Ohm's Law Worksheet Answers: Your Ultimate Guide

⚡ Note: This blog post provides a comprehensive guide on Ohm's Law Worksheet Answers. You might want to grab a calculator, and let's delve into the world of electrical principles!
In the journey of mastering electrical engineering or physics, understanding the foundational principles is crucial. Ohm's Law stands as a cornerstone for anyone looking to grasp how electricity flows through a circuit. This law, which was established by the German physicist Georg Ohm, provides a simple yet powerful formula that relates voltage, current, and resistance. It states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, with the resistance of the conductor being the constant of proportionality. To help you navigate through this fundamental concept, let's explore Ohm's Law worksheet answers in detail.
What is Ohm’s Law?
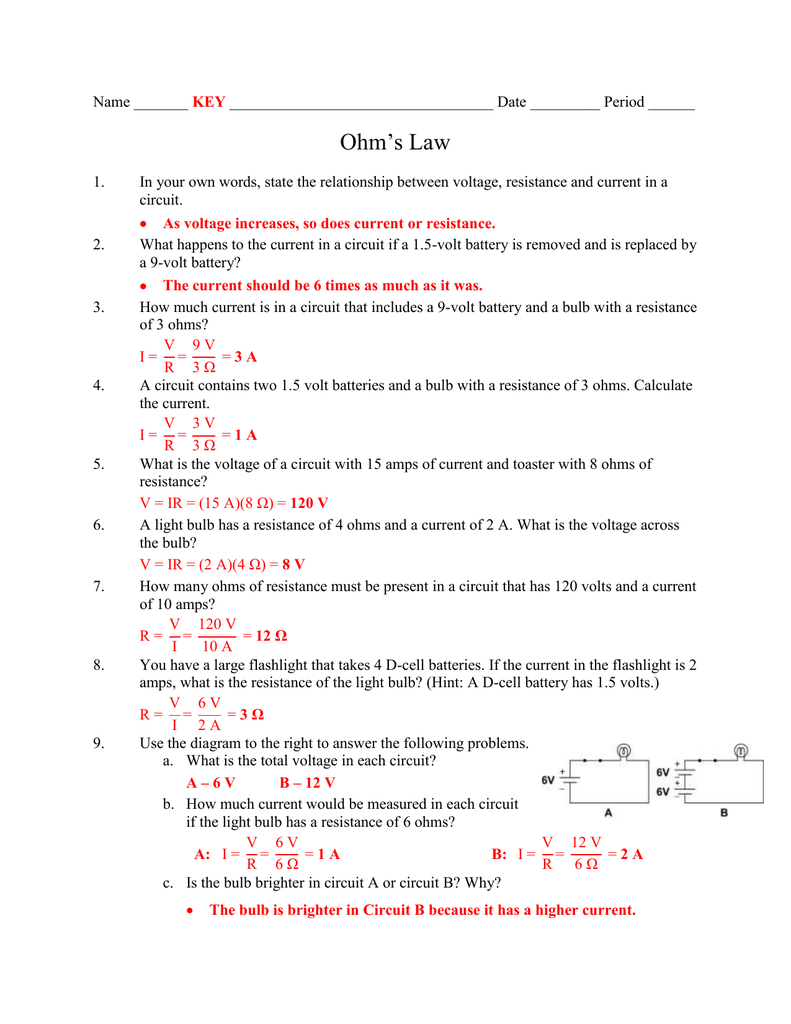
Ohm’s Law can be expressed with the simple equation:
- V = I * R
- Where:
- V stands for Voltage (measured in Volts, V)
- I stands for Current (measured in Amperes, A)
- R stands for Resistance (measured in Ohms, Ω)
🔍 Note: This formula can be rearranged to find any of the three variables if the other two are known.
Ohm’s Law Worksheet Example

Let’s go through a typical worksheet problem to illustrate how Ohm’s Law works in practice:
Question 1

If a light bulb has a resistance of 150 ohms (Ω) and is connected to a 120 volts (V) power source, what is the current flowing through the circuit?
Solution:
- Using the formula I = \frac{V}{R}
- Substitute the values:
- I = 120 V / 150 Ω
- I = 0.8 A
The current flowing through the light bulb is 0.8 Amperes (A).
Question 2

Find the resistance of an electric heater if it draws a current of 2 Amperes when connected to a 240 V outlet.
Solution:
- Using the formula R = \frac{V}{I}
- Substitute the values:
- R = 240 V / 2 A
- R = 120 Ω
The resistance of the heater is 120 Ohms (Ω).
🖋️ Note: Always double-check your units to ensure consistency and correct calculations.
Advanced Applications of Ohm’s Law

As you progress, the principles of Ohm’s Law are used in:
- Power Calculations: P = V * I where P is power (Watts, W)
- Circuit Analysis: Ohm’s Law is the foundation for understanding how components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors interact within circuits.
- Short Circuits: Understanding how Ohm’s Law applies can help in troubleshooting short circuits by analyzing voltage drops.
Understanding Voltage, Current, and Resistance

To delve deeper into Ohm’s Law, let’s look at:
- Voltage (V): This is the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. It pushes electrons to flow, and without voltage, no current can be generated.
- Current (I): It’s the rate at which electric charge flows. Current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
- Resistance ®: Represents the opposition to the flow of current. Materials with high resistance impede current flow, while materials with low resistance facilitate it.
Here's a simple table to help you memorize the relationship:
| What to Find | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | V = I * R | If I = 1A, R = 10Ω, then V = 10V |
| Current (I) | I = V / R | If V = 12V, R = 3Ω, then I = 4A |
| Resistance (R) | R = V / I | If V = 5V, I = 0.5A, then R = 10Ω |

Wrap-Up of Ohm’s Law Worksheet Answers

As we’ve explored in this detailed guide on Ohm’s Law worksheet answers, the law’s application extends beyond simple calculations. It forms the basis for understanding complex electrical systems, troubleshooting circuits, and designing electronic components. The key takeaways from our journey through Ohm’s Law include:
- Mastery of the formula V = I * R allows us to calculate voltage, current, and resistance efficiently.
- Ohm's Law provides a fundamental understanding of how circuits operate, enabling us to design, analyze, and troubleshoot electrical systems.
- Advanced applications involve calculating power and understanding how different components in a circuit interact based on their resistance, current, and voltage.
- The law applies to a wide range of practical scenarios, from household appliances to advanced electronic circuits.
What happens if the resistance in a circuit is zero?

+
When resistance is zero, according to Ohm’s Law, the current would theoretically become infinite. In real-life scenarios, this represents a short circuit, where the voltage source has an extremely high current draw that can lead to overheating, fires, or blown fuses.
How does temperature affect resistance?

+
For most materials, resistance increases with temperature due to increased molecular vibrations which impede electron flow. However, semiconductors and some superconducting materials decrease their resistance at low temperatures.
Can Ohm’s Law be applied to all electrical materials?
+
No, Ohm’s Law is strictly applicable to ohmic materials where the resistance is constant. Non-linear conductors like diodes and transistors exhibit a non-linear relationship between voltage and current.



