Discover the Fascinating World of the Oxygen Cycle
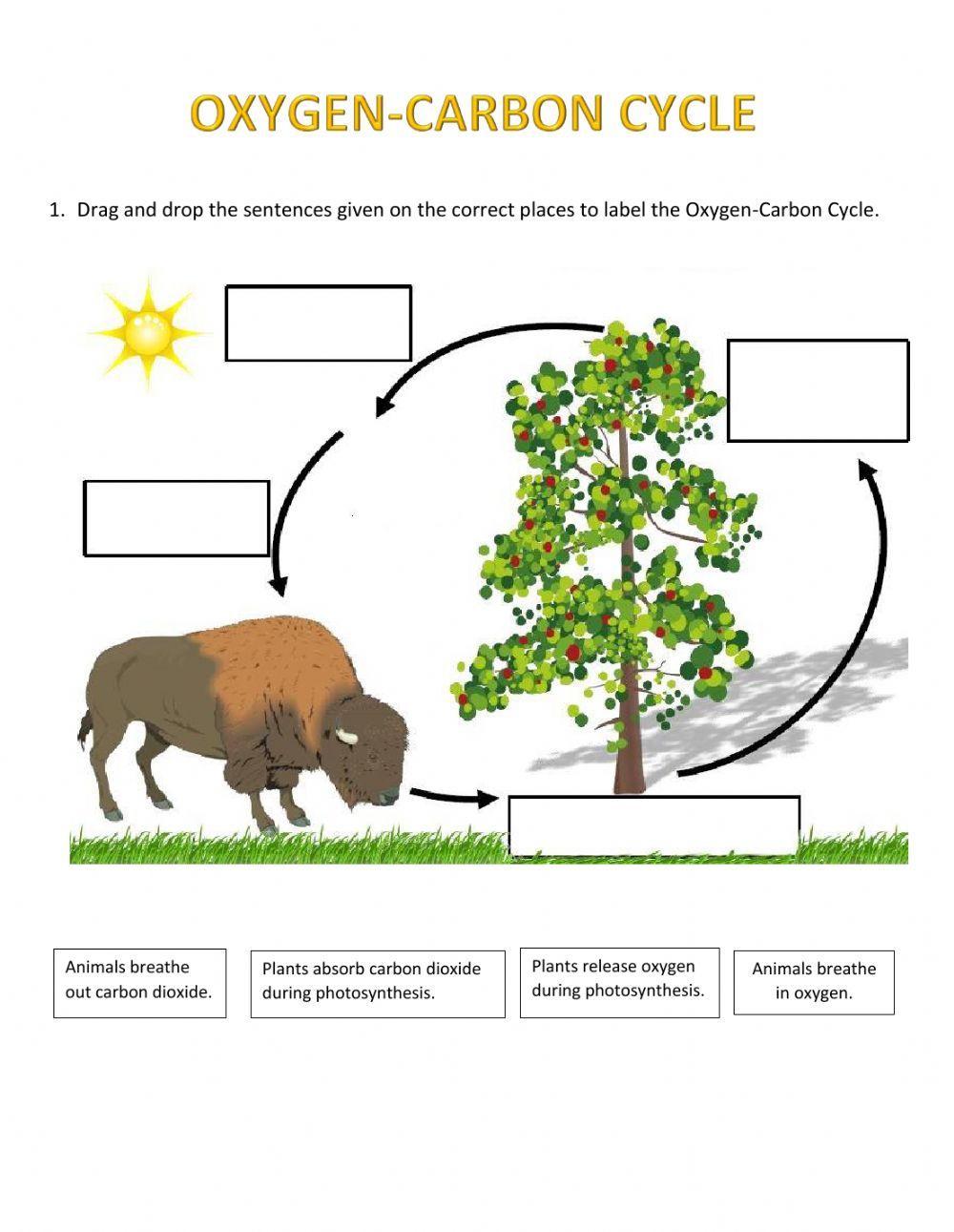
Welcome to the fascinating journey through the Oxygen Cycle. This essential cycle not only sustains life as we know it but also keeps our planet's atmospheric balance in check. From the leaves of the tallest trees to the depths of our oceans, oxygen's journey is an endless loop that involves numerous organisms and geological processes. Let's dive into the intricacies of this vital cycle and understand how it impacts our environment and life itself.
