5 Tips to Ace Pedigree Worksheets in Biology Class
Embarking on the journey through the complexities of genetics often involves a fundamental understanding of pedigree analysis. In biology classes, pedigree worksheets offer students a visual approach to genetic transmission and inheritance patterns. From mastering the interpretation of symbols to predicting the likelihood of genetic traits, working with pedigrees is both a test and a tool for learning genetics. Here, we outline 5 tips to help you excel at working with pedigree worksheets, enhancing your grasp on this essential concept in biology.
1. Understanding Symbols and Notation

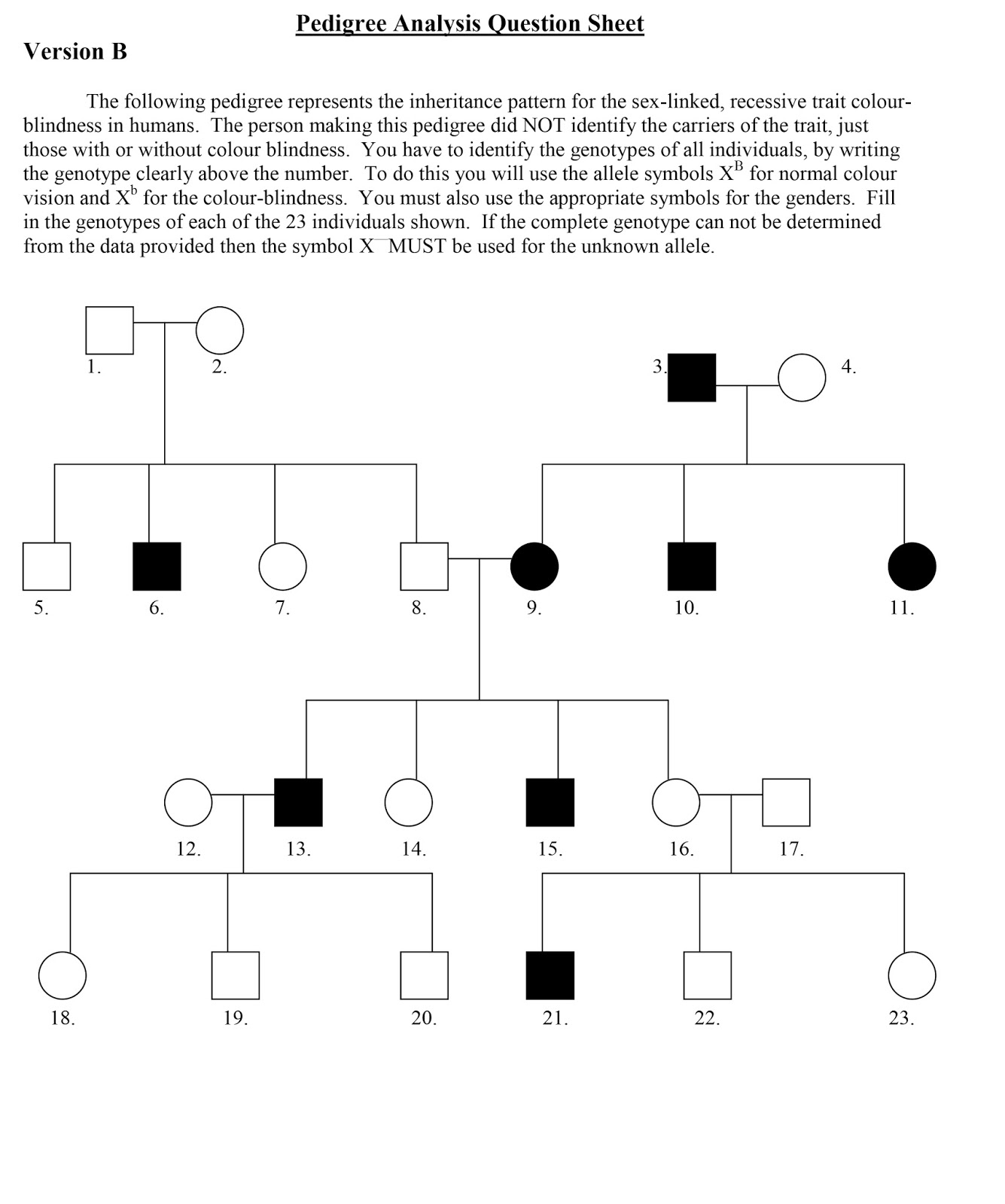
Before you dive into the complexities of genetics, it’s vital to have a clear understanding of the visual language used in pedigrees. Pedigree charts are structured in specific ways to make them universally interpretable. Here are the basics:
- Square: Represents a male.
- Circle: Represents a female.
- Solid shape: Denotes an affected individual or an individual with a particular trait.
- Shaded or patterned shape: Can indicate carriers or asymptomatic individuals.
- Lines: Horizontal lines connect parents, vertical lines connect parents to offspring, and diagonal lines indicate marriages or matings.
By understanding these symbols and notations, you can effectively read and interpret pedigrees, leading to a more profound comprehension of genetic inheritance.

