5 Essential Tips for Limiting Reagent and Percent Yield Calculation
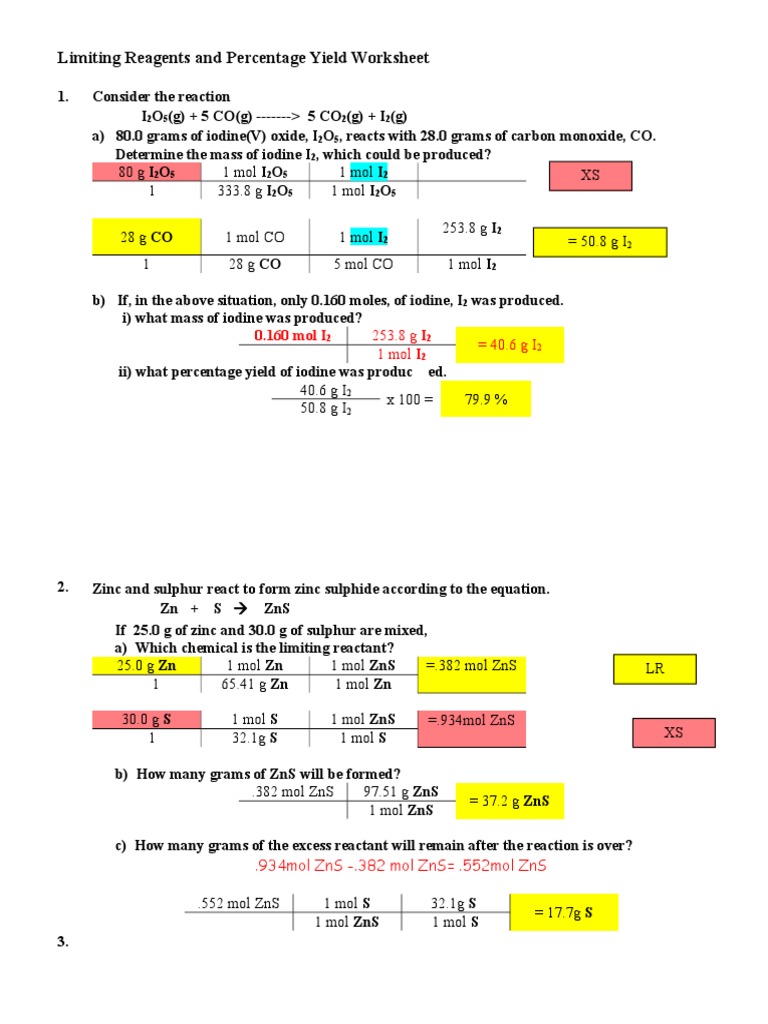
The precise calculation of limiting reagents and percent yield in chemical reactions is a cornerstone for both laboratory work and industrial processes. By understanding and mastering these concepts, you can optimize production, minimize waste, and improve the efficiency of reactions. This article will provide you with five essential tips to accurately calculate limiting reagents and percent yields, thereby ensuring your chemistry projects yield the desired results.