What is the Oxygen Cycle?
The Oxygen Cycle is the process by which oxygen is circulated through various forms within the Earth's system. It includes:
- Production: Oxygen is primarily produced by plants through photosynthesis, where they convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) into oxygen (O₂) and glucose.
- Utilization: This oxygen is then utilized by animals and humans during respiration to produce energy through cellular respiration.
- Exchange: Oxygen also cycles through the atmosphere, water, and soil via various physical and chemical reactions.

Key Players in the Oxygen Cycle
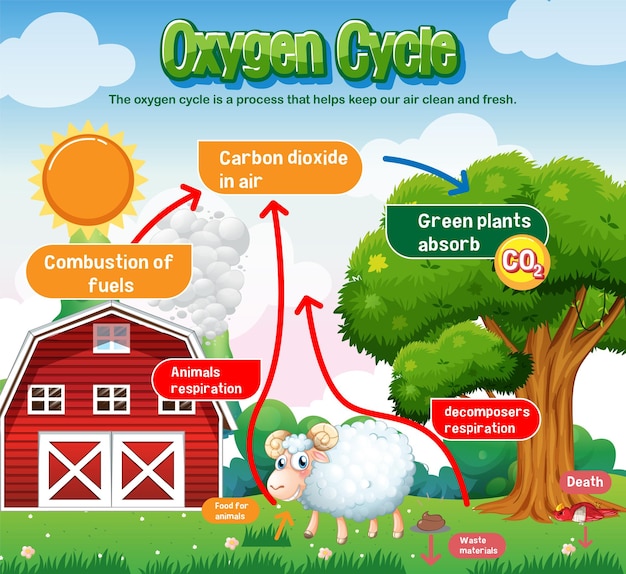
The oxygen cycle involves numerous players, each contributing to its balance:
Plants and Phytoplankton

Photosynthesis is the primary mechanism for oxygen production on land and in water bodies:
- Land plants contribute by capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen.
- Phytoplankton in the oceans performs a similar role, contributing about 50% of the Earth's oxygen.
Animals and Humans
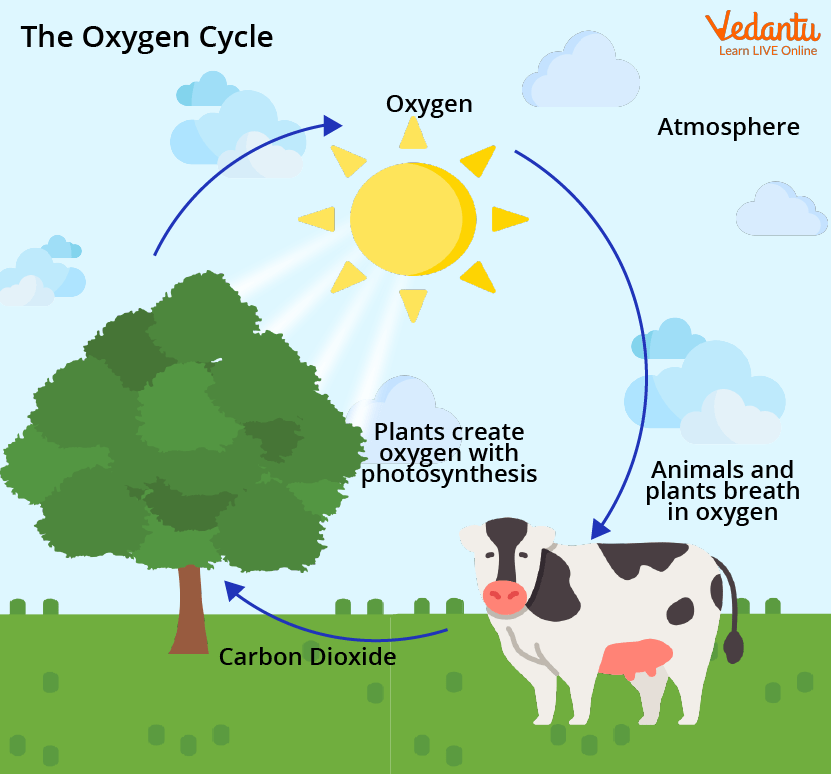
Through respiration, animals and humans use oxygen to break down nutrients to release energy:
- Animals consume plants or other animals, thus indirectly participating in oxygen cycling.
