5 Fun Ways to Teach Multiplication with Arrays
Multiplication is a fundamental concept in mathematics, but for many students, it can be a challenging leap from basic addition and subtraction. However, by using arrays, teachers and parents can transform this learning into an engaging and visually stimulating experience. Arrays not only provide a concrete representation of numbers but also help in understanding the distributive property, place value, and area models. Here are five fun, interactive methods to teach multiplication using arrays:
1. Building with Blocks


Start with something familiar to children: blocks or Lego bricks. Here’s how you can teach multiplication with this hands-on approach:
- Counting Units: Ask children to build a rectangle with blocks. If they make a 3 by 4 rectangle, discuss how it represents 3 groups of 4 or 4 groups of 3, leading to the concept that 3 x 4 = 4 x 3.
- Area Understanding: Help them understand that the rectangle's area, in this case, 12 square units, is the result of the multiplication.
- Group Counting: Encourage grouping the blocks in different ways to reinforce the idea that multiplication is grouping or repeated addition.
🌟 Note: Make sure to provide an ample number of blocks in various sizes and colors for more engaging activities.
2. Array Boards


Create or purchase an array board - a board with evenly spaced pegs or holes where kids can place objects:
- Visual Representations: Use this to visually represent multiplication. For instance, peg 2 rows of 5 beads each for 2 x 5.
- Fill Patterns: Have children fill in different patterns to illustrate various multiplication problems.
- Fill in the Missing Factor: Show a partial array and ask students to complete it, helping them deduce multiplication facts.
3. Interactive Games and Apps
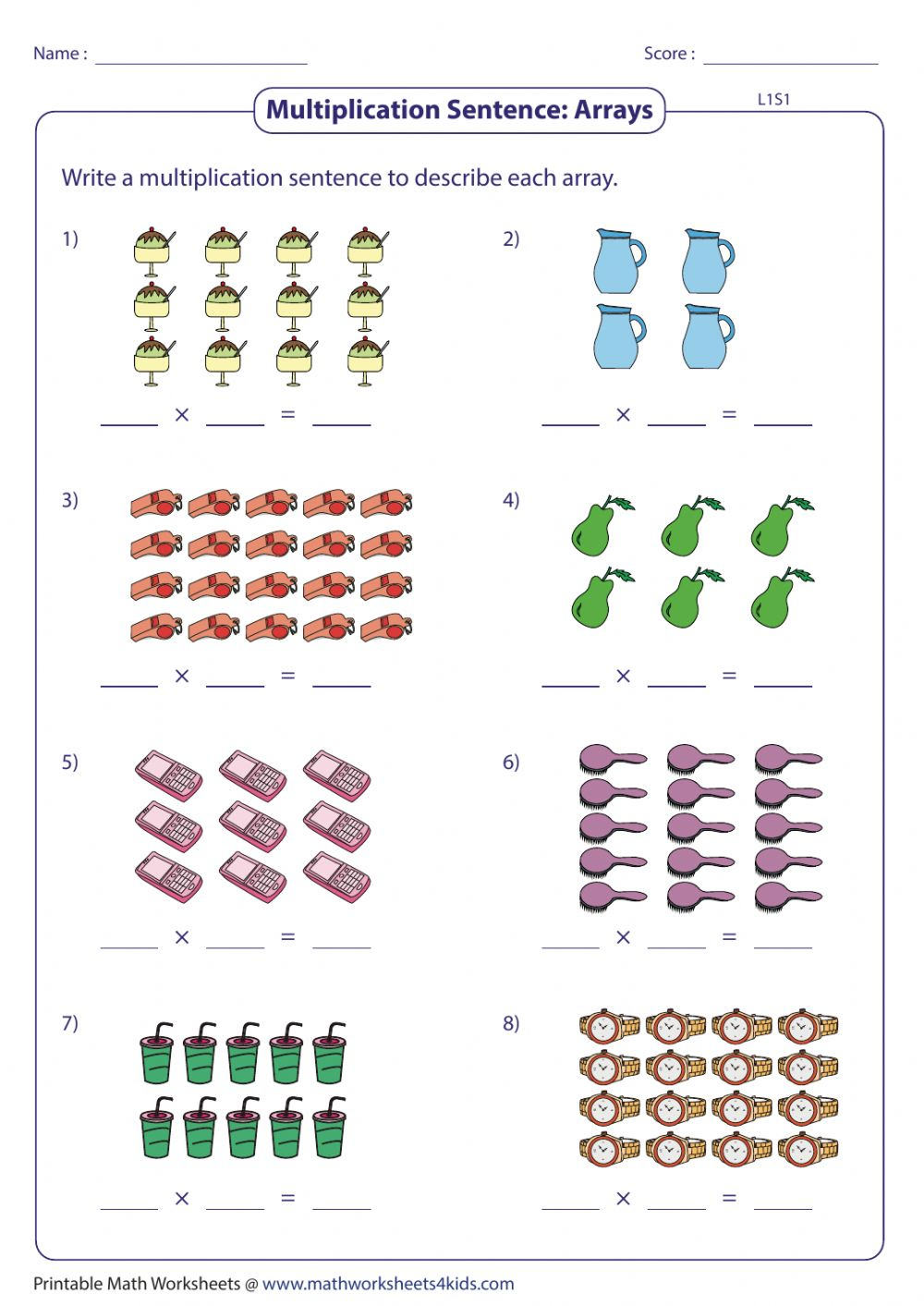
Incorporate technology with educational apps or online games:
- Drag and Drop: Kids can drag objects into an array format, making the learning process interactive.
- Multiplayer Mode: These games often include modes where kids can compete against each other, increasing engagement.
- Levels of Difficulty: Apps like “Multiplication Array” allow kids to progress through increasingly difficult levels, keeping them motivated.
4. Real-Life Scenarios

