6 Ways to Master Limiting Reagent Problems

Understanding the Concept of Limiting Reagent

In chemistry, a limiting reagent is a reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. Identifying the limiting reagent is crucial in determining the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a reaction. In this article, we will explore six ways to master limiting reagent problems, helping you to become more proficient in solving these types of problems.
Method 1: Calculate the Number of Moles of Each Reactant

The first step in identifying the limiting reagent is to calculate the number of moles of each reactant. This can be done using the formula:
moles = mass of reactant / molar mass of reactant
Make sure to use the correct units and significant figures when performing calculations.
📝 Note: Always use the same units for the mass of reactant and the molar mass of reactant.
For example, if we have 50 grams of sodium (Na) and 100 grams of chlorine (Cl2), and we want to determine the limiting reagent for the reaction:
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
First, calculate the number of moles of each reactant:
moles of Na = 50 g / 23 g/mol = 2.17 mol moles of Cl2 = 100 g / 70.9 g/mol = 1.41 mol
Method 2: Determine the Balanced Equation
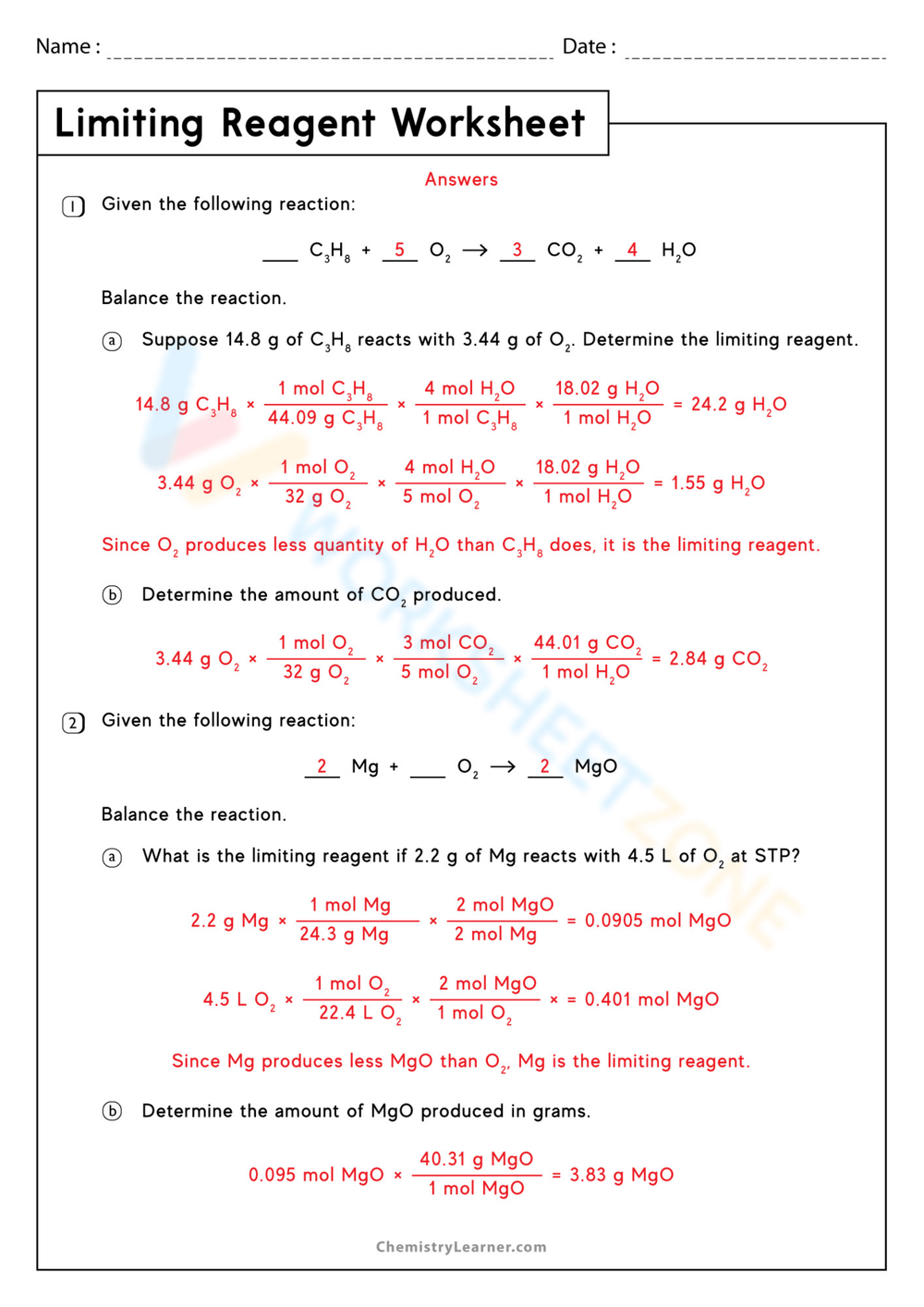
A balanced equation is essential in identifying the limiting reagent. Make sure to balance the equation and identify the stoichiometric coefficients of each reactant.
For example, the balanced equation for the reaction above is:
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
In this equation, the stoichiometric coefficients are 2 for Na and 1 for Cl2.
Method 3: Identify the Reactant with the Least Number of Moles