- Human activity, particularly industry and deforestation, can disrupt this natural balance.
Other Contributors
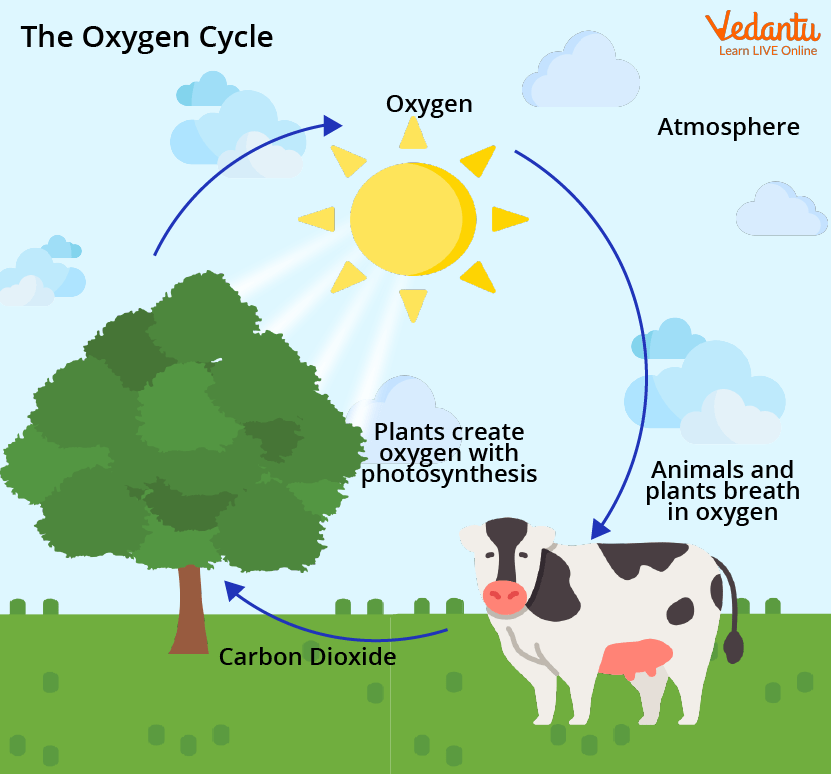
Some microorganisms, like cyanobacteria, also engage in photosynthesis, adding to the oxygen pool:
- Bacteria in the soil and water bodies also partake in this cycle by either consuming or producing oxygen.
