Molarity Practice Worksheet: Master Chemistry Calculations Easily

Understanding chemistry requires a solid grasp of fundamental concepts like molarity. Molarity, often represented as M or mol/L, is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution. It's a critical concept because it allows chemists to determine the amount of substance present in a defined volume, which can influence reactions, mixing ratios, and other chemical processes. Whether you're studying for an exam or working on lab experiments, mastering molarity can greatly simplify your chemistry journey. Here's how you can master molarity calculations through practice and understanding its foundational principles.
What is Molarity?

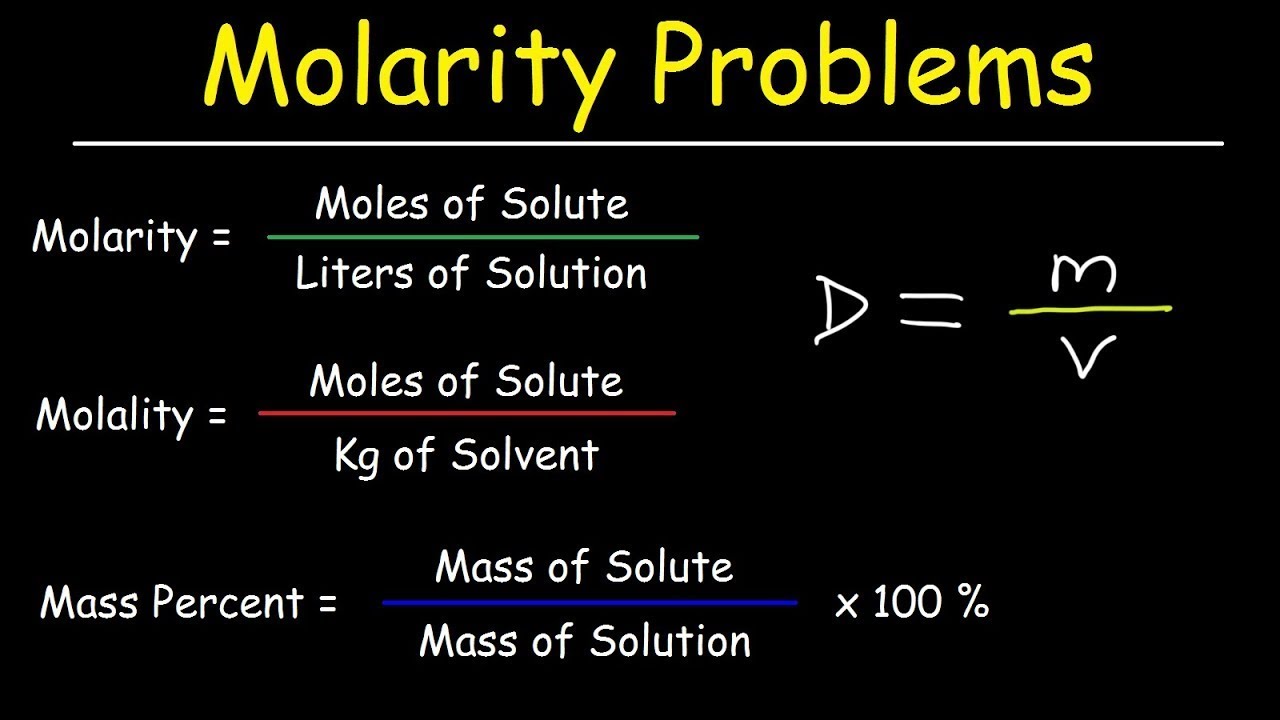
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution. The formula for calculating molarity is:
M = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters
Let’s break this down:
- Moles of Solute: The amount of substance you are dissolving.
- Volume of Solution: The total volume of the final solution, not just the solvent you add to dissolve the solute.
⚗️ Note: Always ensure you're measuring the volume of the solution, not just the solvent, for accurate molarity calculations.
How to Calculate Molarity

Calculating molarity involves a few straightforward steps:
- Determine the moles of solute: Use the formula moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g/mol) to calculate the amount of solute in moles.
- Measure the final volume of the solution: This is the volume after all the solute has dissolved in the solvent.
- Apply the molarity formula: Plug the values into the molarity formula to get your answer.
Example Calculation

Let’s calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 58.5 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl) in enough water to make 2.0 liters of solution.
- Determine the moles of NaCl:
- Volume of solution is given as 2.0 liters.
- Calculate molarity:
moles = 58.5 g / 58.5 g/mol = 1 mol
M = 1 mol / 2.0 L = 0.5 mol/L or 0.5 M
Common Scenarios for Molarity

