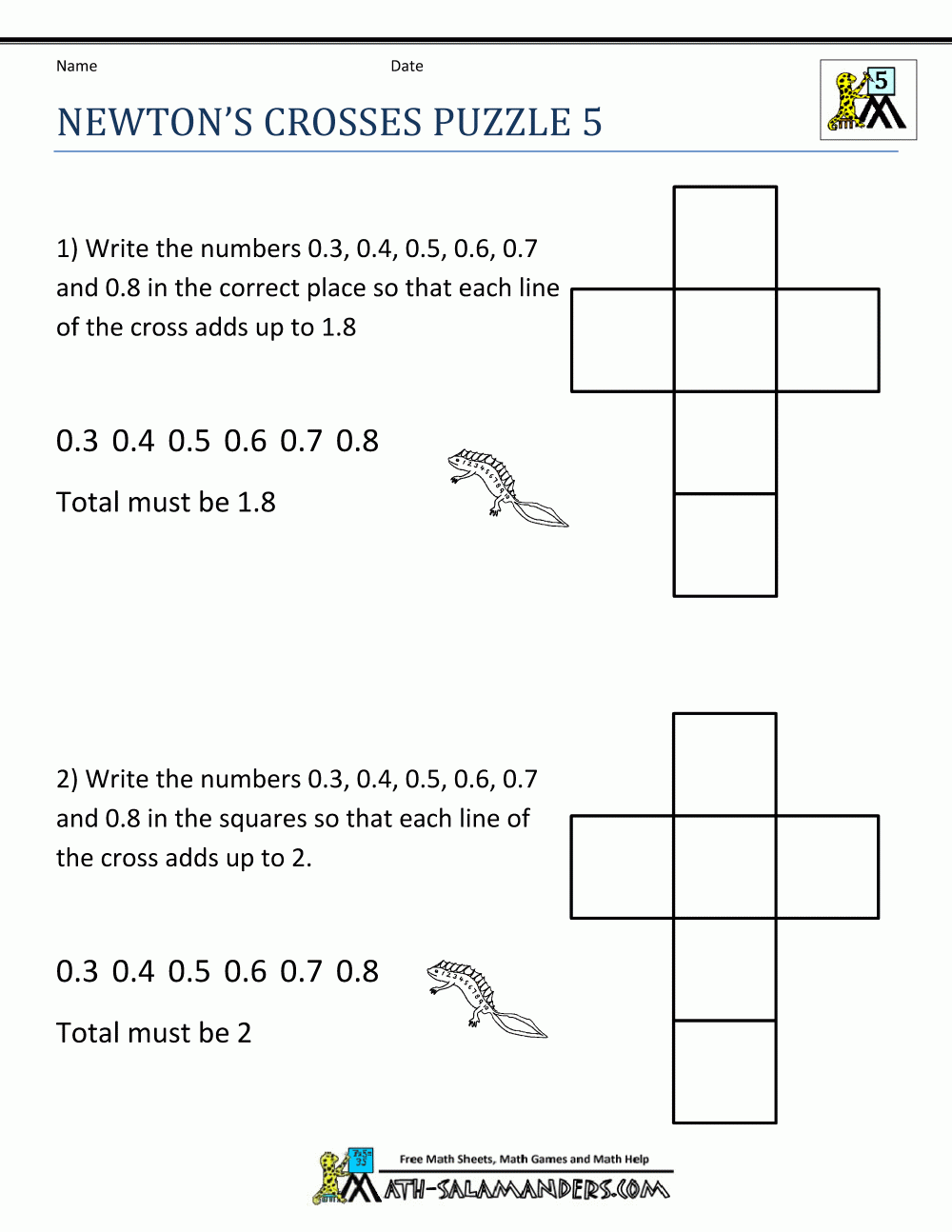
5 Tips to Easily Understand Orbital Diagram Worksheets
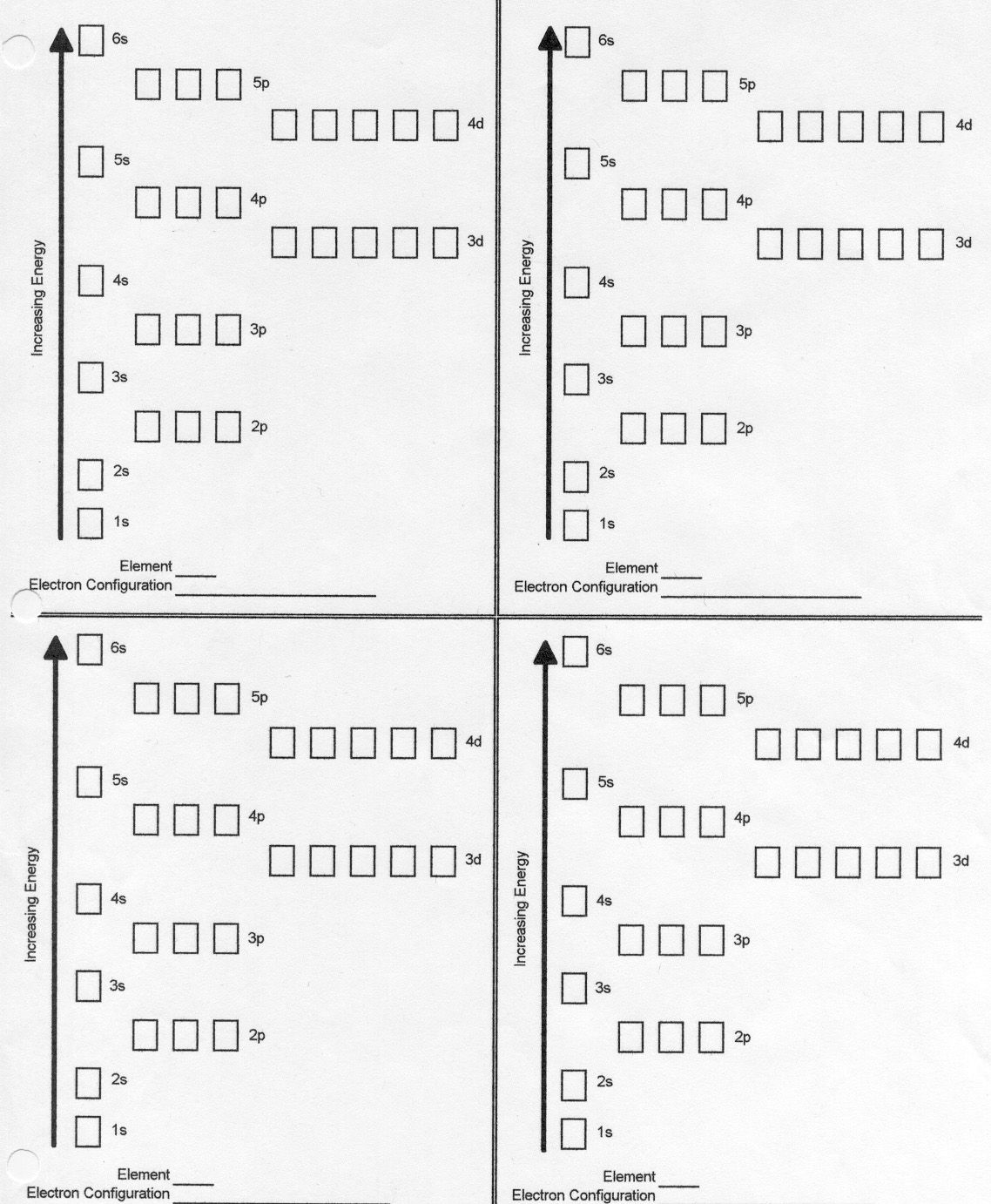
Orbital diagrams are a visual representation of electron configuration, helping students and researchers to visualize how electrons are distributed within an atom's orbitals. Understanding these diagrams is crucial for several fields in science, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to decoding orbital diagram worksheets, making learning this complex topic as straightforward as possible.
