Solving Net Ionic Equations Made Easy

Understanding Net Ionic Equations

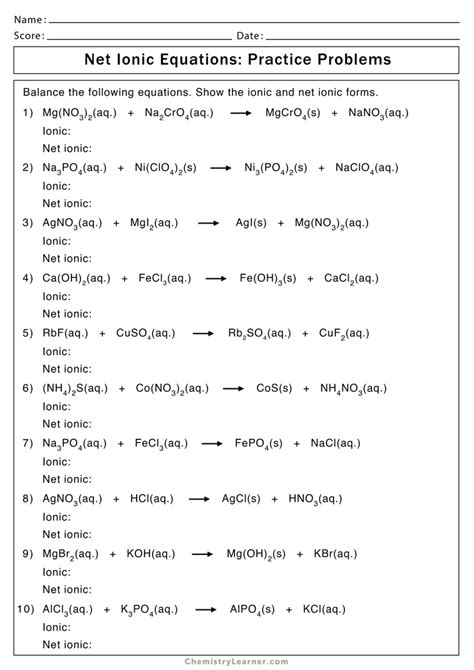
Net ionic equations are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and they can be intimidating at first. However, with a clear understanding of the process, you’ll be able to solve them with ease. In this article, we’ll break down the steps to solve net ionic equations, provide examples, and offer tips to help you master this skill.
What are Net Ionic Equations?
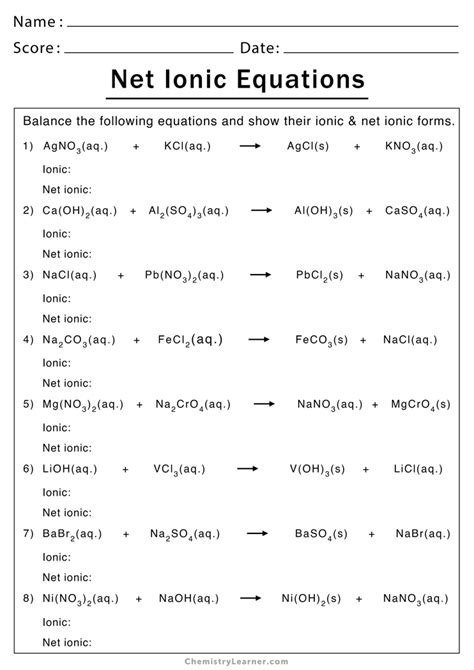
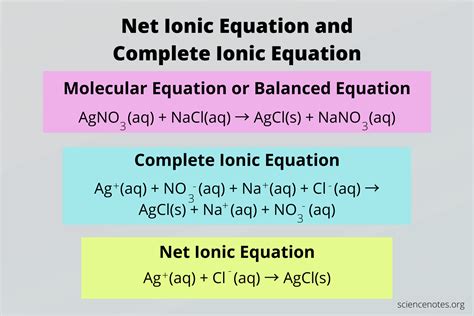
Net ionic equations are a way to represent the reaction between ions in a solution. They show the movement of electrons and the formation of new compounds. To write a net ionic equation, you need to know the reactants, products, and the type of reaction (acid-base, precipitation, or oxidation-reduction).
Step 1: Write the Balanced Molecular Equation
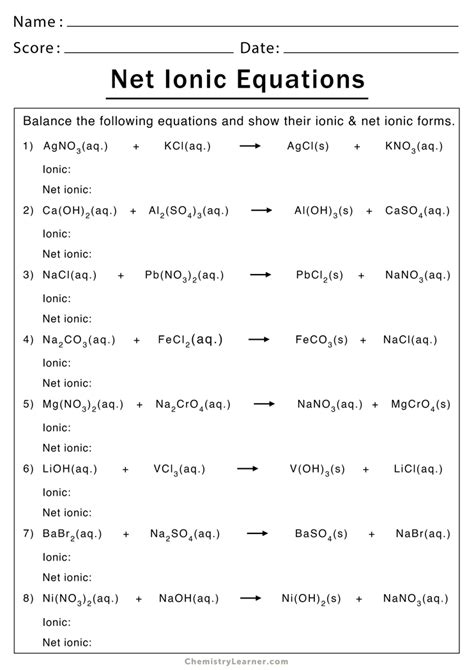
The first step in solving a net ionic equation is to write the balanced molecular equation. This equation shows the reactants and products in their molecular form.
Example: Write the balanced molecular equation for the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Step 2: Break Down the Molecular Equation into Ions
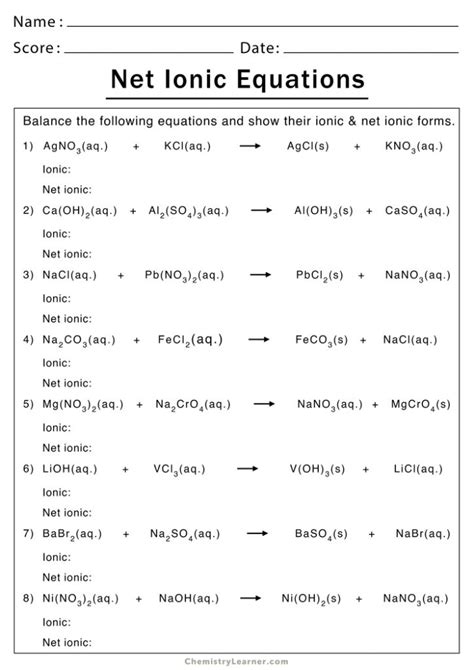
Next, break down the molecular equation into ions. This is where you separate the strong electrolytes into their ions.
Example: Break down the molecular equation into ions.
H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + H2O(l)
Step 3: Eliminate the Spectator Ions