Processes Involved in the Oxygen Cycle
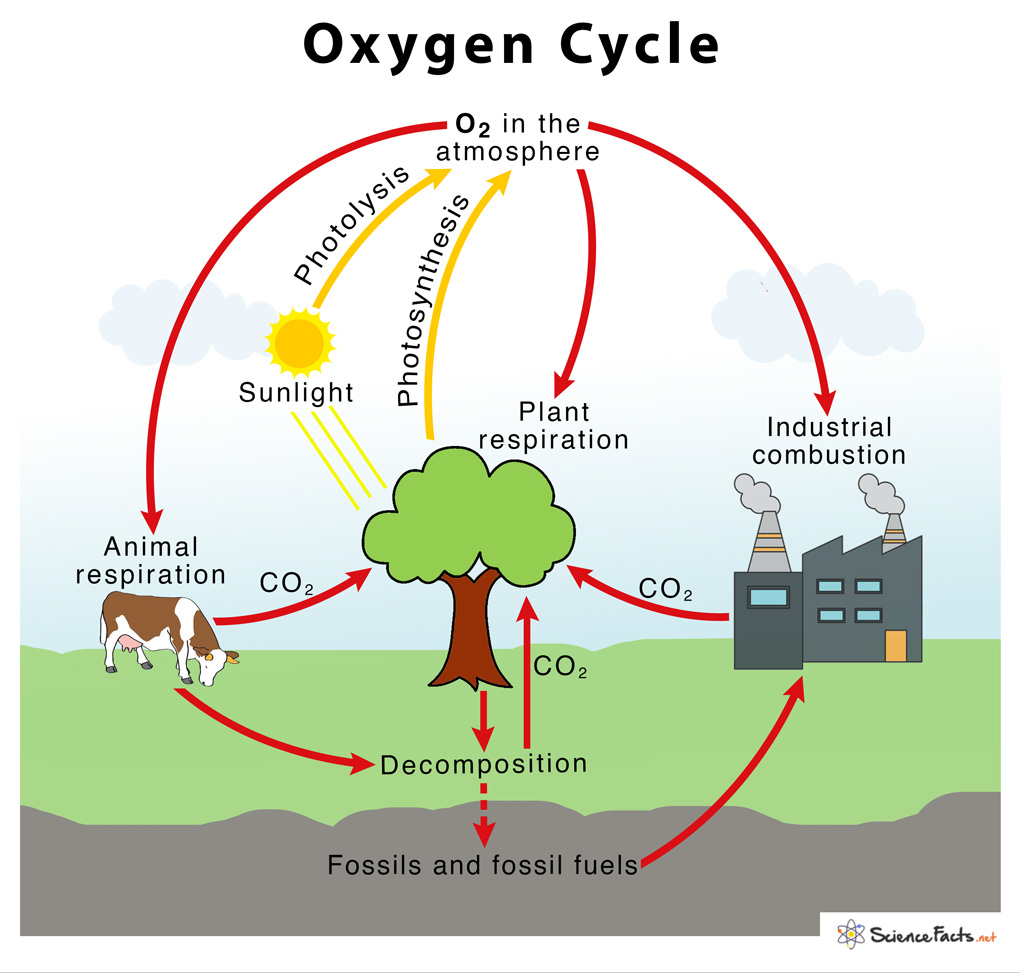
Let's delve deeper into the processes that facilitate the oxygen cycle:
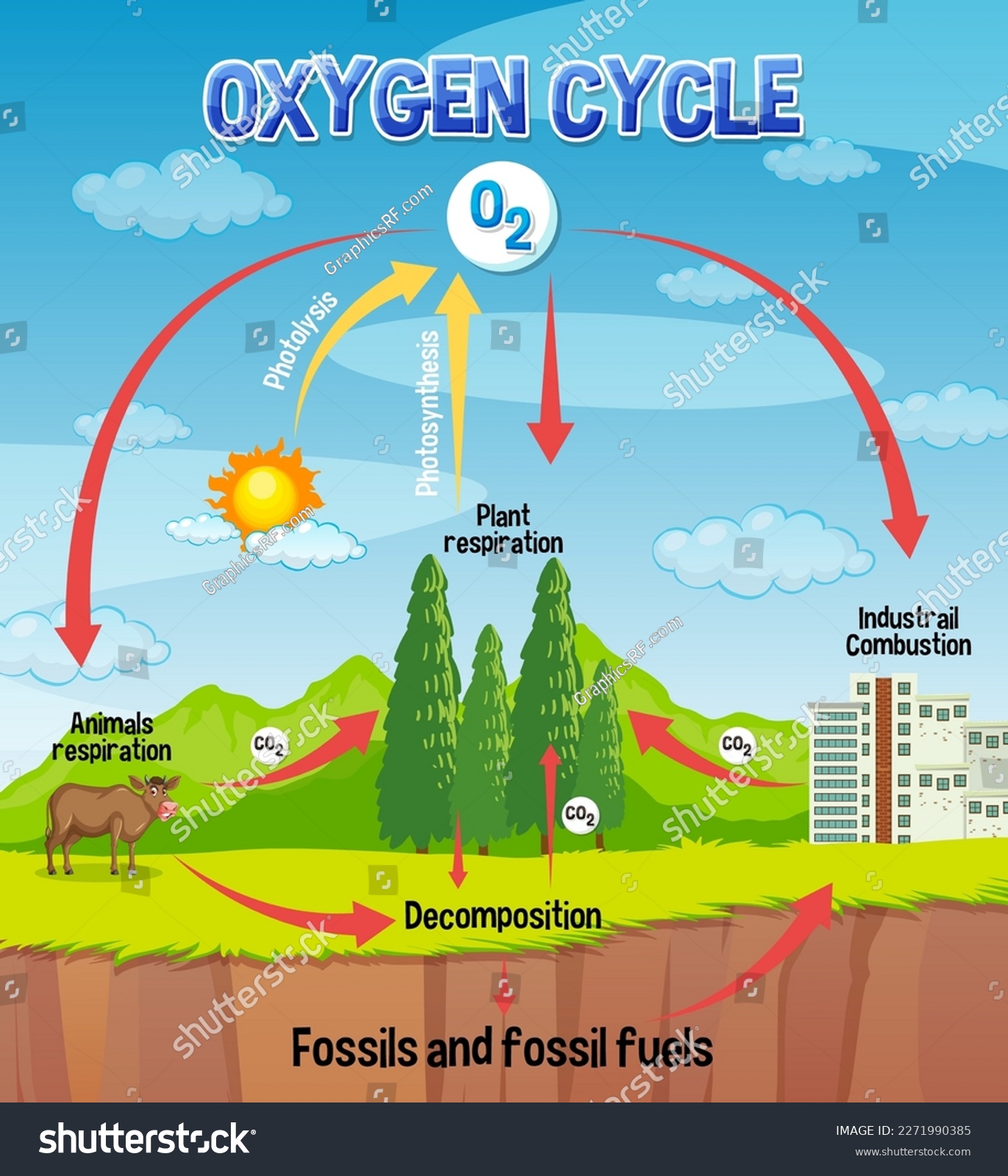
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is where the magic happens:
- Chlorophyll captures light energy, converting CO₂ and water (H₂O) into glucose and oxygen.
- Formula: 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂
