Master Matter and Thermal Energy with This Worksheet

⚠️ Note: This content is tailored specifically for "Master Matter and Thermal Energy with This Worksheet".
Exploring Matter and Thermal Energy

Matter is the physical substance that occupies space and possesses mass, and it interacts with thermal energy in a myriad of ways, affecting its state, temperature, and behavior. This interaction is fundamental to understanding both physical and chemical processes in our everyday lives. From the warmth of a morning coffee to the life-giving cycles in ecosystems, thermal energy plays a critical role in how we perceive and utilize matter.
The Basics of Matter

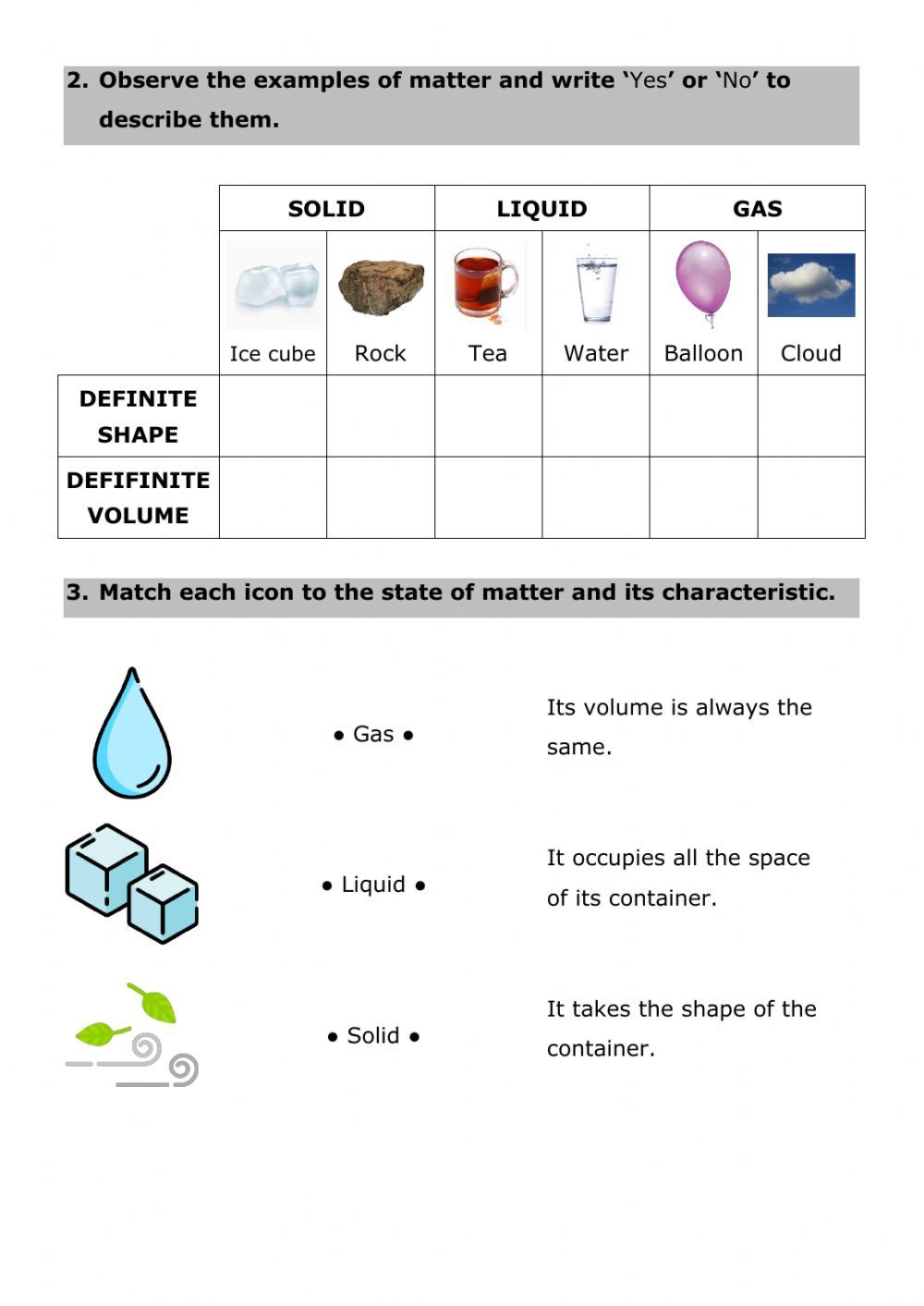
Matter is traditionally categorized into three states:
- Solid: Molecules are closely packed, maintaining a fixed shape and volume.
- Liquid: Molecules flow and take the shape of the container, with a consistent volume.
- Gas: Molecules are well separated, and the volume changes with pressure and temperature.
However, there are other states like plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate that are less common in everyday experiences. Understanding these states is key to:
- Recognizing how matter behaves at different temperatures.
- Exploring how thermal energy changes these states.
Understanding Thermal Energy

