5 Fun Ways to Teach Area Model Multiplication

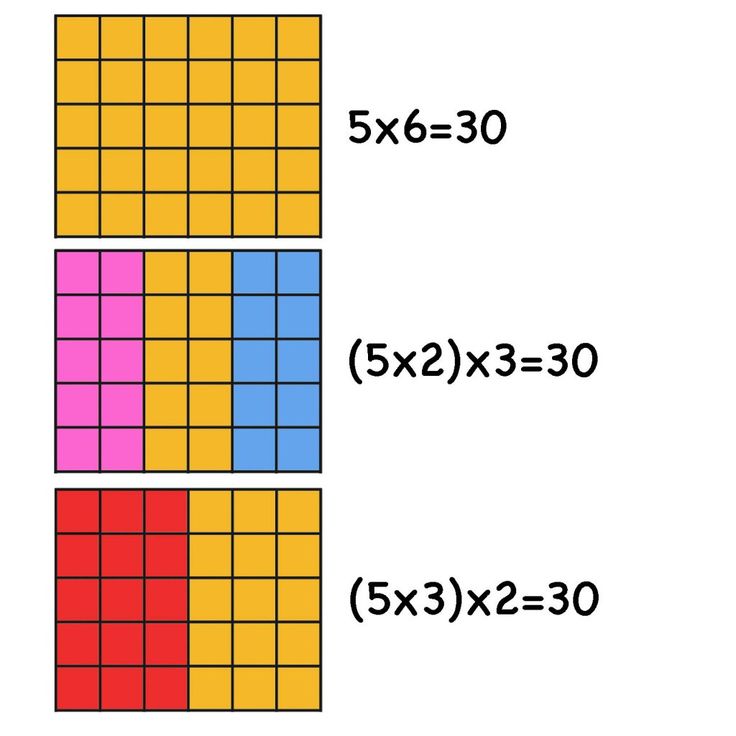
Area model multiplication is a versatile teaching method that breaks down multiplication into manageable parts, making it easier for students to grasp the underlying concepts. This visual approach not only enhances mathematical understanding but also provides an enjoyable learning experience. Here are five fun and effective ways to teach area model multiplication:
1. Building Blocks or LEGO Approach

Using physical objects like blocks or LEGO can turn learning multiplication into an engaging activity:
- Introduce the concept by having students model multiplication problems with LEGO bricks or blocks. For example, for the problem 12 x 3, you could use 12 single units to form the base and then stack three layers high.
- Guide students to visualize the area of the model, connecting each layer to the numbers in the multiplication.
- Benefits: Promotes hands-on learning, fosters teamwork when done in groups, and provides a tangible representation of abstract ideas.
🧩 Note: Ensure to have enough blocks or LEGO pieces for all students. Each student should have the opportunity to participate actively.
2. Interactive Online Platforms

Technology provides numerous resources for visualizing and practicing multiplication:
- Utilize platforms like Khan Academy, Math Playground, or IXL, where students can interact with virtual blocks or grids.
- Engage in activities where they drag, drop, and arrange digital objects to solve problems, making the learning process dynamic and interactive.
- Benefits: Appeals to digital natives, allows for instant feedback, and can be adapted to various skill levels.
3. Art Meets Math: Creating Multiplication Art

Combine mathematics with art for a creative learning experience:
- Challenge students to create art using grids where each grid represents a multiplication problem. For instance, a 5 x 5 grid could represent 25.
- Encourage them to color different sections of the grid based on their understanding of factors and multiples, forming interesting patterns or pictures.
- Benefits: Integrates two subjects, caters to students with artistic interests, and makes multiplication visually appealing.
4. Storytelling with Multiplication
Telling stories where characters solve multiplication problems using the area model:
- Create a narrative where a character needs to solve multiplication to help a friend, save the day, or complete a task.
- Use the area model visually as part of the story, helping students associate the model with real-world scenarios.
- Benefits: Engages students’ imagination, adds context to the math, and makes problem-solving fun.
5. Math Scavenger Hunt

Turn the classroom into an adventure zone with multiplication puzzles:
- Hide cards around the room, each card containing a part of an area model multiplication problem.
- Teams of students collect these clues, reconstruct the problem, and solve it, promoting teamwork, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
- Benefits: Adds excitement to learning, encourages physical activity, and fosters collaboration.
Incorporating these methods into your teaching not only breaks the monotony of traditional classroom instruction but also caters to different learning styles, enhancing retention and engagement. By making multiplication fun, we foster a love for math that goes beyond the classroom, igniting a lifelong interest in this crucial subject.
How does the area model help in understanding multiplication?

+
The area model visualizes the relationship between factors and their products. By dividing a rectangle into smaller segments, students can see how multiplying factors affects the area, making multiplication more tangible and less abstract.
What are some benefits of using interactive online platforms for teaching area model multiplication?

+
Interactive platforms provide instant feedback, allowing students to correct mistakes in real-time. They also cater to different learning paces, offer visual aids, and can be more engaging for digital natives, enhancing both understanding and retention.
Can this method be applied to division as well?

+
Yes, the area model can also be used for division. The rectangle is used to represent the dividend, and students partition it to show how the divisor fits into the dividend, essentially using the model to ‘undo’ multiplication.
Are there any age groups that would particularly benefit from these methods?

+
While these methods can be adapted for all ages, they are particularly effective for children in elementary and middle school, where visual and hands-on learning aids are crucial for understanding abstract concepts like multiplication.