🌿 Note: Photosynthesis is not just essential for oxygen production but also for trapping solar energy, which is crucial for all life forms.
Respiration

Respiration is the mirror image of photosynthesis:
- During cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy and produce water, carbon dioxide, and ATP.
- Formula: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + ATP
Other Processes
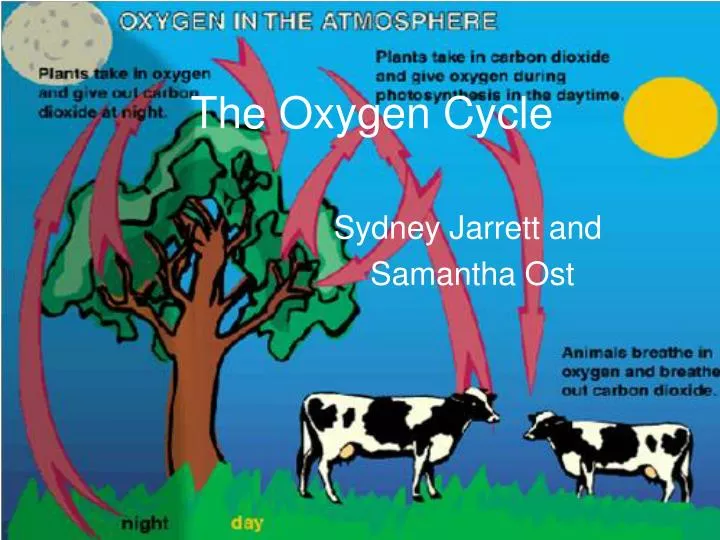
- Decomposition: As organic material decomposes, oxygen is either used by decomposers or released back into the atmosphere.