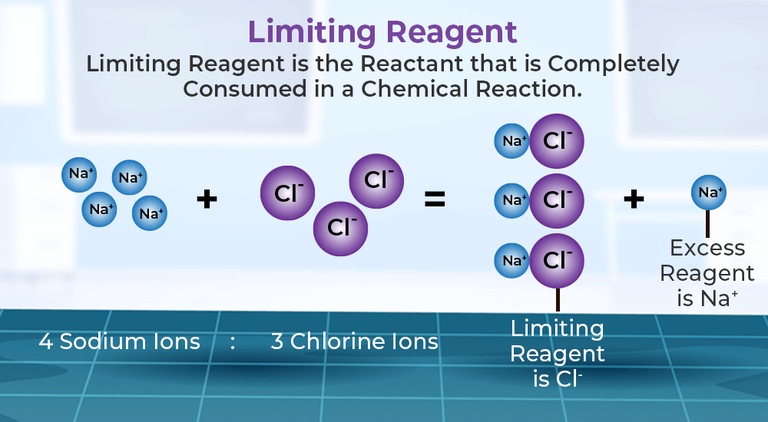
Understanding Limiting Reagent
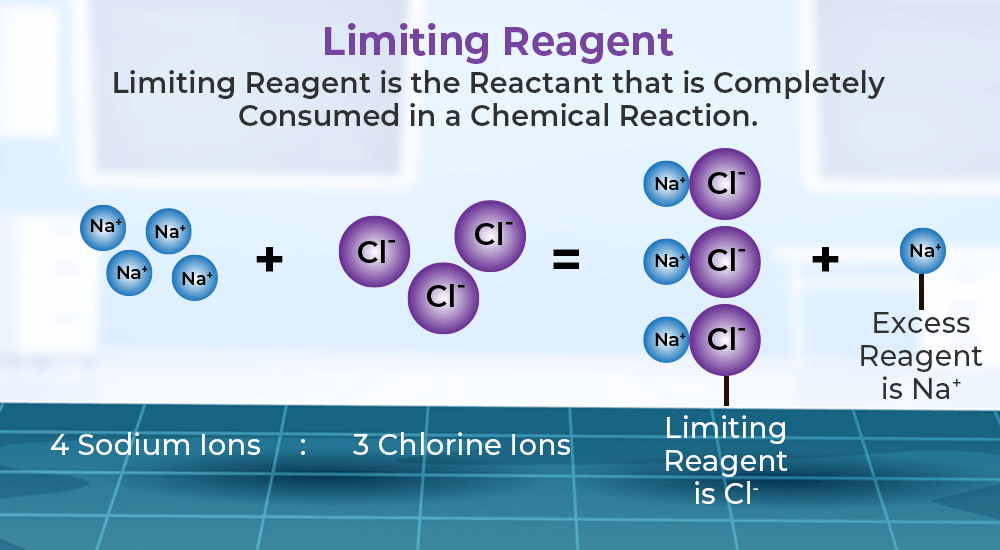
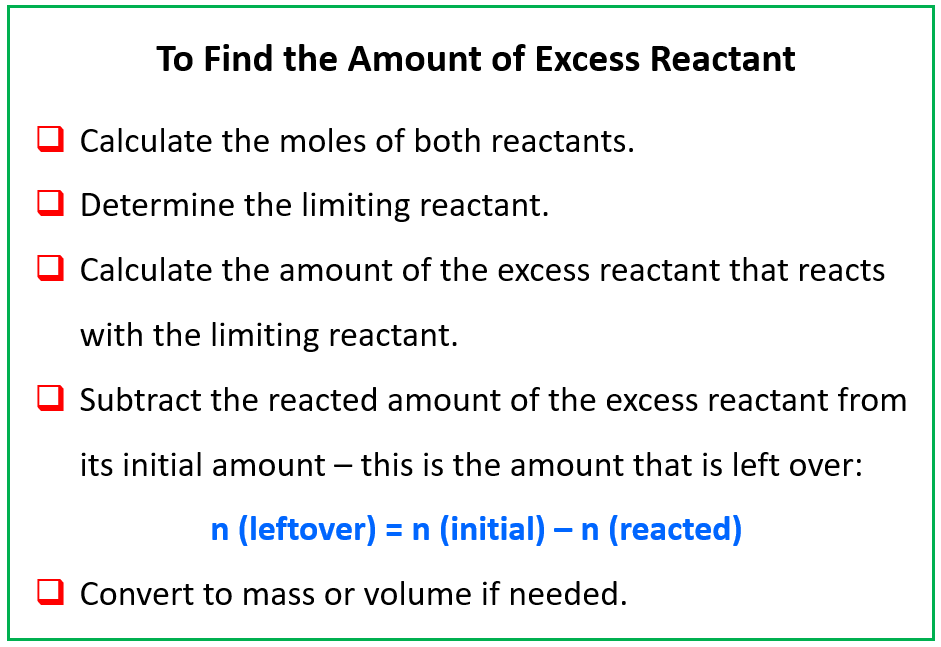
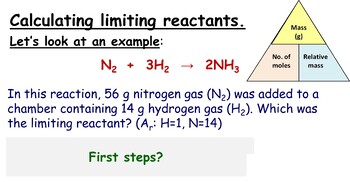
The first step towards mastering these calculations is to understand what a limiting reagent is. In any chemical reaction, the limiting reagent is the reactant that gets entirely consumed first, thus limiting the amount of product that can be formed. Here are steps to identify the limiting reagent:
- List out the reactants and their given quantities.