Thermal energy is the internal energy of an object due to the kinetic energy of its atoms and molecules. Here are some key points:
- As thermal energy increases, so does the kinetic energy of the particles, which in turn can change the state of matter.
- Heat, a form of energy transfer, is what makes this change possible.
- Temperature is a measure of this average kinetic energy, with higher temperatures indicating more kinetic energy.
How Thermal Energy Affects Matter
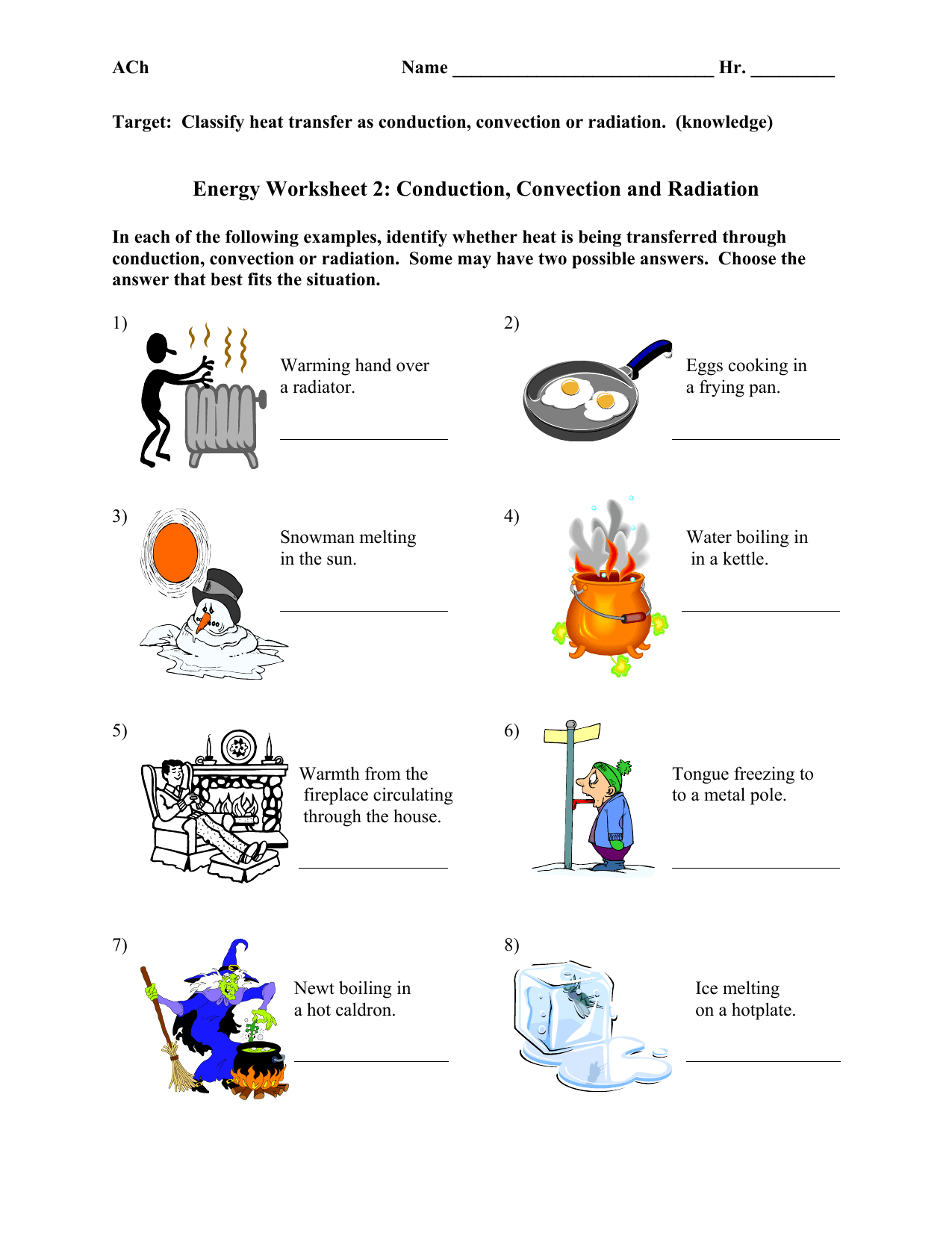
The interaction between thermal energy and matter is not just theoretical; it has practical applications in various fields:
Phase Transitions

