5 Ways Whale Evolution Highlights Marine Biodiversity

The study of whale evolution provides a unique lens through which we can understand the vast biodiversity of marine ecosystems. This exploration not only fascinates us with tales of ancient creatures adapting to the depths of the ocean but also underscores the intricate balance of life beneath the waves. Here are five ways in which the evolutionary journey of whales showcases marine biodiversity:
1. Divergent Evolution and Speciation
Whales have evolved from land-dwelling ancestors over the span of millions of years. This transformation from terrestrial mammals like Pakicetus to modern-day cetaceans illustrates divergent evolution – a process where species split into several, each adapted to different environmental niches. This highlights the rich variety of marine life, from the tiny plankton-feeding whales like the blue whale to the giant predators like the orca.
- Example: The split between baleen whales (mysticetes) and toothed whales (odontocetes).
- Whale ancestors adapted differently to various ecological niches, leading to:
- Large baleen whales that filter feed on krill and plankton.
- Smaller, highly specialized toothed whales that hunt prey.
- Streamlined Bodies: Enhancing swimming efficiency.
- Flippers and Flukes: Allowing for maneuverability and speed.
- Loss of External Ears and Modification of Internal Ear Structures: This allowed for better auditory reception in water.
- Whale Falls: When whales die, their bodies sink to the ocean floor, providing a habitat for numerous deep-sea species.
- Nutrient Cycling: Through their feeding habits and excretions, whales redistribute nutrients, fueling the growth of phytoplankton which forms the base of the oceanic food web.
- Ancient Whale Populations: Paleontological studies reveal how whale populations and their prey fluctuated over geological time, indicating changes in oceanic biodiversity.
- Climate and Sea Level Changes: Whale fossils help reconstruct ancient marine habitats, providing clues about historical climate changes and their impact on marine life.
- Threats to Diversity: Human activities like whaling, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to whale populations and, by extension, to marine biodiversity.
- Conservation Efforts: Efforts to protect whale habitats and species illustrate the broader importance of preserving marine biodiversity.
📌 Note: Whale evolution is a testament to how natural selection can lead to the creation of diverse species from a common ancestor.
2. Adaptations for Marine Life
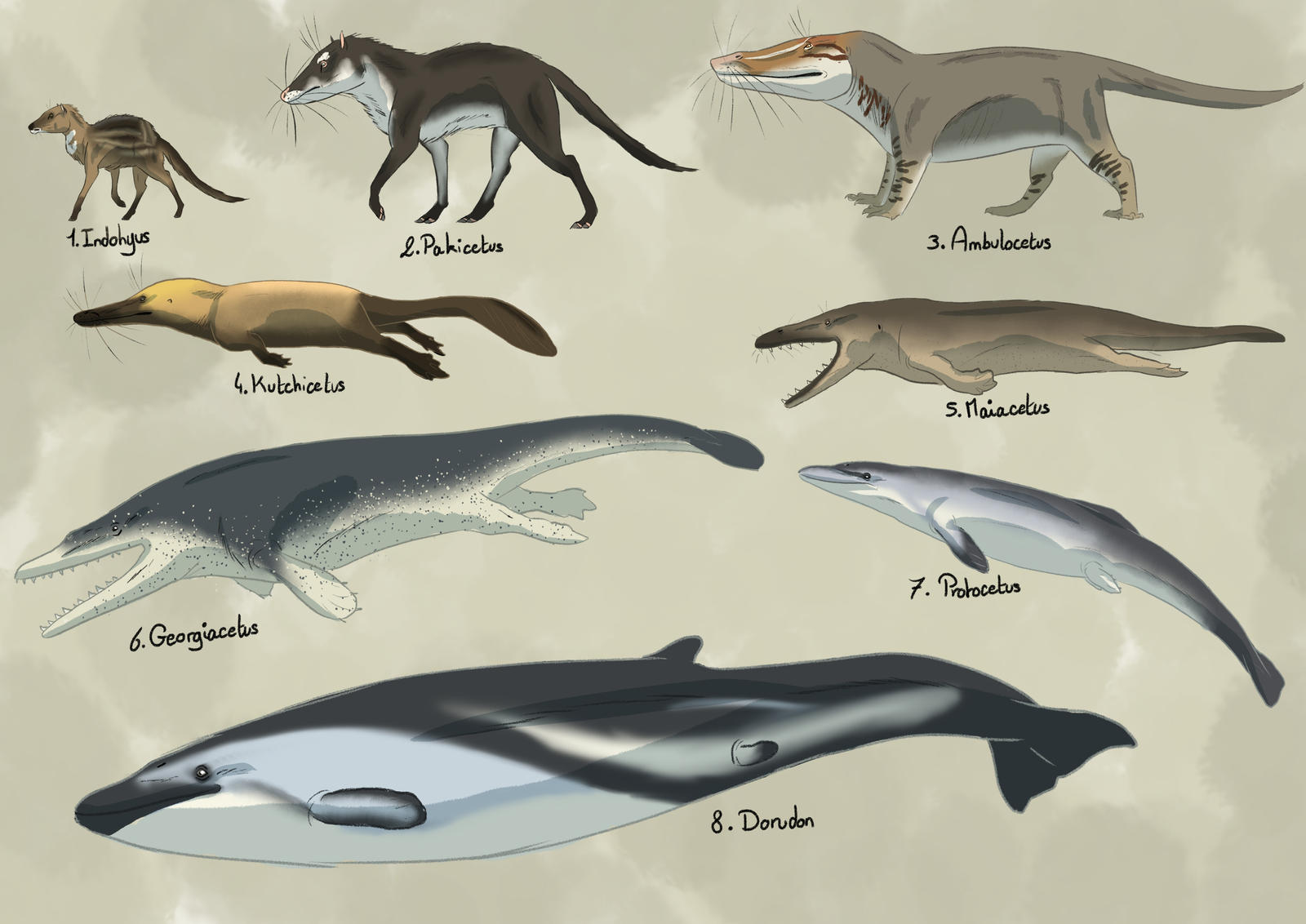

