Organic Molecules: Simple Review Guide

Organic molecules play an integral role in every aspect of life on Earth. Their study is crucial not just for chemistry enthusiasts but for anyone interested in biology, medicine, pharmaceuticals, and even environmental sciences. This guide aims to delve into the world of organic molecules, providing an in-depth review while maintaining accessibility for readers with diverse backgrounds. Whether you're preparing for a biology or chemistry exam or simply looking to expand your understanding of life's building blocks, this guide will walk you through the essential concepts and components of organic chemistry.
What are Organic Molecules?

Organic molecules, also known as organic compounds, primarily contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. These molecules are known for their complexity and the unique ability of carbon to form stable chains, rings, and networks, leading to the vast diversity of life forms and substances.
Here are key characteristics of organic molecules:
- Carbon Backbone: Carbon's ability to form four covalent bonds allows it to create a backbone or framework for organic molecules.
- Covalent Bonds: These molecules are built around covalent bonds, which share electrons between atoms.
- Functional Groups: Organic molecules often contain specific groups of atoms (functional groups) that determine the molecule's chemical properties and reactivity.
🔍 Note: The backbone of organic molecules allows for the immense diversity seen in nature, from the simplest amino acids to complex biomolecules like DNA.
Types of Organic Molecules


Organic molecules can be classified into several major types based on their structure and function:
Alkanes

Alkanes, or paraffin hydrocarbons, consist of single bonds between carbon atoms, making them the simplest form of organic compounds. Their general formula is CnH2n+2.
Alkenes

Alkenes contain at least one double bond, with a general formula of CnH2n. They are more reactive than alkanes due to the instability of the double bond.
Alkynes

Characterized by triple bonds, alkynes have the formula CnH2n-2. Their reactivity is even higher due to the high-energy triple bond.
Aromatic Compounds

These are compounds with delocalized pi electrons spread over conjugated planar rings, often following Hückel’s Rule (4n+2 pi electrons), exemplified by benzene.
Functional Groups
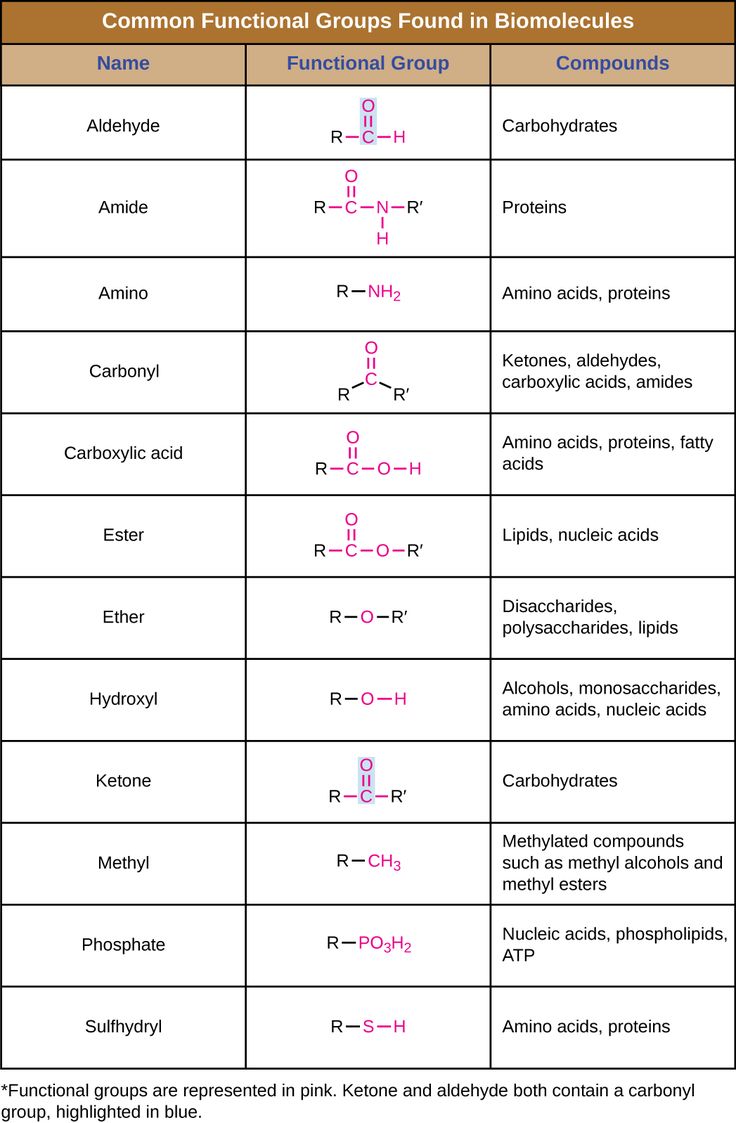
The functional group is the part of an organic molecule where most of the reactivity takes place. Here’s a brief overview:
| Functional Group | Structure | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohols (-OH) | R-OH | Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) |
| Aldehydes (-CHO) | R-C(=O)H | Formaldehyde (HCHO) |
| Ketones (>C=O) | R-C(=O)-R | Acetone (CH3COCH3) |
| Carboxylic Acids (-COOH) | R-COOH | Acetic acid (CH3COOH) |
| Amines (-NH2) | R-NH2 | Ethylamine (CH3CH2NH2) |

