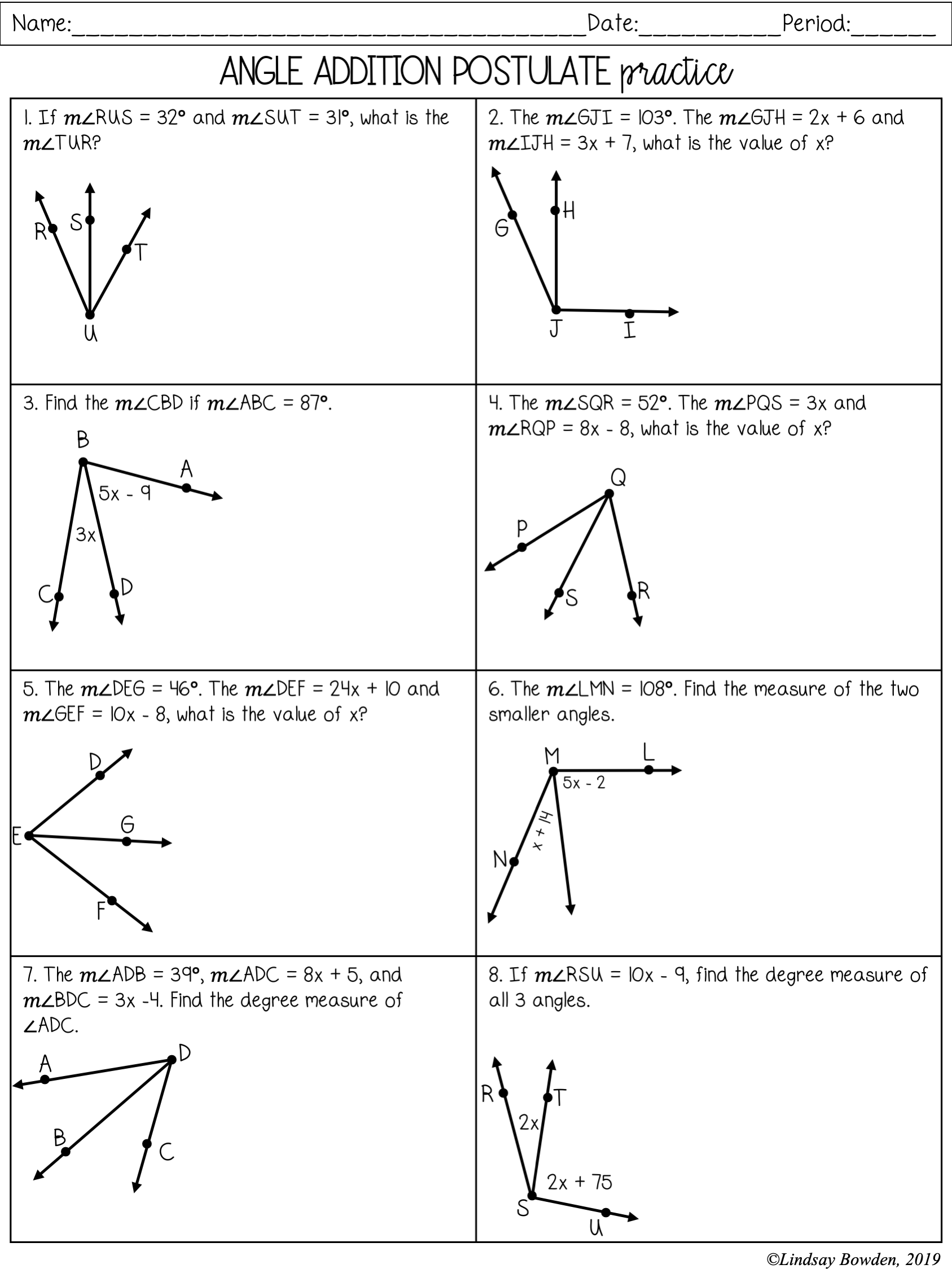
North America 1754 Map Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

Exploring history through interactive worksheets is a fascinating way to learn about the pivotal moments that have shaped the modern world. One such essential piece of history is the map of North America from 1754, which offers a glimpse into the geopolitical landscape just before the French and Indian War escalated. In this blog post, we'll unravel the secrets of the North America 1754 Map Worksheet answer key, shedding light on its significance, historical context, and the essential components you need to know. Whether you are a history buff or a teacher looking to enrich your curriculum, understanding this map will provide you with valuable insights.
Historical Context of 1754 North America

To understand the intricacies of the 1754 North America map, it's crucial to delve into the historical backdrop:
- Colonial Powers: By 1754, North America was predominantly divided between the British and French territories, with Spain controlling Florida and parts of the Southwest.
- French and Indian War: This war, known in Europe as the Seven Years' War, was an international conflict that began in the colonies due to competing claims over the Ohio Country.
- Native American Alliances: Many native tribes were caught in the middle of European rivalries, often forming alliances with either the French or British based on strategic advantages.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The map reflects a period of high tension where conflicts were imminent due to the overlapping territorial claims and interests.

