Mastering Square Roots: Free Operations Worksheet

Understanding the intricacies of square roots forms a cornerstone of mathematical learning. It bridges the transition from simple arithmetic to the complex realms of algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide delves into the realm of square roots, elucidating on their nature, importance, and practical operations through a meticulously crafted worksheet.
What Are Square Roots?

The square root of a number (x) is defined as a value (y) such that (y^2 = x). In simpler terms, square root reverses the operation of squaring. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- The square root of 4 is 2, since (2 \times 2 = 4).
- The square root of 9 is 3, as (3 \times 3 = 9).
Importance of Square Roots

From engineering to financial modeling, square roots are ubiquitous in:
- Measurement of distances: The Pythagorean theorem uses square roots to calculate distances in a 2D or 3D space.
- Geometry: Areas and volumes often require square root calculations.
- Scientific and engineering applications: From physics where they’re pivotal in calculating velocity and acceleration, to electrical engineering where they’re integral to voltage and current relationships.
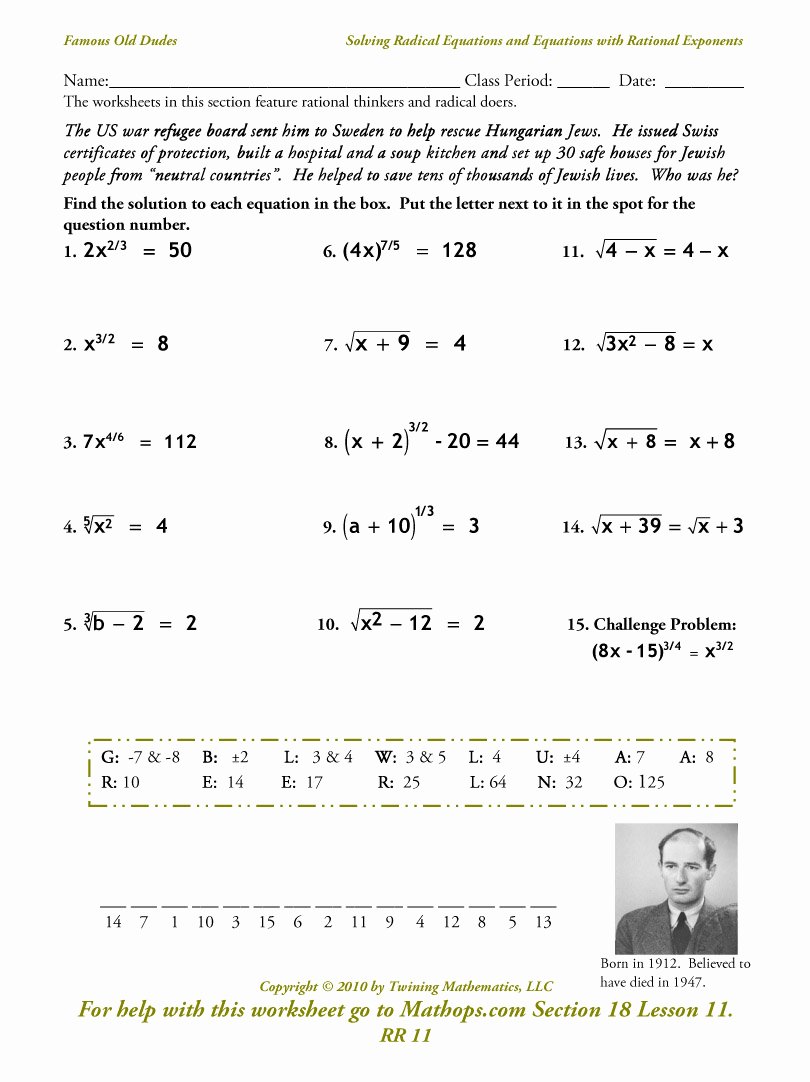
The Square Root Operations Worksheet

Below is a worksheet to test your understanding of square root operations:
| Number | Square Root | Operations |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | 3 | Add 4, then find square root |
| 16 | 4 | Multiply by 2, then find square root |
| 4 | 2 | Subtract 1, then find square root |

💡 Note: Operations involve altering the original number before calculating the square root.
Performing Square Root Operations

To perform operations with square roots, consider the following steps:
- Alter the number: Follow the operation specified in the worksheet (add, subtract, multiply, or divide).
- Calculate the square root: After altering the number, find its square root.
Let’s solve the above examples:
- 9: Add 4, resulting in 13. Then, find the square root: (\sqrt{13} \approx 3.6055)
- 16: Multiply by 2, getting 32. Then, find the square root: (\sqrt{32} \approx 5.6568)
- 4: Subtract 1, to get 3. Then, find the square root: (\sqrt{3} \approx 1.7320)
Tips for Mastering Square Roots