- Combustion: Burning fossil fuels consumes oxygen, releasing CO₂ and other pollutants.
- Ocean-Atmosphere Gas Exchange: The interaction between ocean waters and the atmosphere allows oxygen to dissolve into water or escape into the air.
The Role of the Oxygen Cycle in the Biosphere
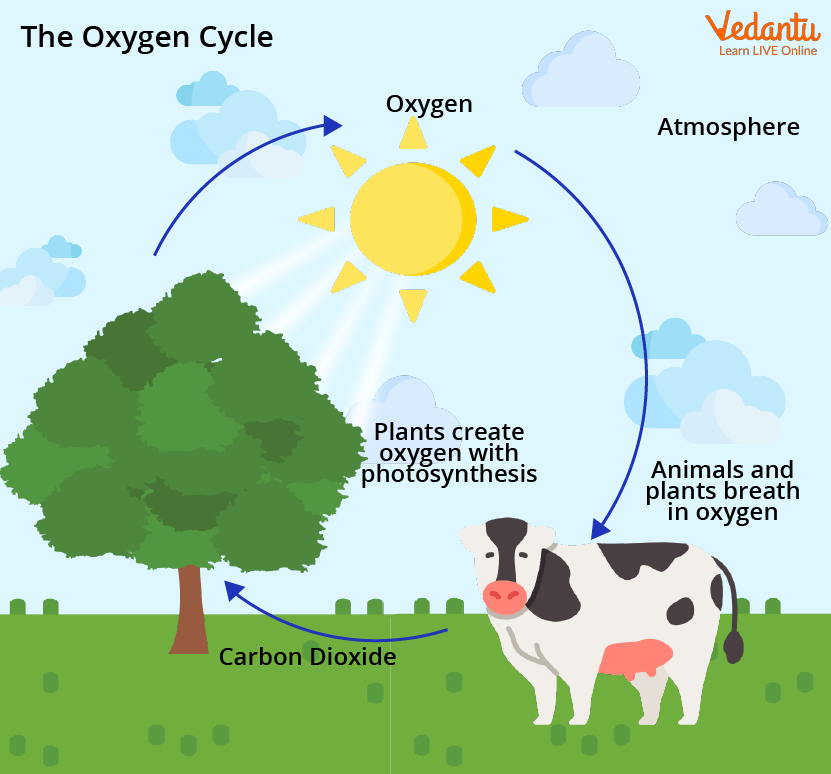
The oxygen cycle plays several critical roles in the biosphere:
Maintaining Atmospheric Oxygen Levels

The balance between oxygen consumption and production ensures that the atmosphere contains around 21% oxygen:
- A decrease in oxygen levels could make life unsustainable for aerobic organisms.
- An increase might lead to atmospheric oxidation and environmental shifts.
