | Acidic |
| 7 | Green | Neutral |
| 7.1-14 | Blue | Alkaline |

Real-Life pH Scenarios

Create scenarios where students have to decide the appropriate pH for different situations:
- Adjusting soil pH for optimal plant growth.
- Calculating the pH for safe swimming pool water.
- Formulating a buffer solution for a lab experiment.
The pH in Everyday Life

Understanding pH isn’t just for scientists; here are some practical applications:
- Health and Nutrition: The pH of the body influences digestion, nutrient absorption, and disease prevention.
- Cooking: The acidity or alkalinity can affect food’s texture, taste, and microbial activity.
- Beauty and Skin Care: Many skin products aim to balance skin pH to prevent irritation and promote health.
🥛 Note: The pH of milk should be closely monitored during cheese-making as it significantly affects the final product.
To summarize, mastering pH is not only an essential part of understanding chemistry but also has wide-ranging applications that touch upon various aspects of our daily lives. From ensuring our environment's health to making our favorite beverages, pH plays a pivotal role. Engaging in practical exercises through worksheets allows for a deeper grasp of these concepts, making pH an intriguing field of study.
What household items can I use to make a pH indicator?

+
You can use red cabbage, turmeric, beetroot juice, or grape juice as natural pH indicators. When combined with an acidic or basic solution, they change color, allowing for a rudimentary pH measurement.
How often should I calibrate a pH meter?

+
A pH meter should be calibrated before every use for the most accurate results, particularly in precise applications like labs or industrial settings.
Can pH affect plant growth?

+
Absolutely, soil pH impacts nutrient availability. Most plants prefer a pH between 6.0 and 7.5, but some, like blueberries, thrive in more acidic soil.