Evolutionary adaptations for aquatic life in whales have resulted in a plethora of traits that showcase the diversity of marine adaptations:
| Feature | Advantage in Marine Environment |
|---|---|
| Blubber | Insulation and energy reserve |
| Echolocation (in toothed whales) | Navigation and hunting in dark or deep waters |
| Baleen Plates | Filter feeding on small organisms |

3. Ecosystem Engineers

Whales act as ecosystem engineers by influencing the structure, function, and species composition of marine environments:
🌊 Note: Whale carcasses can support entire communities of organisms, highlighting their role in deep-sea biodiversity.
4. Clues to Past Biodiversity

Fossil records of whale ancestors give us insight into the past biodiversity of the seas:
5. Current Challenges and Conservation

The evolutionary journey of whales also intersects with contemporary issues, highlighting the need for marine conservation:
🚨 Note: The conservation of whales is a direct action towards maintaining the health and diversity of marine ecosystems.
In summary, the evolutionary history of whales is a fascinating narrative that underscores the diversity of marine life. From the genetic divergence leading to different whale species to their role as ecosystem engineers, whales highlight the complex interplay of species within marine environments. Their journey from land to sea not only showcases the power of adaptation but also underscores the need for us to conserve these majestic creatures and the vibrant ecosystems they support. Through understanding and protecting whales, we are, in essence, safeguarding the health of the entire ocean.
Why did whales evolve from land animals?

+
Over millions of years, whales evolved from land-dwelling ancestors to exploit untapped resources in the marine environment, driven by ecological opportunities and evolutionary pressures.
What role do whales play in the ocean’s biodiversity?

+
Whales contribute significantly to marine biodiversity by cycling nutrients, influencing plankton growth, providing habitats for deep-sea species through whale falls, and more.
Can whales indicate the health of marine ecosystems?

+
Yes, the health of whale populations can serve as an indicator of the ocean’s health due to their role in the food web and their sensitivity to environmental changes.