Climate Regulation
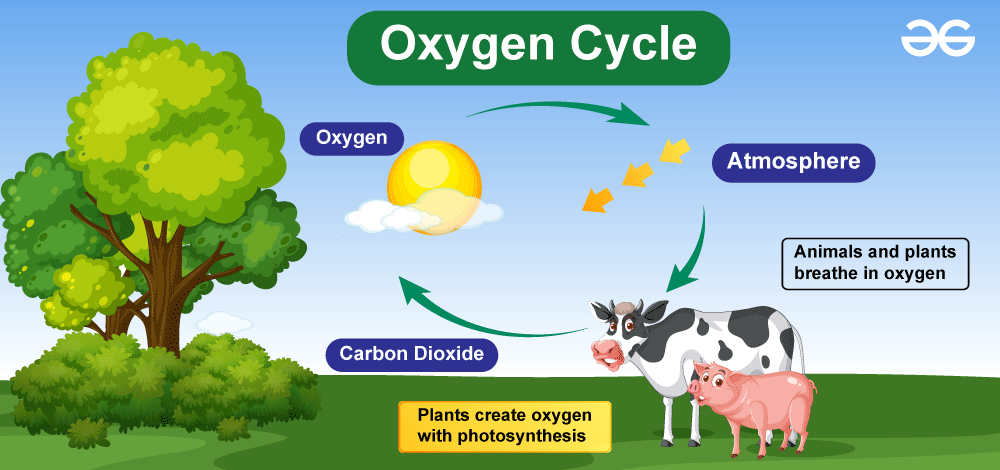
Oxygen affects the Earth's climate indirectly:
- By supporting the life forms that contribute to other cycles like the carbon cycle, which helps regulate greenhouse gases.
Ecosystem Health
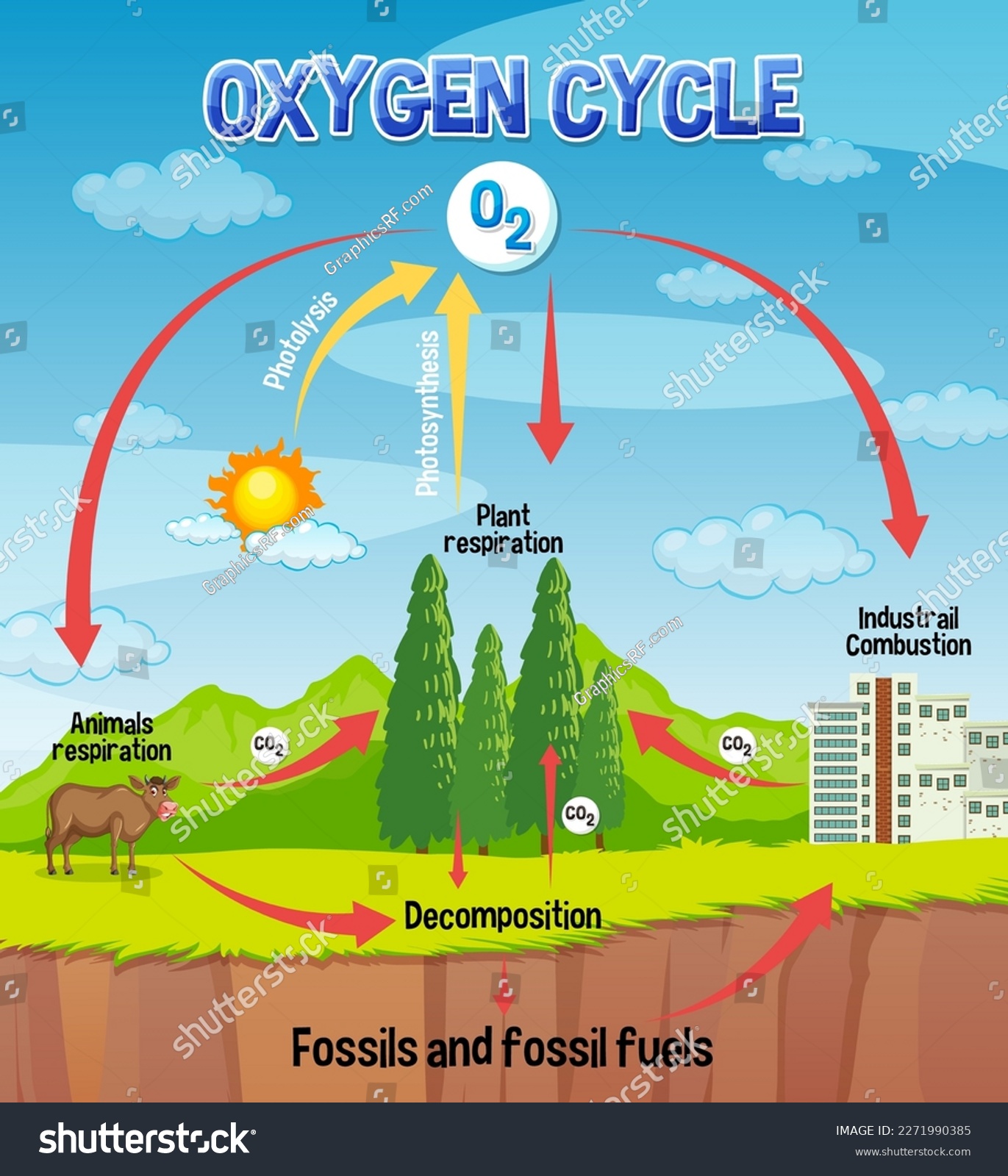
The health of various ecosystems relies on the oxygen cycle:
- From the roots of plants absorbing oxygen for soil respiration to the fish needing dissolved oxygen in water to survive.
Understanding the importance of maintaining this cycle leads us to consider the broader impact of human activities on it.
Human Impact on the Oxygen Cycle

The activities of humans have started to influence the oxygen cycle in profound ways:
Deforestation

Deforestation reduces the number of plants available for photosynthesis, thus affecting oxygen production:
- Loss of rainforests significantly diminishes global oxygen levels.
Fossil Fuel Combustion
The burning of fossil fuels for energy releases CO₂ while consuming oxygen:
- This not only affects atmospheric oxygen levels but also contributes to climate change.
Pollution
Pollution can disrupt natural oxygen-producing ecosystems:
- Pollutants can hinder photosynthesis or kill phytoplankton, reducing oxygen output.
Agricultural Practices
Intensive agriculture can lead to soil degradation, affecting the soil's ability to cycle oxygen:
- Over-fertilization might result in eutrophication, leading to aquatic dead zones with low oxygen levels.
While the natural oxygen cycle is robust, human intervention has started to affect its balance. Here's how we can contribute positively:
Conservation and Mitigation Strategies

The good news is, we can take steps to mitigate our impact:
Reforestation and Restoration