1. Learn the Basics of Atomic Structure
Before diving into the complexities of orbital diagrams, familiarize yourself with the basic structure of an atom:
- Protons: Positive particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negative particles that orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
Each electron can be in a specific orbital, determined by quantum numbers. The principle quantum number (n) indicates the energy level, while the angular momentum quantum number (l) describes the shape of the orbital, and the magnetic quantum number (ml) specifies the orientation.
🌟 Note: Electron shells are denoted by numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.), subshells by letters (s, p, d, f), and each can contain a specific number of electrons - 2 for s, 6 for p, 10 for d, and 14 for f.
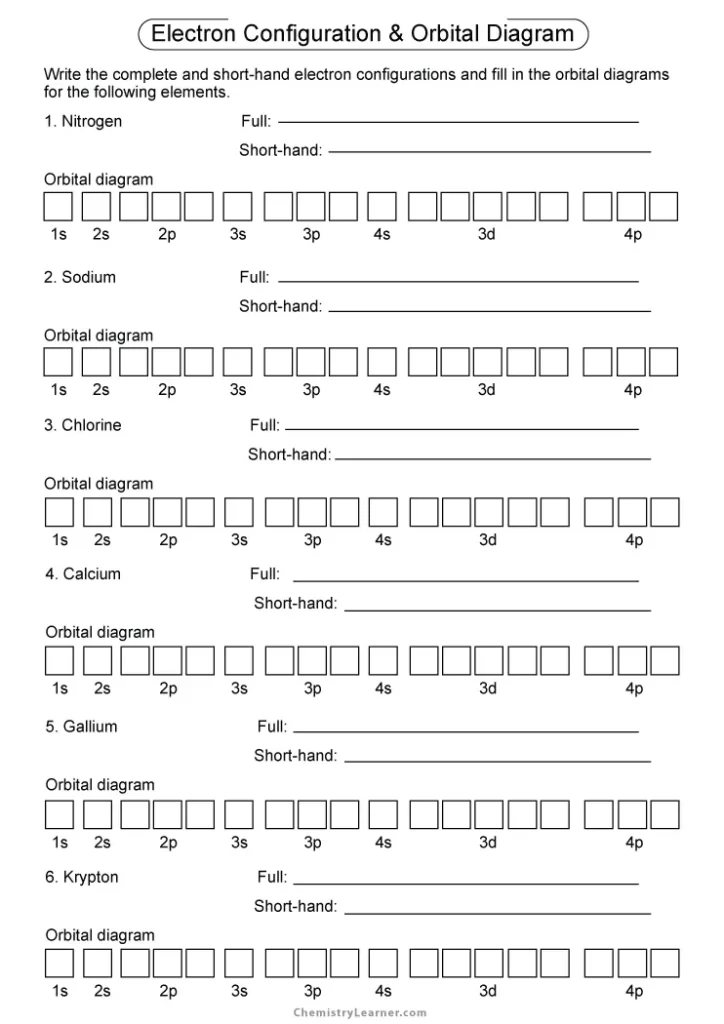
2. Understand Electron Configuration Notation

Orbital diagrams visually represent electron configurations:
- The Aufbau Principle states electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals available.
- Hund’s Rule suggests electrons will singly occupy orbitals of equal energy before pairing up.
- The Pauli Exclusion Principle mandates that each orbital can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins.
An electron configuration might look like this for oxygen (atomic number 8): 1s² 2s² 2p⁴. The diagram shows boxes representing orbitals with arrows for electrons.
| Energy Level | Sublevel | Orbitals | Maximum Electron Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | s | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | s | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | p | 3 | 6 |
| 3 | s | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | p | 3 | 6 |

3. Diagram Drawing Techniques

To draw an orbital diagram:
- List all orbitals from 1s up to the highest energy level needed for the atom.