Link math to everyday life to show its relevance:
- Setting the Table: Lay out tableware in an array pattern to show how multiplication occurs naturally in everyday tasks.
- Building Structures: Discuss or demonstrate how engineers or builders use arrays when planning structures or gardens.
- Cooking and Baking: Use recipes to demonstrate how quantities can be multiplied (e.g., if a recipe serves 2, how many ingredients would we need for 6?)
💡 Note: Always adapt real-life scenarios to the age and interest of the child for maximum engagement.
5. Storytelling with Arrays
Narratives can make learning fun:
- Adventure Tales: Create a story where characters have to solve problems using arrays.
- Art and Craft: Tell a story where characters create art or craft projects using arrays (e.g., making a quilt with a specific pattern).
- Animal Adventures: Use animals or pets in stories to show how they could understand multiplication through arrays (e.g., laying out dog bones or hamster balls).
Each of these methods not only helps students understand multiplication through arrays but also leverages creativity, physical activity, and real-life connections to make learning enjoyable. The key is to keep the activities varied and adapt them to suit different learning styles, ensuring that every child finds a way to connect with the material. Engaging children in this manner transforms multiplication from an abstract concept to a tangible, fun, and visual skill. Encouraging them to see patterns, use their hands, and understand through stories or games instills a deep understanding and a love for mathematics, setting a strong foundation for more complex math concepts in the future.
How do arrays help in understanding multiplication?

+
Arrays provide a visual and tactile representation of numbers, making abstract concepts like multiplication more concrete. They help students visualize grouping and see the distributive property in action, which supports understanding of number relationships and math facts.
Can arrays be used for division as well?
+
Yes, arrays can also illustrate division. If you start with a total number of objects in an array and divide them into smaller groups, this represents division as sharing. For example, if you have a 12-square array and you divide it into 3 rows, each row represents 12 ÷ 3.
What age is appropriate to start teaching multiplication with arrays?

+
Children as young as 5 or 6 can start exploring multiplication concepts using arrays. However, the complexity of the tasks should be adjusted to their cognitive development level, starting with simple groupings and progressing to more complex patterns as they grow.
Are there any digital tools for teaching multiplication with arrays?

+
Yes, several educational apps and online tools are available that incorporate interactive array games and activities to teach multiplication. These tools can be particularly useful for reinforcing concepts at home or in a blended learning environment.