5 Essential Tips for Monomial X Polynomial Worksheet Solutions

Mastering polynomial expressions is a fundamental aspect of algebra, and understanding how to solve monomials and polynomials together can greatly enhance your mathematical prowess. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into 5 Essential Tips for Monomial x Polynomial Worksheet Solutions, providing you with the tools to tackle these problems with confidence and ease.
1. Understand the Basics

Before diving into complex solutions, ensuring a solid grasp of the foundational concepts is essential. Here’s a quick refresher:
- Monomials: These are expressions with one term. They can be numbers, variables, or products of numbers and variables with whole number exponents.
- Polynomials: An expression consisting of more than one monomial, joined by addition, subtraction, or both, with non-negative integer exponents.
- Multiplication of a Monomial by a Polynomial: Each term in the polynomial gets multiplied by the monomial.
📌 Note: Ensuring your monomial and polynomial concepts are clear will make solving these worksheets much smoother.
2. Apply the Distributive Property

The distributive property is your ally in solving monomial x polynomial problems. Here’s how it works:
- Distribute: Multiply the monomial by each term within the polynomial. For instance, if you’re multiplying 3x by (2x + 1), you distribute the 3x to get (3x*2x) + (3x*1).
- Multiply: Carry out the multiplication for each term.
Example:
| Expression | Multiplication | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 3x (2x + 1) | (3x * 2x) + (3x * 1) | 6x2 + 3x |

🔄 Note: Remember to follow the order of operations when multiplying; this includes dealing with exponents correctly.
3. Use Coefficients and Variables Judiciously
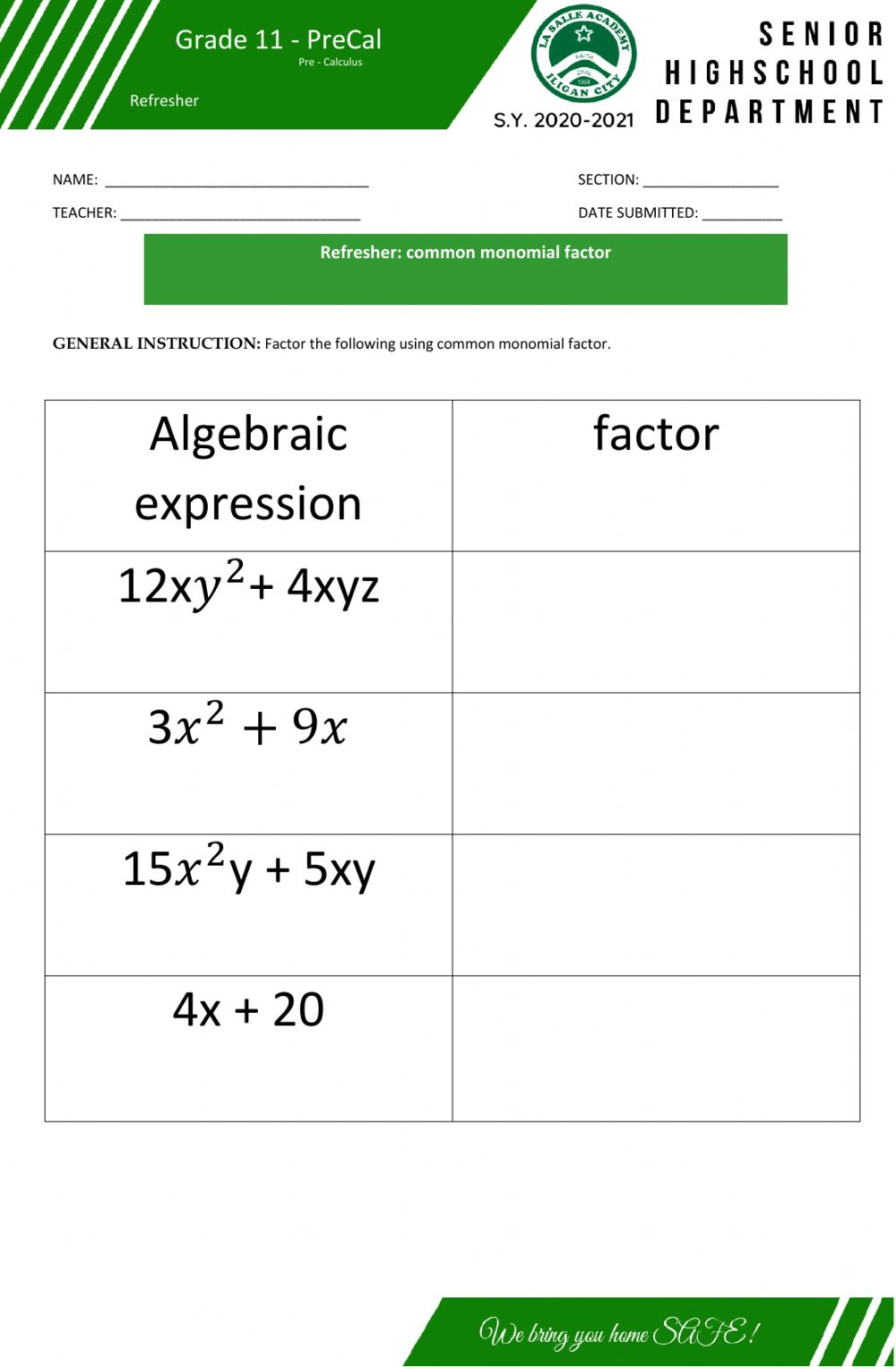
When dealing with the multiplication:
- Coefficients: Simply multiply the numerical coefficients directly.
- Variables: Use the rules of exponents, where you add the exponents of the same base (e.g., x).
This step is crucial for accuracy, especially when dealing with larger and more complex polynomials.
4. Simplify Your Results

After applying the distributive property, you’ll often find expressions that can be simplified further:
- Combine like terms: Look for terms that can be merged, reducing the polynomial to its simplest form.
- Check exponents: Ensure you correctly handle the exponents during simplification.
This step ensures your answers are both correct and in a readable form, which is particularly important in exams or when checking work.
5. Practice with Variations

Monomial x Polynomial multiplication can vary, so practice is key:
- Varied Monomials: Use different numbers and variables for the monomial.
- Polynomials of Different Degrees: Multiply monomials with polynomials of varying degrees to become adept at handling different levels of complexity.
- Word Problems: Translate word problems into algebraic expressions to apply these concepts practically.
By engaging with varied practice, you’ll develop a robust understanding and versatility in solving these problems.
Algebra might seem daunting, but with a strategic approach to monomial x polynomial solutions, you can navigate these challenges with confidence. We've covered understanding the basics, utilizing the distributive property effectively, managing coefficients and variables, simplifying results, and the importance of practice. Armed with these tips, your proficiency in algebra will surely grow, and you'll be better prepared for more advanced mathematical concepts. Continuous practice, understanding the principles, and strategic simplification will lead you towards mathematical success.
Why is understanding monomials and polynomials crucial in algebra?

+
Understanding monomials and polynomials is key because they form the building blocks of algebraic expressions. They allow for the manipulation of complex equations, simplification of expressions, and are foundational in calculus, physics, and many engineering fields.
Can the distributive property be applied to all polynomial multiplications?

+
The distributive property is indeed applicable to all polynomial multiplications. It simplifies the process by allowing you to multiply each term in the polynomial by the monomial.
What if my polynomial has negative exponents?

+
Polynomials by definition have only non-negative integer exponents. If you encounter negative exponents, you’re dealing with rational expressions, not polynomials. You would handle these using the properties of fractions and exponents.


