5 Essential Nursing Math Worksheets With Answers

Nursing professionals regularly deal with life and death matters, making mathematical accuracy a critical component of their work. From administering medications to interpreting diagnostic tests, precision in calculations can mean the difference between recovery and harm. This blog will delve into five essential nursing math worksheets that are pivotal for nursing students and practitioners to master their numerical proficiency. These worksheets cover a range of scenarios that a nurse might encounter, ensuring they are well-prepared for real-life healthcare challenges.
1. Medication Dosage Calculation

One of the core responsibilities of nurses involves administering medication to patients. Correct dosing requires not only the knowledge of pharmacology but also precision in math.
- Order Dosing: Understanding physician’s orders to convert them into milligrams or micrograms per dose.
- Volume Calculation: Determining the amount of medication to draw up when the drug is in liquid form.
- IV Flow Rates: Calculating drip rates for IV medications to ensure they deliver over the specified time.
Here is a basic example of dosage calculation:
| Problem | Calculation | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| The physician orders 50 mg of Drug A. The available tablets are 25 mg each. | 50 mg needed / 25 mg per tablet = 2 tablets | 2 Tablets |
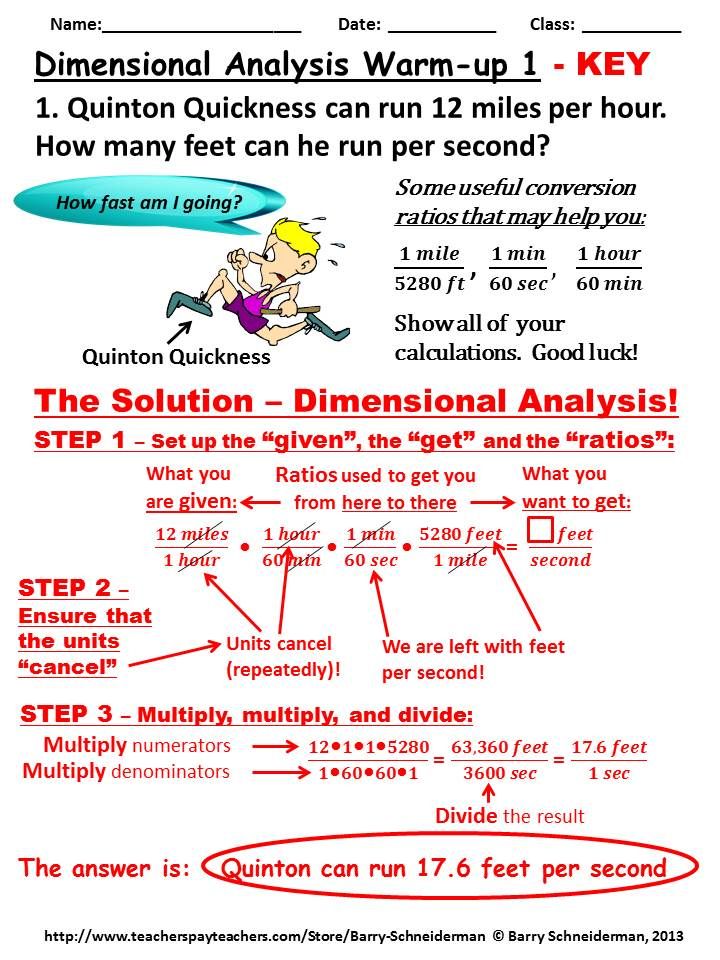
💊 Note: Always double-check your calculations for critical medications to prevent dosing errors.
2. Fluid Intake and Output

Monitoring a patient’s fluid balance is crucial, especially in cases of renal failure, heart failure, or post-operative care.
- Input Calculation: Recording and summing up all fluid intake, including IV fluids, oral intake, and tube feedings.
- Output Calculation: Measuring urine, vomit, drainage, and diarrhea.
- Net Fluid Balance: Comparing the input and output to determine hydration status or identify fluid overload.
💦 Note: Accurate I&O records can significantly influence treatment decisions in patients with fluid restrictions.
3. Intravenous (IV) Infusion Rate Calculations

IV medication administration often requires precise control over the rate of delivery to maintain efficacy and safety.
- Drops per Minute (gtt/min): Calculating the rate of IV fluids using a manual IV set.
- Volume in Time: Determining how long it will take to infuse a certain volume of IV fluid.
- Microdrip and Macrodrip: Understanding the difference between microdrip sets (60 gtts/mL) and macrodrip sets (varies).
4. Pediatric Dosage Adjustments

Pediatrics necessitates a different approach to medication calculation due to weight-based dosing.
- Body Surface Area (BSA): Using BSA to adjust doses for children to minimize toxicity.
- Weight-Based Dosage: Converting adult doses to safe pediatric doses based on weight.
- Growth and Maturation: Considering the impact of growth and organ maturation on drug metabolism.
🍼 Note: Pediatric patients are particularly sensitive to over or under-dosing, which can have serious consequences.
5. Calculating Conversions for Administration of Medications

Nurses often work with different forms of medication and must convert between units of measure accurately.
- Unit Conversions: Milligrams to micrograms, liters to milliliters, etc.
- Time Conversion: From hours to minutes or vice versa.
- Temperature Conversion: Fahrenheit to Celsius, or other scales needed in clinical settings.
📊 Note: Remember that small calculation errors can result in significant variations in patient care outcomes.
In summary, mastering these five types of math problems is indispensable for nursing professionals. Correct medication dosage, fluid management, IV rate calculations, pediatric dosing, and unit conversions are fundamental skills that ensure patient safety and effective treatment. By using worksheets and practicing these calculations regularly, nurses can develop the confidence and precision needed for their daily responsibilities. The ability to think critically and perform accurate calculations is a mark of professional competence in nursing, directly impacting patient care and outcomes.
Why is math so important in nursing?

+
Math is crucial in nursing because accurate calculations are necessary for correct medication dosages, IV drip rates, fluid management, and patient monitoring. Errors in these areas can lead to serious health risks or even fatalities.
How often should nurses practice math?

+
Nurses should engage in regular practice, especially when transitioning to new roles or units where the required calculations might change. Continuous professional development and practice sessions can help maintain mathematical proficiency.
What happens if a nurse makes a calculation error?

+
Calculation errors can result in under or over-dosing of medication, improper fluid management, or incorrect IV administration, potentially leading to adverse patient outcomes. It’s critical to double-check calculations and have systems in place to catch mistakes.



