5 Tips for Mastering Literal vs. Figurative Language
Understanding the nuances between literal and figurative language can greatly enhance your communication skills. Whether you're writing, speaking, or reading, knowing how to use and interpret these forms of language can make your message clearer, more engaging, or even poetic. In this article, we'll dive into five tips that will help you master the art of distinguishing and employing literal versus figurative language effectively.
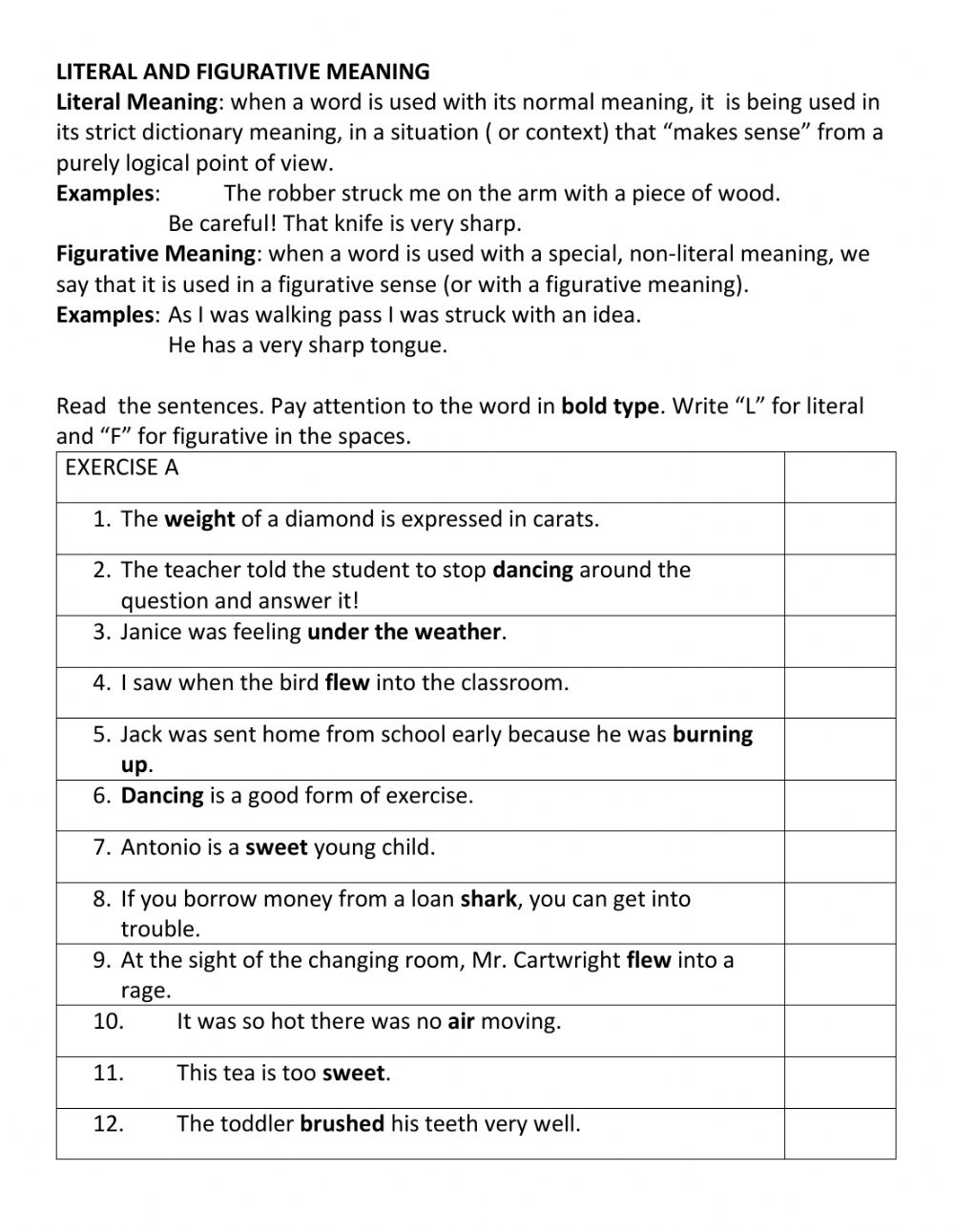
The Basics of Literal and Figurative Language