- Dilution: When you dilute a solution, you change its concentration but keep the total moles of solute constant. The formula C1V1 = C2V2 is often used, where C is concentration and V is volume.
- Making Solutions: When you need to prepare a solution with a specific molarity, you’ll use the formula M = n/V where n is the amount of solute in moles, and V is the volume of the solution.
- Titration: During a titration, you’re essentially calculating the concentration of an unknown solution by adding a solution of known molarity.
🔬 Note: Always remember to record all quantities in their appropriate units. Molarity is concentration in moles per liter, so both moles and volume must be in correct units.
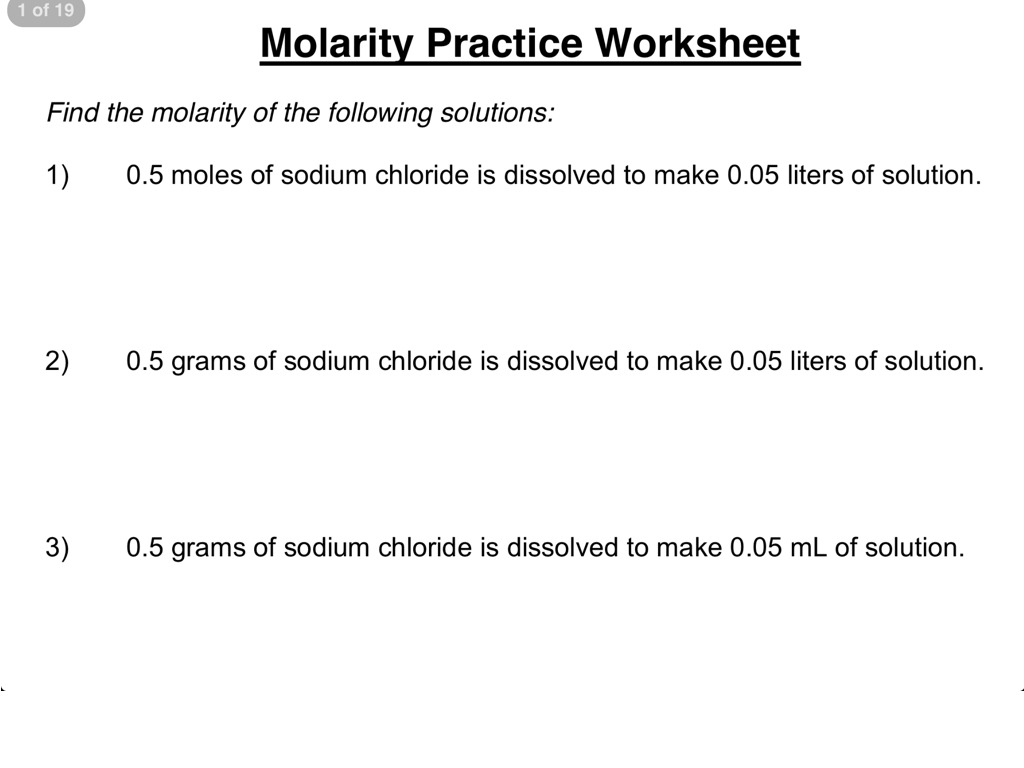
Practice with a Molarity Worksheet

To solidify your understanding of molarity, here’s a simple worksheet designed for practice:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 25 grams of NaOH in 1.5 liters of water. |
|
| Find the volume of a 0.5 M solution needed to obtain 0.25 moles of solute. |
|

Tips for Mastery
- Practice Regularly: Regularly work on molarity problems to become familiar with the calculations.
- Understand Units: Make sure you’re aware of all units and can convert between them if necessary.
- Use Visual Aids: Sometimes, drawing out the solution’s components can help visualize the dilution process or concentration changes.
- Understand Stoichiometry: Molarity often ties into stoichiometry, so understanding both concepts can enhance your problem-solving skills.
Recap

Calculating molarity is an essential skill in chemistry that allows you to precisely measure and work with the concentration of solutions. Through understanding the definition, formula, and applying it in various scenarios, you can master this concept. Remember, the key to success in chemistry is practice, understanding units, and visual aids. With the practice worksheet provided, you’re now equipped to tackle molarity calculations with confidence. Keep refining your understanding, and the calculations will become second nature, opening the door to more advanced chemistry experiments and analyses.
Why is molarity important in chemistry?
+
Molarity provides a measure of concentration that is critical for understanding and controlling chemical reactions, ensuring correct stoichiometry, and analyzing reaction kinetics.
How does temperature affect molarity?

+
Temperature affects the volume of the solution, particularly for gases dissolved in liquid, which in turn changes the molarity. However, for non-gaseous solutes, the effect is often minimal as long as the solution remains liquid.
Can molarity be used with solids or gases?

+
Molarity is primarily used for liquid solutions. However, you can still calculate molarity for gases if you convert the volume to liters under standard temperature and pressure (STP) conditions.
What’s the difference between molarity and molality?

+
Molarity is the concentration of a solute in moles per liter of solution, while molality is the concentration in moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Molality is temperature-independent, whereas molarity changes with temperature due to changes in the solution’s volume.