Planting trees and restoring degraded lands can help:
- It not only increases oxygen production but also sequesters carbon dioxide.
Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable practices can reduce our carbon footprint:
- Using renewable energy sources to reduce the consumption of oxygen during combustion.
- Reducing waste through the circular economy, minimizing environmental impact.
Policy and Education
Governmental policies and education can play pivotal roles:
- Legislation to protect natural oxygen-producing habitats.
- Educational programs to raise awareness about the cycle's importance and its fragility.
Scientific Research
Continued research into ecological cycles helps:
- Develop technologies like artificial photosynthesis to support the cycle artificially.
- Study the broader ecological impacts of human activity on Earth's systems.
By understanding and respecting the oxygen cycle, we ensure the sustainability of life on Earth. The cycle, which has evolved over billions of years, is now facing unprecedented challenges. It's a call for us to act responsibly, ensuring that future generations breathe as freely as we do today.
Why is the oxygen cycle important?
+The oxygen cycle is crucial for life as it ensures the continuous supply of oxygen for respiration and helps maintain the Earth’s atmospheric balance.
How do plants contribute to the oxygen cycle?
+Plants absorb carbon dioxide and through the process of photosynthesis, release oxygen into the atmosphere, maintaining atmospheric oxygen levels.
What is the impact of deforestation on the oxygen cycle?
+Deforestation reduces the number of plants capable of producing oxygen through photosynthesis, thus lowering overall oxygen production and altering atmospheric composition.