Before we delve into our tips, let’s clarify what these terms mean:
- Literal Language: This is straightforward language where the words convey their exact, dictionary meaning. For instance, “The sky is blue.”
- Figurative Language: Here, words are used in a non-literal way to create more vivid, imaginative descriptions or to suggest hidden meanings. Examples include metaphors, similes, and personification.
Tip #1: Recognize Contextual Clues

One of the key skills in understanding language is identifying the context in which it is used. Contextual clues help determine whether a phrase is meant literally or figuratively:
- Surrounding Words: Words or phrases that might exaggerate, describe in unusual ways, or not make literal sense often signal figurative language.
- Tone and Intention: Understanding the speaker or writer’s tone can help decipher whether they’re speaking literally or using figurative language for effect.
Here are some examples:
| Literal | Figurative |
|---|---|
| He ran very fast. | His feet had wings. |
| The dog barked all night. | The dog barked the stars awake. |

🔍 Note: Context is the king when differentiating literal from figurative language. Pay close attention to how language is used around a phrase or sentence.
Tip #2: Use Imagery for Figurative Language

When you want to convey more than the plain facts, figurative language can paint a picture in the reader’s mind. Here’s how:
- Metaphors and Similes: Compare two unlike things in a way that reveals their similarities.
- Personification: Give non-human or inanimate objects human characteristics to create a deeper connection.
For instance:
- His voice was music to her ears. - Here, voice and music are metaphorically connected.
- The wind howled in anger - The wind is personified as having emotions and voice.
Tip #3: Practice Literal Interpretation in Technical Writing

In fields like engineering, medicine, or law, literal language is paramount. Here, accuracy and clarity are crucial, so:
- Avoid Ambiguity: Use precise terminology to ensure your message is clear.
- Define Terms: If using technical language, ensure it’s defined for those not familiar with the jargon.
Example:
- Instead of saying “The system is good,” say “The system meets performance criteria at X efficiency.”
Tip #4: Employ Figurative Language to Enhance Emotional Impact

When the goal is to evoke emotion or stir imagination, lean on figurative language:
- Hyperbole: Exaggeration for effect, like “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.”
- Idioms: Phrases that mean something different from their literal meaning, enhancing cultural resonance.
Use figurative language to:
- Create mood and atmosphere in literature.
- Make speeches or presentations more engaging.
- Add depth to your poetry or creative writing.
Tip #5: Recognize and Avoid Misunderstandings

Figurative language, while expressive, can sometimes lead to misunderstandings if not used or interpreted correctly:
- Be Aware of Cultural Differences: Idioms or figurative expressions may not translate well across cultures.
- Use Clarification: If you sense your reader or listener might be confused, clarify whether you’re speaking literally or figuratively.
Example:
- If someone says, “It’s raining cats and dogs,” clarify by saying, “Just to be clear, I mean it’s raining very heavily, not actual animals.”
By honing these skills, you'll not only improve your communication abilities but also your understanding of others. These tips provide a roadmap to better distinguish and use literal and figurative language. Remember, effective communication involves both clarity and creativity. Understanding when to use each type of language ensures you can convey your message with precision or imagination as the situation demands.
How can I tell if someone is using figurative language?

+
Look for unusual comparisons, exaggerated statements, or expressions where the literal meaning would not make sense in the context provided.
Can figurative language be used in professional settings?

+
Yes, but with caution. In fields like marketing, advertising, or public speaking, figurative language can be very effective if it supports the message without compromising clarity.
Why is it important to understand the difference between literal and figurative language?

+
Understanding this difference can prevent misunderstandings, ensure accurate communication, and enrich your interpretation of literature, poetry, and everyday speech.