To get better at square roots, here are some tips:
- Memorize Common Roots: Knowing the square roots of perfect squares can make calculations quicker.
- Understand the Concept: Realize that square roots exist even for non-perfect squares; they might not be rational numbers.
- Practice: Use online tools, worksheets, or perform manual calculations to enhance your skills.
Real-Life Applications of Square Roots
Consider these practical applications:
- Architecture: Architects often use the Pythagorean theorem to design buildings and landscapes.
- Navigation: GPS systems calculate distance using square roots.
- Art: Artists use perspective and proportion, which often require square root calculations.
In wrapping up our exploration of mastering square roots, the importance of understanding this mathematical concept cannot be overstated. From everyday tasks to sophisticated scientific applications, the ability to effortlessly work with square roots opens up numerous avenues of problem-solving and creativity. By internalizing the methods presented in this worksheet, and through consistent practice, you'll unlock a fundamental skill that underpins much of modern mathematics. Remember, the journey with numbers is endless, and square roots are just one fascinating stop along the way.
Why are square roots important?
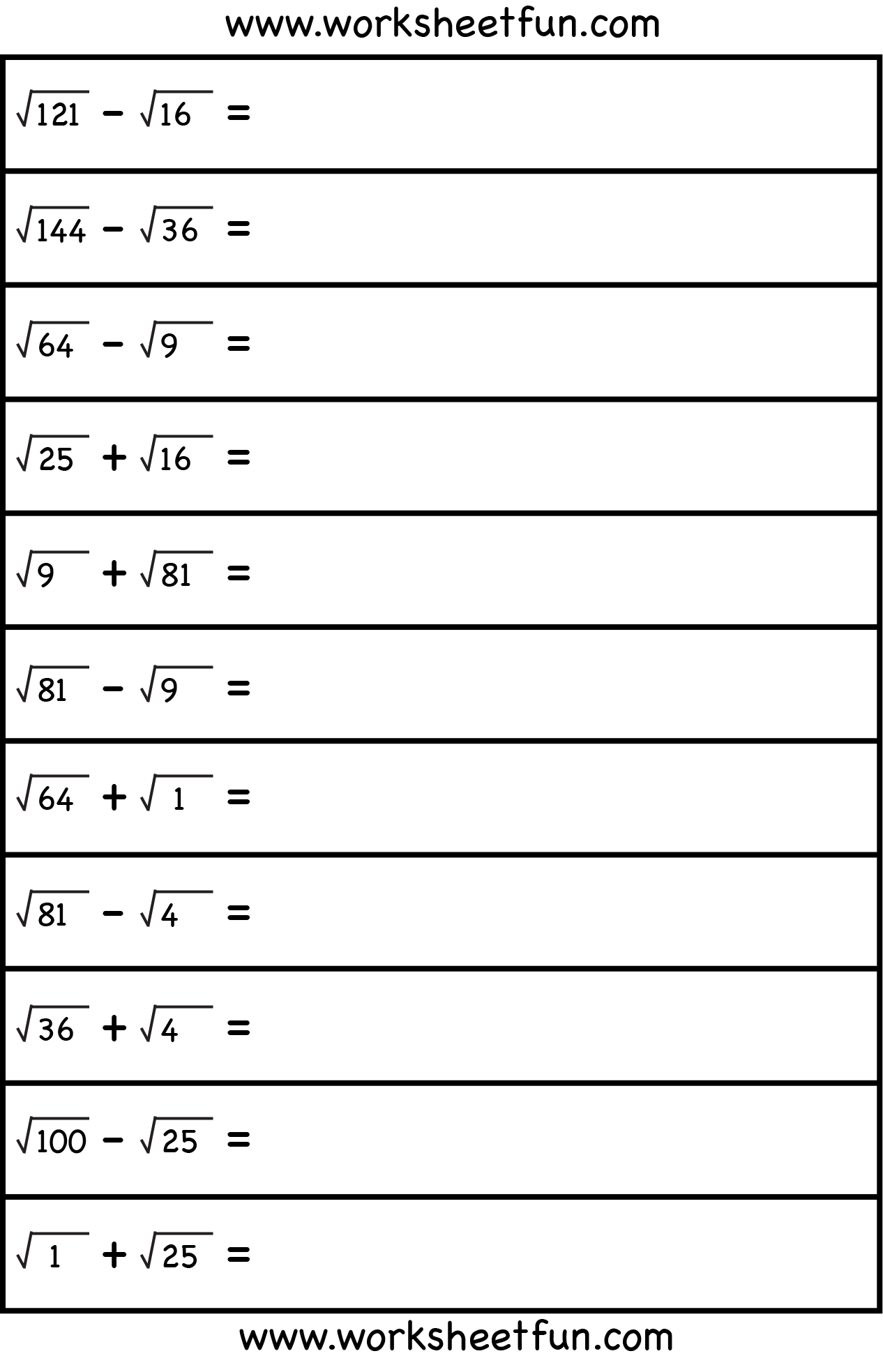
+
Square roots are essential in various mathematical and scientific domains. They help solve equations, calculate distances, and understand relationships in geometry, physics, and engineering.
How do you calculate the square root of a non-perfect square?

+
For non-perfect squares, you often use estimation or technology like calculators or software to get an approximate value, since these numbers typically have irrational square roots.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with square roots?

+
Common mistakes include forgetting the negative square root, not simplifying radical expressions, or overlooking the impact of operations on the original number before taking the square root.