- Fill the orbitals in order of increasing energy according to the Aufbau principle.
- Apply Hund’s Rule by distributing electrons singly in orbitals of the same energy level before pairing.
- Ensure that electrons are drawn with arrows (spin up or down) to show their spin state.
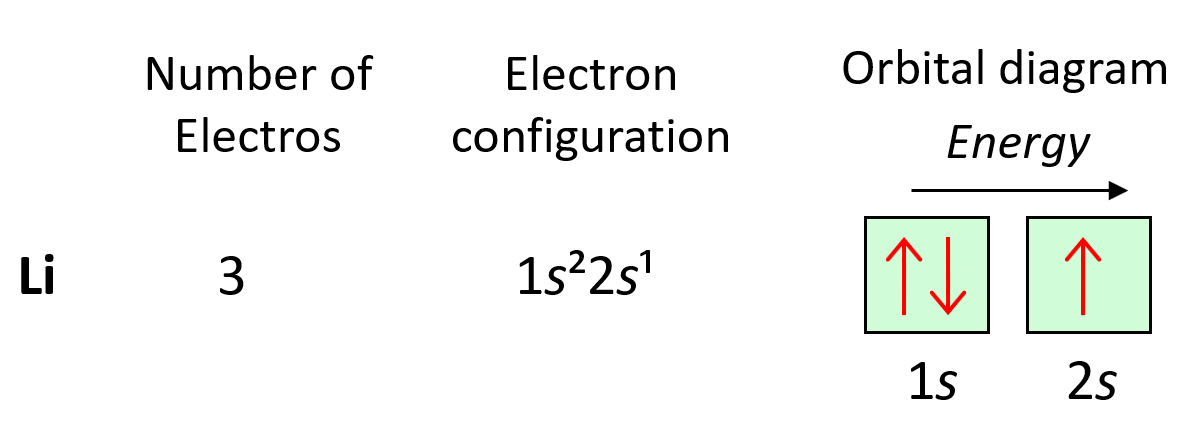
Here’s an example for Helium:
| 1s| | 2s|
⇅ | |
📝 Note: The ↑ and ↓ represent the spin states of the electrons; paired electrons must have opposite spins.
4. Reading and Interpreting Orbital Diagrams

Interpreting an orbital diagram involves:
- Identifying the electron configuration from the diagram.
- Recognizing anomalies like half-filled subshells, which can be more stable.
- Noticing trends in electron placement according to the periodic table.
Consider the iron atom (atomic number 26), its configuration can be read from an orbital diagram, showing exceptions to the filling order due to stability.
5. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them

When working with orbital diagrams, avoid these common errors:
- Misplacing Electrons: Filling orbitals in the wrong order or missing subshells.
- Ignoring Electron Spin: Each orbital can hold two electrons with opposite spins.
- Overlooking Hund’s Rule: Not spreading electrons singly across degenerate orbitals first.
Practice with different elements and compare your diagrams with established electron configurations.
Mastering orbital diagrams isn't just about memorizing rules, but about understanding the logic behind electron behavior in atoms. Each tip in this post is designed to make the learning process more intuitive and less daunting. With regular practice and an awareness of the principles governing electron arrangement, you can decode any orbital diagram worksheet with confidence.
Why is it important to understand orbital diagrams?
+
Orbital diagrams provide a visual representation of electron configurations, which is essential for understanding chemical reactivity, predicting molecular bonding, and interpreting spectroscopic data.
What does each arrow in an orbital diagram represent?
+
Each arrow represents an electron, with the arrow pointing up or down to indicate the spin state of the electron. Opposite spins are represented by opposing arrows in the same orbital.
How do I know when to fill orbitals in a specific order?

+
Follow the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy level. Use the periodic table as a guide; elements are ordered by increasing atomic number, which also indicates the filling order of orbitals.