Spectator ions are ions that appear on both sides of the equation and do not participate in the reaction. Eliminate these ions to get the net ionic equation.
Example: Eliminate the spectator ions.
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
Step 4: Simplify the Equation

Finally, simplify the equation by removing any duplicate ions or molecules.
Example: Simplify the equation.
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
This is the net ionic equation.
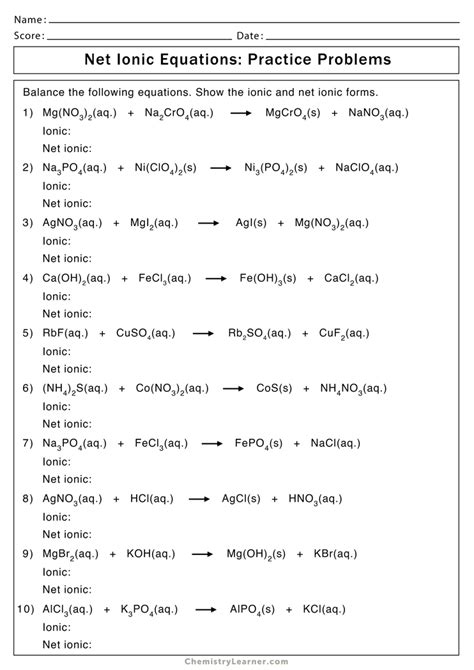
Examples of Net Ionic Equations

Here are a few more examples of net ionic equations:
- Precipitation Reaction: Write the net ionic equation for the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl). Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
- Acid-Base Reaction: Write the net ionic equation for the reaction between sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
- Oxidation-Reduction Reaction: Write the net ionic equation for the reaction between zinc metal (Zn) and copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4). Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Important Notes
💡 Note: Always write the balanced molecular equation first before attempting to write the net ionic equation.
📝 Note: Make sure to eliminate the spectator ions to get the net ionic equation.
Conclusion
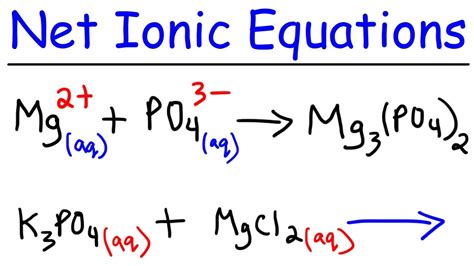
Solving net ionic equations is a straightforward process that requires a clear understanding of the steps involved. By following these steps and practicing with examples, you’ll become proficient in solving net ionic equations. Remember to always write the balanced molecular equation first and eliminate the spectator ions to get the net ionic equation.
What is the purpose of writing net ionic equations?
+
Net ionic equations show the movement of electrons and the formation of new compounds in a reaction. They help us understand the chemical changes that occur in a reaction.
What are spectator ions?
+
Spectator ions are ions that appear on both sides of the equation and do not participate in the reaction.
How do I know if an ion is a spectator ion?
+
If an ion appears on both sides of the equation and its coefficient does not change, it is a spectator ion.
Related Terms:
- Ionic equations Worksheet and answers
- Net ionic equation Worksheet pdf
- Ionic equations Worksheet pdf
- ionic equations gcse practice questions
- net ionic equation answer key
- ionic formulae questions and answers