- Calculate the moles of each reactant using the molecular weight or mass.
- Using the balanced chemical equation, determine the stoichiometric mole ratio.
- Compare the moles to find which reactant will be consumed first.
🔍 Note: Always ensure your balanced chemical equation is accurate; an incorrect equation can lead to miscalculations in the amount of limiting reagent.
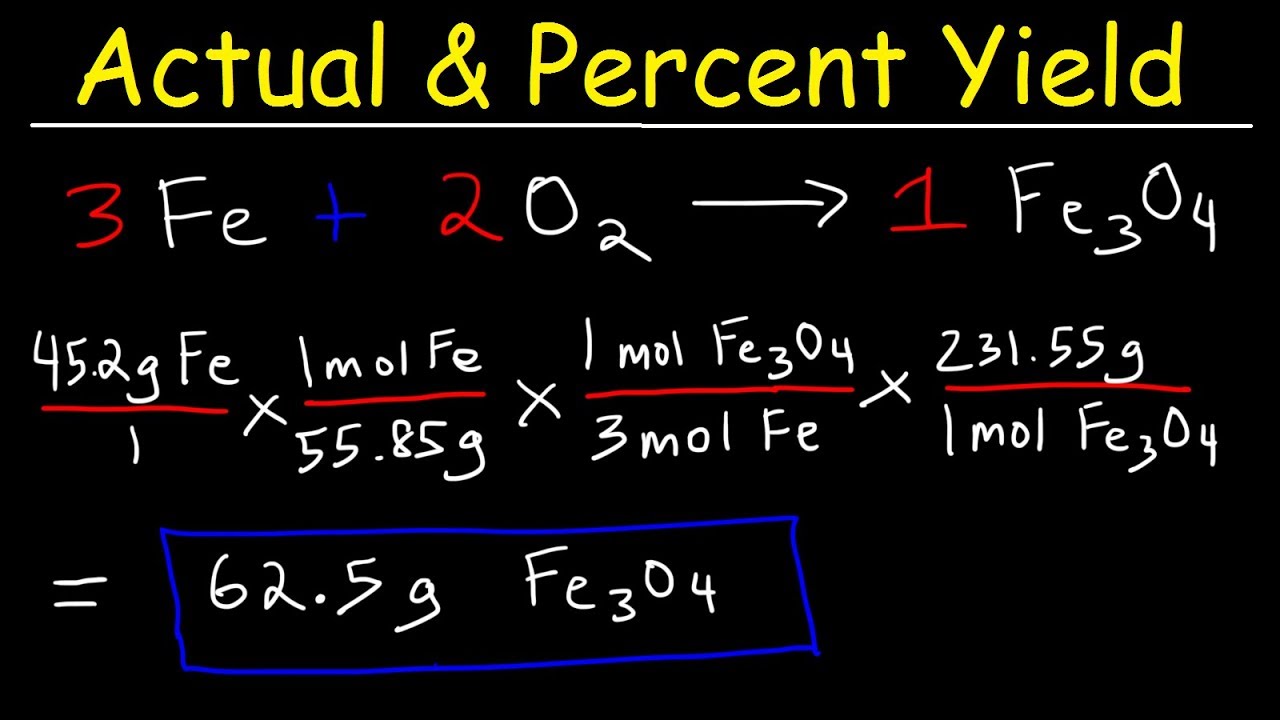
Calculating Theoretical and Actual Yield

Once you've identified your limiting reagent, you can proceed to calculate both theoretical and actual yield:
- Theoretical Yield: This is the maximum amount of product that could theoretically be produced based on the limiting reagent. It's calculated by using stoichiometry from the balanced equation.
