Meiosis Worksheet Answers: Your Ultimate Study Guide

Understanding the Basics of Meiosis
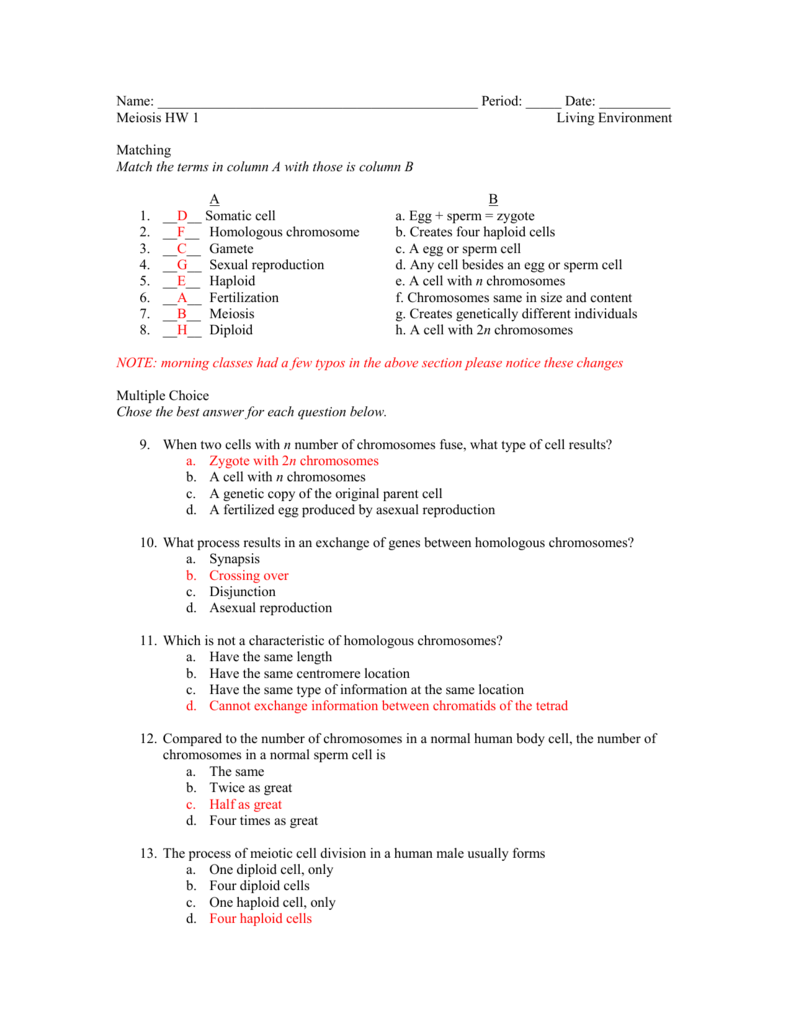
Meiosis is a fundamental process in biology, crucial for the reproduction and genetic diversity of eukaryotic organisms. This process involves two successive divisions that reduce the chromosome number by half in daughter cells, producing gametes or spores that are haploid (n). Let's delve into the phases of meiosis to better understand this intricate process.
Phases of Meiosis

Meiosis can be broken down into several key phases:
Meiosis I

- Prophase I: Chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and crossing over (genetic recombination) occurs between homologous chromosomes.
- Metaphase I: Homologous pairs align at the metaphase plate.
- Anaphase I: Homologs are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I: The cell starts to divide into two, chromosomes begin to de-condense, and nuclear envelopes may reform.
Interkinesis