- Freezing: When thermal energy is removed from a liquid, it turns into a solid through freezing, at the freezing point.
- Melting: Adding thermal energy to a solid raises its temperature until it melts into a liquid.
- Boiling: At the boiling point, a liquid absorbs thermal energy, turning into a gas.
- Sublimation: Some substances can transition directly from solid to gas, bypassing the liquid phase, when heated under low pressure.
⏱️ Note: Phase transitions are pivotal in technologies like refrigeration, where matter changes states to remove heat from systems.
Thermal Expansion

- As matter heats up, particles move more, leading to an increase in volume. This principle is used in applications like thermometers and thermal engines.
Chemical Reactions

- Thermal energy can provide the activation energy required to initiate reactions, affecting reaction rates and the products formed.
Worksheet: Applying Concepts of Matter and Thermal Energy

This worksheet will help you solidify your understanding of these concepts through practical exercises:
Questions:

- Explain the relationship between thermal energy and the state of matter, providing an example for each state transition.
- Define and differentiate between heat and thermal energy.
- Describe how thermal expansion can be observed in everyday life.
- Explain how thermal energy influences the rate of a chemical reaction, including an example.
Exercises:
| Exercise | State Change | Heat Added or Removed |
|---|---|---|
| Ice melting to water | Solid to Liquid | Added |
| Steam condenses to water droplets | Gas to Liquid | Removed |
| Sugar sublimates directly from crystals to gas | Solid to Gas | Added (under low pressure) |

Integrating Knowledge with Practical Understanding

By actively engaging with these exercises, you’re not just learning facts but also developing a deeper, practical understanding of how matter and thermal energy interact. This isn’t just about passing a test; it’s about empowering you to appreciate and apply scientific principles in real-world scenarios.
In Summary

In our exploration of matter and thermal energy, we’ve covered:
- The fundamental nature of matter, including its states and transitions.
- How thermal energy affects these states through phase changes, thermal expansion, and its role in chemical reactions.
- A practical approach through a worksheet, allowing you to apply this knowledge actively.
This comprehensive guide not only helps you understand the theoretical aspects but also prepares you for real-life applications where matter and energy converge.
How does thermal energy affect the state of matter?

+
Thermal energy affects the state of matter by altering the kinetic energy of its particles. When thermal energy is added, particles move faster, potentially causing a change in state, like melting or boiling. Conversely, removing thermal energy slows the particles down, leading to processes like freezing or condensation.
Can matter change from a solid to a gas without becoming a liquid?

+
Yes, this process is called sublimation, where matter transitions directly from solid to gas under specific conditions, typically low pressure or vacuum. Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) sublimates at room pressure and temperature.
Why is understanding thermal expansion important?

+
Thermal expansion can affect the design and functionality of many systems. For instance, structures like bridges and railways must accommodate expansion to prevent damage, and devices like thermostats rely on thermal expansion principles to control temperature.