2. Analyze Generation Patterns

The structure of pedigrees provides clues to inheritance patterns. Here's how you can analyze them:
- Vertical Analysis: If a trait appears consistently in vertical lines through multiple generations, it suggests an autosomal dominant inheritance.
- Horizontal Analysis: Traits found more horizontally among siblings might indicate autosomal recessive inheritance.
- Mitochondrial Analysis: Mitochondrial traits are maternally inherited, showing a pattern from mother to all offspring.
- Consanguinity: Pedigrees showing marriages between related individuals can complicate inheritance patterns, often leading to autosomal recessive disorders.
❗ Note: Understanding generation patterns can significantly improve your ability to predict genetic outcomes based on the pedigree structure.
3. Proper Notation of Probabilities

When working with pedigrees, you’ll often be tasked with calculating the probability of certain traits appearing in future generations. Use these tips:
- Determine Genotypes: Start by deducing the genotypes of known individuals using the pedigree.
- Punnett Square: Create Punnett squares to calculate the probability of inheriting a specific trait.
- Probability Notation: Use fractions or decimals to represent probabilities. For example, 1⁄2 for 50% chance.
- Conditional Probability: If you’re given information about carriers or specific traits, incorporate conditional probabilities into your calculations.
The accurate use of probability notation not only helps in solving the worksheet but also in understanding the statistical aspects of genetics.
4. Common Pedigree Problems and Solutions