Understanding the Worksheet Components

The worksheet typically includes the following key areas:
- Identifying Territories: Recognize the British, French, and Spanish territories on the map.
- Key Regions: Locate and label significant regions like the Ohio Valley, Acadia, and New France.
- Native American Tribes: Mark the approximate locations of tribes involved in the conflict, like the Iroquois, Huron, and Algonquin.
- Major Colonial Cities: Identify and label key colonial cities such as Quebec, Montreal, New Orleans, Boston, and New York.
- Trade Routes and Forts: Note the trade routes and strategic forts which were critical for military and economic activities.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| British Territories | Includes the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast and parts of Canada like Nova Scotia. |
| French Territories | Encompassed New France (modern-day Quebec and parts of Eastern Canada) down to Louisiana. |
| Spanish Territories | Covered Florida and New Spain (present-day Mexico and the Southwestern United States). |

Answer Key Breakdown

Identifying Territories

Here's how to identify each major territory:
- British Territory: This would include everything from Massachusetts down to Georgia along the eastern seaboard and parts of Canada.
- French Territory: Encompass New France, stretching from the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico including the Mississippi River Valley.
- Spanish Territory: Mark Florida and parts of the Southwest, often overlooked in this context.
Key Regions and Cities

- Ohio Valley: Mark the disputed region between the French and British, pivotal in starting the French and Indian War.
- Acadia: Locate this region, known for its contested control and later known as Nova Scotia after British victory.
- New France: Highlight this vast area stretching from the Great Lakes to New Orleans.
- Significant Cities:
- Quebec: A major stronghold for the French.
- New Orleans: Strategic due to its control of the Mississippi River.
- Boston: An important British colonial city.

🌍 Note: Understanding the geopolitical situation of 1754 requires recognizing the intricate web of alliances, trade routes, and territorial ambitions that characterized this era.
Native American Tribes and Their Alliances

Here’s a quick rundown of the tribes and their allegiances:
- Iroquois Confederacy: Often allied with the British due to treaties and trade agreements.
- Huron and Algonquin: Frequently aligned with the French, benefiting from their trading posts and cultural exchange.
- Other Tribes: Many other tribes, like the Cherokee and Delaware, had varying alliances or remained neutral.
The significance of native alliances in the war cannot be understated, as they often played a crucial role in military engagements.
Trade Routes and Forts

Military forts and trade routes were lifelines in the colonies:
- Forts: Identify key forts like Fort Duquesne (French) and Fort Necessity (British). These were pivotal in conflicts.
- Trade Routes: Mark the main trade routes, especially those along the rivers, which were crucial for economic and strategic control.

📌 Note: The Ohio River was particularly strategic due to its location at the center of the dispute between the French and British.
Understanding the 1754 map of North America provides not just a historical snapshot but also lessons in geopolitical strategy, colonial diplomacy, and the complex interplay of cultures and power during this era. As we look back, we see how the seeds of modern geopolitics were sown in the soil of colonial ambitions and alliances.
Why was the Ohio River Valley so crucial in the French and Indian War?

+
The Ohio River Valley was a linchpin in the struggle for control of North America because it provided access to the Mississippi River and the lucrative fur trade routes, making it a focal point for British and French colonial expansion.
What role did Native American tribes play in the French and Indian War?

+
Native American tribes were critical allies in the war, often choosing sides based on trade benefits, cultural affiliations, and to counter the encroachment of European settlers on their lands. Their alliances significantly influenced the outcome of battles and the war itself.
How did the British victory change the political landscape of North America?

+
The British victory led to the Treaty of Paris (1763), where France ceded almost all of its North American territories to Britain, except for a few Caribbean islands and fishing rights off Newfoundland. This dramatically altered the colonial landscape, leading to tensions that eventually contributed to the American Revolution.