Unlock the Mystery: Participles and Participial Phrases Worksheet Guide

In the world of English grammar, participles and participial phrases are like hidden gems, often used but not always understood in their full depth. These linguistic elements add color and detail to sentences, making them more vibrant and expressive. For both students learning English as a second language and native speakers looking to polish their grammar skills, understanding participles and participial phrases is invaluable. Here's your guide to mastering this grammatical treasure through practical exercises and examples.
Understanding Participles

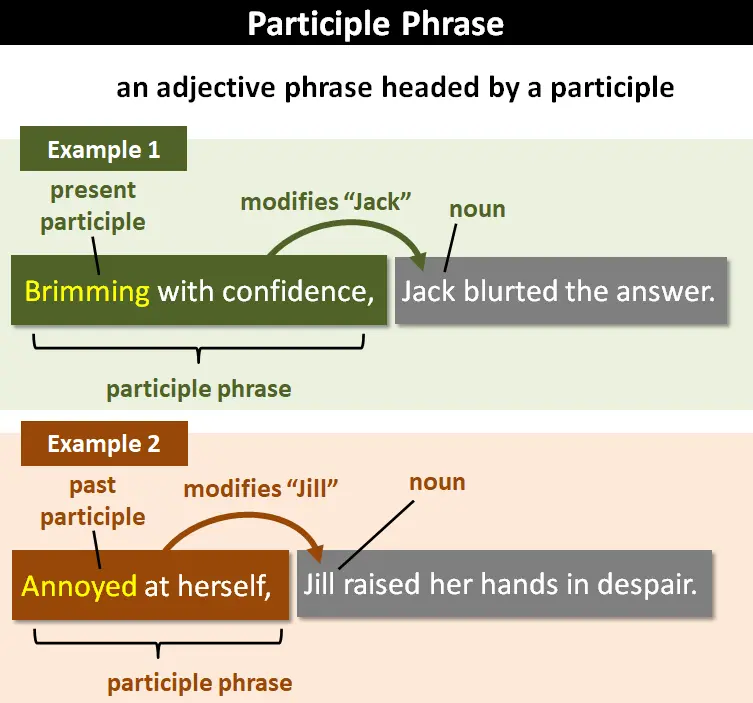
A participle is a form of a verb that acts as an adjective or modifies a noun. There are two types:
- Present Participle: Ending in -ing, it expresses an ongoing action or state of being. Example: "The running water."
- Past Participle: Often ending in -ed or -d, it describes a completed action. Example: "The cooked meal."
👍 Note: Some verbs have irregular past participle forms, like "seen," "gone," or "been."
Participial Phrases

When participles combine with other words to describe a noun, they form participial phrases. These phrases can add complexity and layers of meaning to your sentences:
- Present Participle Phrases: "The child, laughing loudly, entertained everyone."
- Past Participle Phrases: "Exhausted after the game, the players rested."
Worksheet Guide

To help you understand and practice participles and participial phrases, here's a structured worksheet guide:
Exercise 1: Identify the Participles
In the following sentences, identify whether the underlined word is a present participle or a past participle:
- "The flying bird is beautiful."
- "She read the written letter."
- "I saw the fallen tree on the road."
Exercise 2: Create Sentences with Participial Phrases

Using the participles provided, create sentences with a participial phrase:
| Participle | Sentence |
|---|---|
| Smiling | |
| Broken | |
| Raining |

Exercise 3: Rewrite Sentences

Rewrite the following sentences by incorporating a participial phrase:
- "The students played games. They were tired after school."
- "The photographer won the contest. His work was displayed in the gallery."
🔍 Note: Be careful with dangling modifiers. Ensure the participle or phrase correctly modifies the intended noun.
Exercise 4: Error Detection

In the sentences below, find and correct the use of participles or participial phrases:
- "The movie was boring, so I falling asleep."
- "Having been ignored, Mary left the room in anger."
⚠️ Note: Pay attention to verb forms and tense consistency when correcting sentences.
Practical Uses

Understanding participles and participial phrases opens up a variety of writing possibilities:
- Describing Characters: "Eyeing the prize, she planned her next move."
- Creating Atmosphere: "The room, bathed in soft light, was serene."
- Providing Backstory: "The man, scared from his past, lived quietly."
These examples show how these grammatical structures can enhance narrative and descriptive writing by providing more depth and detail.
The Benefits of Mastering Participles

Mastering participles and participial phrases will:
- Improve your sentence structure and variety.
- Help you convey more complex ideas efficiently.
- Enhance your creative and expressive writing capabilities.
By now, you've dived deep into the nuances of participles and how they can transform a basic sentence into something more dynamic. Each exercise and example provided has been designed to give you practical experience, which is essential for internalizing these grammatical concepts.
The key takeaways from this guide include:
- Participles are verbs turned into adjectives.
- Participial phrases enhance sentence detail and structure.
- Practical application through exercises helps solidify understanding.
We've explored the ways participles can be integrated into your writing to create rich, descriptive, and engaging content. Whether you're crafting stories, essays, or even professional reports, these elements can significantly uplift the quality and sophistication of your language.
What is the difference between a participle and a gerund?
+
While both are verb forms ending in -ing, a participle functions as an adjective (modifying a noun or pronoun), and a gerund acts as a noun in a sentence. Example: “I love swimming” (gerund) vs. “The swimming pool is large” (participle).
Can participles be used in different tenses?

+
Yes, participles can reflect different tenses: present participle for ongoing actions and past participle for actions completed. However, they do not change their form to indicate tense changes; they are static in form but can refer to different time frames depending on context.
What are some common mistakes with participles?
+
One common error is the dangling modifier, where the participle phrase doesn’t clearly modify the subject. Another mistake is tense confusion, using past participles where present participles are needed or vice versa, which can lead to unclear or grammatically incorrect sentences.