Facing challenges with pedigree problems is common. Here’s how to tackle them:
- Understanding Sex-Linked Inheritance: Traits linked to X or Y chromosomes follow specific patterns in pedigrees. X-linked traits often show affected males linked to affected carrier females.
- Resolving Incomplete Information: Use all available data and infer likely genotypes from family patterns.
- Pedigree Errors: Sometimes, pedigrees contain errors or inconsistencies. Identify them by checking for unlikely scenarios.
- Mendelian Laws Application: Apply Mendel’s laws to solve complex pedigree problems by inferring inheritance modes.
By addressing these common issues, you'll become adept at overcoming pedigree worksheet challenges.
| Problem | Approach |
|---|---|
| Incomplete Data | Infer likely genotypes and apply Mendelian principles. |
| Genetic Heterogeneity | Consider different modes of inheritance if the pattern isn't clear. |
| Sex-Linked Traits | Focus on X and Y chromosome inheritance patterns. |
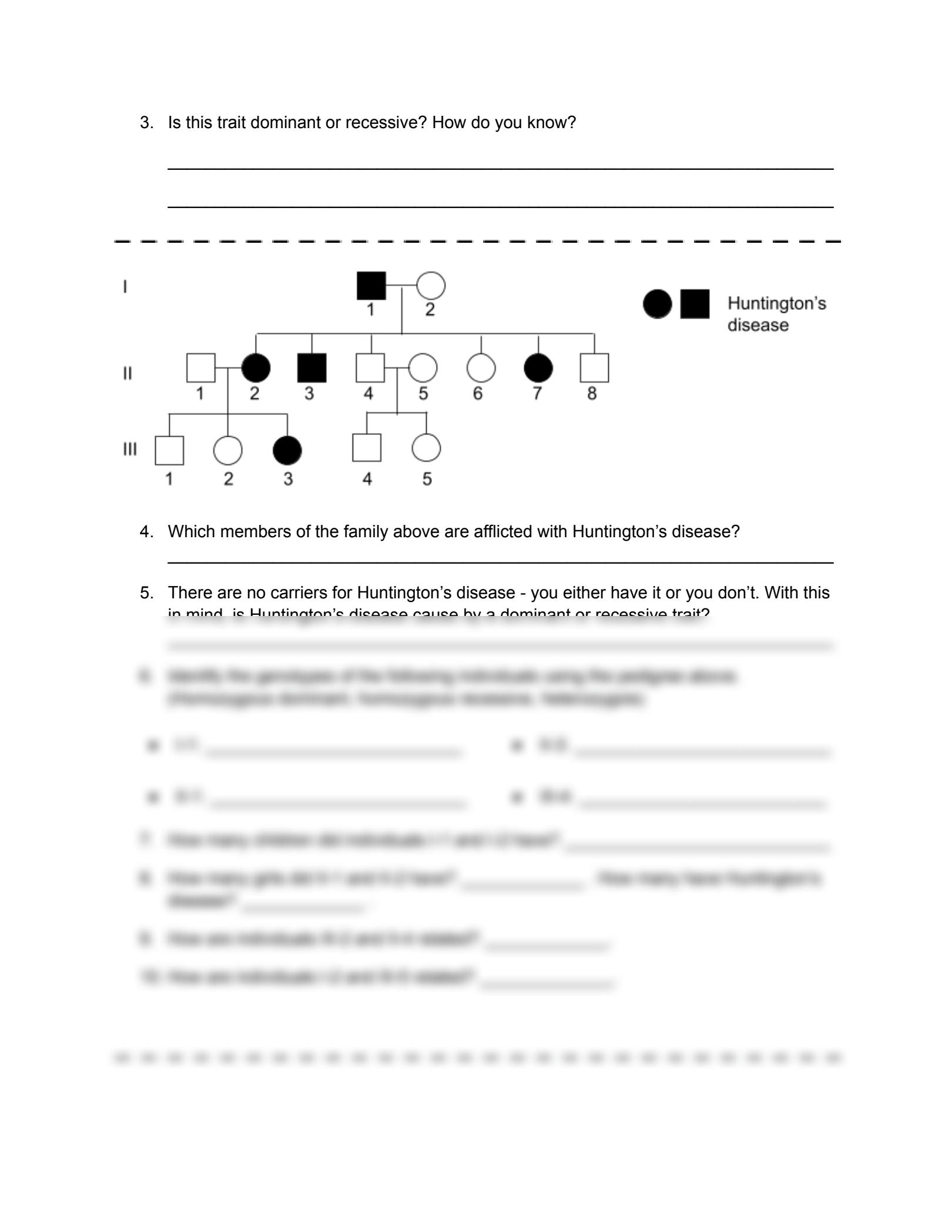
5. Practice and Revision

No skill is sharpened without practice. Here are some strategies:
- Use Pedigree Generators: Online tools can generate random pedigrees for practice.
- Group Study: Discuss and solve pedigree problems with peers to benefit from different perspectives.
- Review Past Papers: Exam questions often repeat, giving you a practical exposure to the types of problems you'll face.
- Revise Regularly: Consistently revisiting key concepts ensures they are cemented in your memory.
Practicing regularly not only improves your proficiency but also your confidence in handling pedigree worksheets.
The mastery of pedigree analysis in biology is more than just a classroom exercise; it's a practical tool for understanding genetic inheritance. By understanding symbols, analyzing patterns, using correct notation, tackling common issues, and practicing consistently, you're setting yourself up for success in not only acing your biology class but also in comprehending the principles of genetics. Remember, genetics isn't just about filling in squares and circles on a worksheet; it's about unraveling the mysteries of life itself.
How can I tell if a trait is autosomal or sex-linked?

+
Autosomal traits appear equally in males and females, while sex-linked traits show distinct patterns. For X-linked traits, males are usually more affected than females, and they inherit it from their mother. Y-linked traits are passed from fathers to sons.
Why are pedigree worksheets important in biology?

+
They visually represent how traits and diseases are passed down through generations, helping students understand genetic inheritance, predict genetic outcomes, and identify carriers and risks within families.
What if the pedigree chart doesn’t make sense?

+
Look for possible errors or inconsistencies. Consider alternative inheritance patterns like incomplete penetrance, new mutations, or even non-Mendelian inheritance which might not follow typical patterns.