- Actual Yield: This is the amount of product actually obtained from the experiment.
| Step | Process |
|---|---|
| 1 | Find moles of limiting reagent. |
| 2 | Use stoichiometry to find theoretical moles of product. |
| 3 | Convert moles of product to grams using the molecular weight. |
🧪 Note: Precision in measurements is key for accurate yield calculations. Small inaccuracies can skew results significantly.
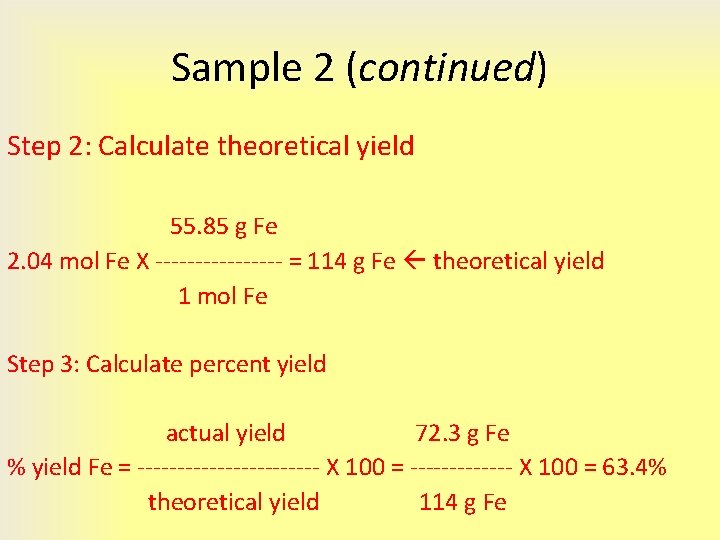
Calculating Percent Yield

Percent yield is a way to express how efficient your reaction was. Here's how to calculate it:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%- Ensure both actual and theoretical yields are in the same units.
- Divide the actual yield by the theoretical yield.
- Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Maximizing Reaction Efficiency
To ensure that your chemical reactions yield the most product with the least waste:
- Optimization: Adjust conditions like temperature, pressure, and reactant concentration.
- Purification: Use techniques like crystallization, filtration, or distillation to remove impurities.
- Scale-Up Considerations: When scaling up, keep in mind that not all reactions scale linearly. Consider factors like mixing, heat dissipation, and reagent interaction.
🔎 Note: Scaling up can change the dynamics of a reaction, potentially leading to different yields due to inefficiencies in mixing or temperature control.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Even with careful planning, several issues can arise in yield calculations:
- Incomplete Reaction: Not all reactions go to completion. Monitor the reaction progress, and extend the reaction time if necessary.
- Side Reactions: These can lead to unexpected products, reducing the yield of the desired product.
- Measurement Errors: Errors in measuring reagents or products can skew yield calculations. Use high-precision instruments and double-check your measurements.
By mastering these tips, you'll not only improve your lab skills but also enhance your understanding of chemical reactions, their limitations, and potential optimizations. This knowledge is invaluable in various scientific and industrial applications where reaction efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and product purity are critical.
Why is identifying the limiting reagent important?

+
Identifying the limiting reagent is critical because it determines how much product can be produced in a reaction. It helps in optimizing the reaction conditions to ensure maximum yield and minimal waste.
How can one increase percent yield?
+
To increase percent yield, consider optimizing reaction conditions, ensuring reactants are pure, minimizing side reactions, and using stoichiometry to avoid wastage of reagents.
Can percent yield exceed 100%?

+
No, percent yield cannot exceed 100%. A yield greater than 100% indicates errors in measurement or calculation, often due to impurities or side reactions producing additional substances.
What if the theoretical yield is lower than the actual yield?
+
This suggests an error in calculations, an overestimation of reactant quantities, or impurities in the product. Review your methodology and ensure accurate stoichiometric analysis.
How can reaction efficiency be measured?

+
Reaction efficiency can be measured by percent yield, comparing the amount of product formed to the theoretical maximum. Other indicators include rate of reaction, by-product formation, and energy efficiency.