Interkinesis is a brief intermission where the cell prepares for the second meiotic division. DNA replication does not occur during this stage.
Meiosis II
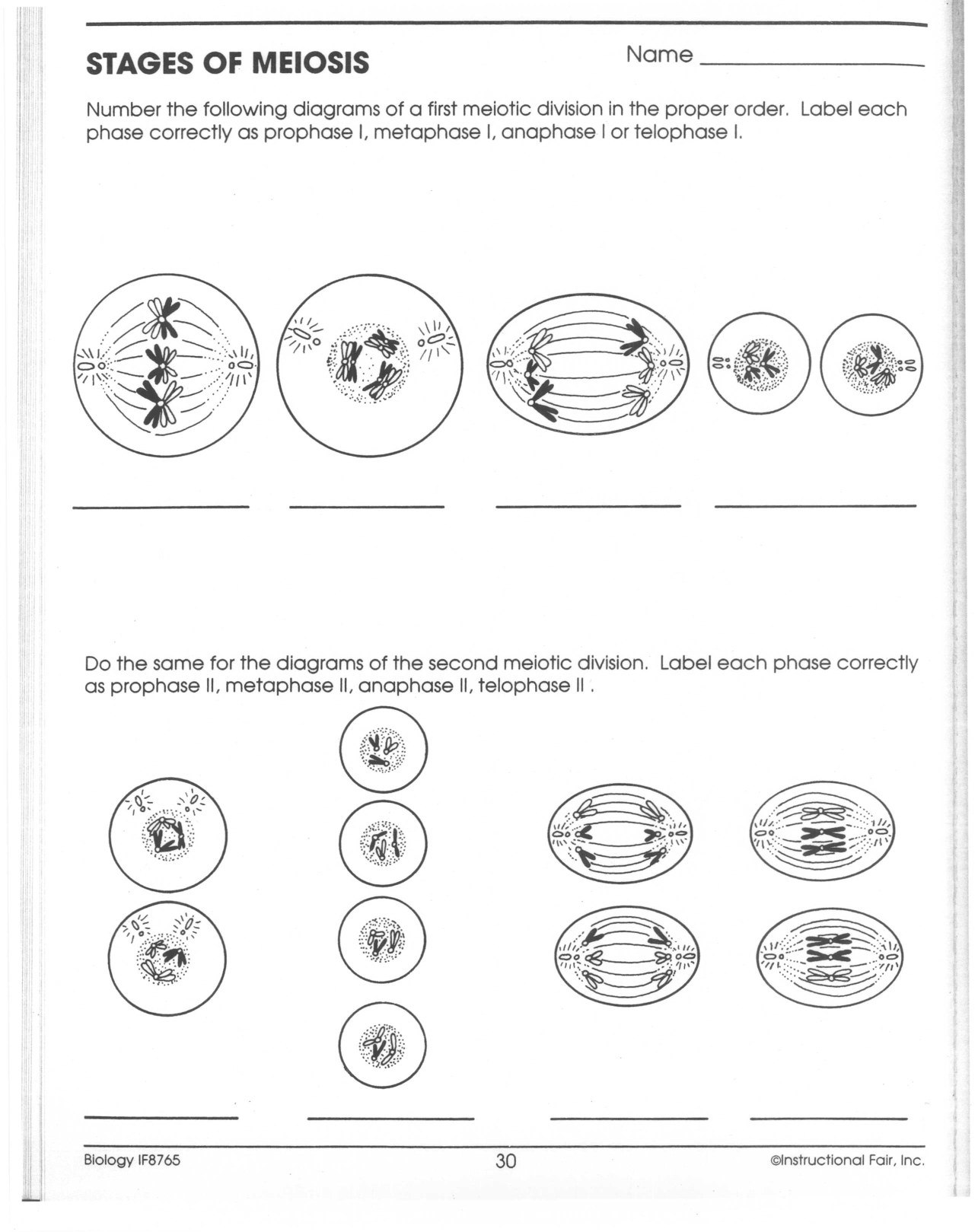
- Prophase II: Chromosomes condense again.
- Metaphase II: Individual chromosomes align at the equator.
- Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles.
- Telophase II: The cell divides again, producing four haploid cells.
Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis

| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Divisions | 1 | 2 |
| Number of Daughter Cells | 2 | 4 |
| Genetic Variation | Identical to parent cell | Varied due to crossing over and independent assortment |
| Chromosome Number | Same as parent cell (diploid) | Reduced by half (haploid) |

How Meiosis Ensures Genetic Diversity

Genetic diversity is critical for evolution and species survival. Here's how meiosis contributes:
- Crossing Over: Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I.
- Independent Assortment: Random alignment of homologous pairs during Metaphase I, leading to various combinations of chromosomes in gametes.
- Random Fertilization: The random union of gametes from different parents.
Why Meiosis Matters in Human Health

Errors in meiosis can lead to genetic disorders:
- Nondisjunction: When chromosomes fail to separate, resulting in aneuploidy conditions like Down syndrome.
- Gamete Abnormalities: Can cause infertility or the transmission of genetic diseases.
🔬 Note: Knowledge of meiosis is crucial for advancements in reproductive technologies and genetic counseling.
To summarize, understanding meiosis is essential not only for grasping biological concepts but also for appreciating its implications in human health, genetics, and evolution. This process ensures the continuity of life while introducing necessary genetic variations for the survival and adaptability of species.
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?

+
Mitosis produces identical cells used for growth and repair, while meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half to create genetically varied gametes for reproduction.
Why is crossing over important in meiosis?

+
Crossing over exchanges genetic material, leading to new combinations of genes which increase genetic diversity in the offspring.
What happens if there are errors during meiosis?

+
Errors can result in conditions like aneuploidy, leading to genetic disorders like Down syndrome, or can affect fertility.