5 Key Achievements of Qin and Han Dynasties

Throughout the annals of Chinese history, few eras have left as indelible a mark on the cultural, political, and economic landscape as the Qin and Han Dynasties. These dynasties, which collectively spanned over four centuries, introduced groundbreaking achievements in governance, infrastructure, technology, and culture. Here are five key achievements of the Qin and Han Dynasties that have profoundly influenced China and, indeed, the world.
1. Legalist Governance and the Centralized State
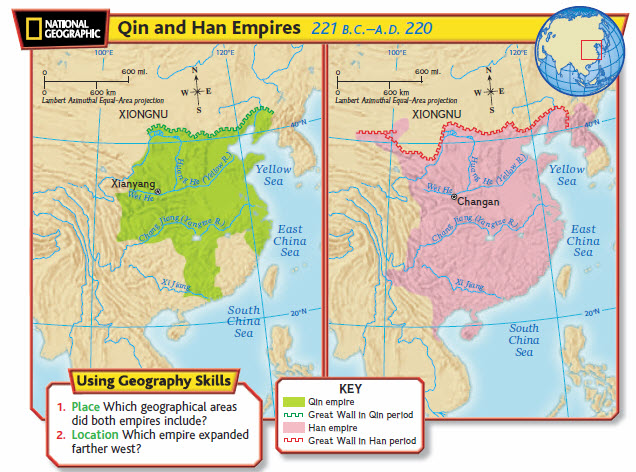
The Qin Dynasty, under Emperor Qin Shi Huang, introduced a form of government based on Legalism, a philosophical doctrine emphasizing strict laws, severe punishments, and a highly centralized, authoritarian state.
- Unification of China: Qin Shi Huang unified various warring states into a single empire, setting the foundation for Chinese identity.
- Bureaucracy: He replaced the feudal system with a bureaucratic structure, where officials were appointed based on merit rather than birth.
- Standardization: Weights, measures, currency, and even written script were standardized, ensuring uniformity across the vast empire.
The Han Dynasty, which followed the Qin, refined these systems, blending Legalism with Confucianism, promoting a more humane and ethical administration.
2. The Great Wall of China

The construction of the Great Wall, although started by earlier states, was significantly expanded under Qin Shi Huang. It wasn't until the Ming Dynasty that the Wall reached its well-known colossal scale, but the Qin's efforts were pivotal.
- Purpose: Initially designed to keep out nomadic invasions, it also served as a symbol of power and state control.
- Scale: The Qin Wall, though less extensive than later versions, was still an architectural marvel, running over thousands of miles.
- Legacy: It stands as one of the most enduring symbols of China, illustrating the might and ambition of the dynasty.
3. Innovations in Science and Technology

The Han Dynasty, particularly, is renowned for its technological advancements:
- Paper Making: Although paper had existed before, the Han improved its quality and production, which revolutionized documentation and literacy.
- Seismograph: Invention of the world's first seismograph by Zhang Heng in 132 AD, allowing for the detection of earthquakes.
- Silk Production: Further refined and widely traded, leading to the Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting East and West.
- Agriculture: Introduction of the "wheelbarrow," the "ploughshare," and advanced irrigation systems.
4. The Terra Cotta Army

Perhaps one of the most famous archaeological discoveries in the world, the Terracotta Army was buried with Emperor Qin Shi Huang, crafted to guard him in the afterlife:
- Artistry: Over 8,000 life-size sculptures depict the emperor's army in intricate detail, showcasing the remarkable skill of Qin artisans.
- Techniques: Moulding and assembly-line production techniques were used, displaying early mass-production methods.
- Cultural Significance: It reflects the emperor's power and the cultural and artistic achievements of the time.
⚠️ Note: The terra cotta warriors are now preserved under the protection of UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
5. Expansion and Interaction with Foreign Cultures

The Han Dynasty significantly expanded China's territory and cultural influence:
- Silk Road: Trade routes were established, facilitating not only commerce but also cultural and religious exchanges.
- Exploration and Diplomacy: Envoys like Zhang Qian were sent to the West, opening up new markets and diplomatic relations.
- Military Campaigns: The Han pushed into Central Asia, influencing neighboring states and establishing control over the Western Regions.
In wrapping up the exploration of the Qin and Han Dynasties, we find ourselves marveling at their enduring legacies. They set the foundation for China as a united nation-state, implemented systems of governance that would last for centuries, and left behind cultural treasures that continue to captivate and inspire. Their achievements in law, architecture, science, and culture underscore the dynamic historical period these dynasties represent, influencing not only Chinese history but also global civilization. As we ponder these accomplishments, we understand that they were not just rulers, but pioneers in their own right, shaping the future for generations to come.
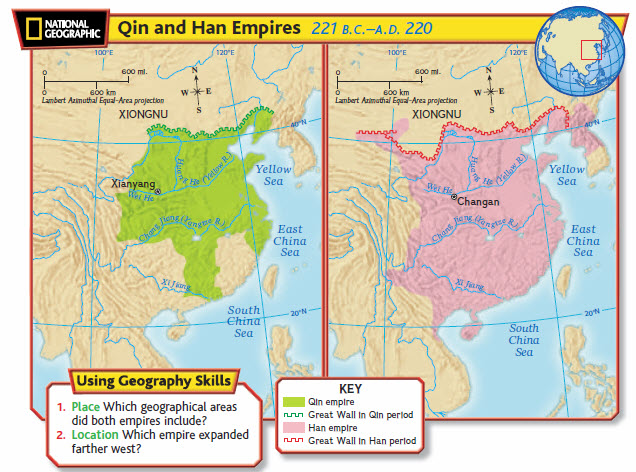
What was the Legalist approach to governance in the Qin Dynasty?
+
The Legalist philosophy promoted strict laws and punishments to enforce order, with the state being the central authority. This approach allowed for the unification and management of a diverse and vast empire.
How did the Han Dynasty refine the bureaucratic system?

+
The Han Dynasty introduced Confucian ideals into governance, aiming for a more ethical and benevolent rule. They emphasized scholarly learning and used examinations to select government officials based on merit.
Why was the Silk Road important during the Han Dynasty?

+
The Silk Road was crucial for the Han as it facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of Chinese innovations to the West. It also opened diplomatic channels and brought foreign goods and ideas into China.