Once you have calculated the number of moles of each reactant and determined the balanced equation, identify the reactant with the least number of moles. This reactant is the limiting reagent.
In the example above, we calculated that we have 2.17 mol of Na and 1.41 mol of Cl2. Since Cl2 has the least number of moles, it is the limiting reagent.
Method 4: Calculate the Number of Moles of Product Formed

Using the number of moles of the limiting reagent, calculate the number of moles of product formed.
For example, in the reaction above, we calculated that Cl2 is the limiting reagent with 1.41 mol. Using the stoichiometric coefficients, we can calculate the number of moles of NaCl formed:
moles of NaCl = 2 x moles of Cl2 = 2 x 1.41 mol = 2.82 mol
Method 5: Compare the Calculated and Theoretical Yields

Compare the calculated yield (number of moles of product formed) with the theoretical yield (number of moles of product that can be formed from the initial amounts of reactants).
If the calculated yield is less than the theoretical yield, the reaction is said to be limited by the limiting reagent.
Method 6: Practice, Practice, Practice

Finally, the best way to master limiting reagent problems is to practice. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones.
Here’s an example of a limiting reagent problem:
A reaction between 20 grams of Ca and 50 grams of O2 produces CaO. If the balanced equation is:
2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
Which reactant is the limiting reagent?
Answer:
moles of Ca = 20 g / 40 g/mol = 0.5 mol moles of O2 = 50 g / 32 g/mol = 1.56 mol
Since Ca has the least number of moles, it is the limiting reagent.
What is a limiting reagent?
+
A limiting reagent is a reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
How do I calculate the number of moles of a reactant?

+
Calculate the number of moles of a reactant using the formula: moles = mass of reactant / molar mass of reactant.
What is the importance of balancing the equation in limiting reagent problems?

+
A balanced equation is essential in identifying the limiting reagent, as it provides the stoichiometric coefficients of each reactant.
In conclusion, mastering limiting reagent problems requires a combination of calculating the number of moles of each reactant, determining the balanced equation, identifying the reactant with the least number of moles, calculating the number of moles of product formed, comparing the calculated and theoretical yields, and practicing, practicing, practicing. With these six methods, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a pro at solving limiting reagent problems.
Related Terms:
- Limiting reagent worksheet answers pdf
- Limiting reagent Worksheet 2 answers
- Limiting reagent Worksheet pdf
- Limiting reagent Worksheet 1
- Limiting reagent worksheet w324
- limiting reactant worksheet pdf