🔍 Note: Functional groups can alter the physical and chemical properties of molecules significantly, for example, adding polarity or the ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Importance in Life Sciences

Organic molecules are the foundation of life, playing critical roles in:
- Energy Storage: Carbohydrates like glucose provide energy through cellular respiration.
- Genetic Information: Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) store and transmit genetic information.
- Structure and Transport: Proteins build cellular structures and facilitate transport within and between cells.
- Catalysis: Enzymes, which are proteins, speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
Key Reactions of Organic Molecules


Understanding the reactions of organic molecules is pivotal for grasping their role in chemical synthesis and biological processes:
Substitution Reactions

These occur when one functional group is replaced by another. For example, halogenation where a hydrogen atom is replaced by a halogen:
- CH4 + Cl2 -> CH3Cl + HCl
Addition Reactions

Common in alkenes and alkynes where a double or triple bond breaks to form new single bonds. Here’s an example of hydrogenation:
- C2H4 + H2 -> C2H6
Elimination Reactions

The inverse of addition reactions, where two atoms or groups are removed from a molecule to form an alkene or alkyne:
- CH3CH2Cl -> C2H4 + HCl
🔍 Note: Organic reactions underpin drug synthesis, food processing, and metabolic pathways in organisms, highlighting their practical significance.
Organic Molecules in Modern Applications

The versatility of organic chemistry extends to numerous industries:
- Pharmaceuticals: The design and synthesis of drugs require a thorough understanding of how organic molecules interact with biological systems.
- Materials Science: From plastics to advanced materials, the manipulation of organic molecules allows for the creation of materials with specific properties.
- Environmental Science: Understanding the behavior of organic pollutants and their remediation involves organic chemistry principles.
- Food Science: Flavors, preservatives, and food additives are all products of organic chemistry research.
In wrapping up this exploration of organic molecules, it's clear that their study is not confined to chemistry classrooms or research labs. Their influence spans across biological systems, industrial applications, and environmental sciences, showcasing their paramount importance in our world. From the smallest organic molecule to the most complex biomolecules, the principles of organic chemistry help us understand the fundamental processes of life and how we might manipulate these for beneficial purposes. The dynamism and complexity of these compounds are what make them both a challenge and a marvel to study, underscoring their significance in our everyday lives.
What are the common elements in organic compounds?

+
The most common elements are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
Why is carbon crucial to organic chemistry?

+
Carbon’s ability to form stable bonds with other carbon atoms and to bond with various elements allows for the creation of an extensive array of organic molecules.
How do functional groups affect the properties of organic molecules?
+
Functional groups define the chemical reactivity, polarity, and solubility of organic compounds, influencing their behavior in various chemical environments.