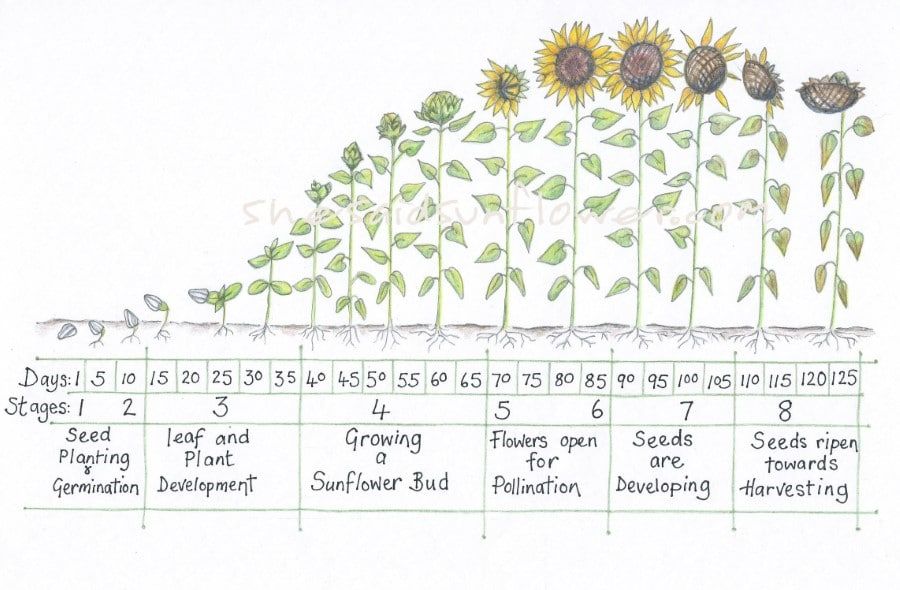
7 Stages of Sunflower Growth: Free Worksheet Included
The growth journey of a sunflower is a fascinating demonstration of nature's engineering, from a simple seed to a towering plant crowned with a burst of yellow. Understanding the 7 Stages of Sunflower Growth not only provides insight into plant biology but also highlights the beauty of life's natural cycles. This article will guide you through these stages, ensuring you grasp how sunflowers develop over time. Along with our detailed explanation, we've included a free worksheet that you can use to track the growth of your own sunflowers at home or in your classroom.
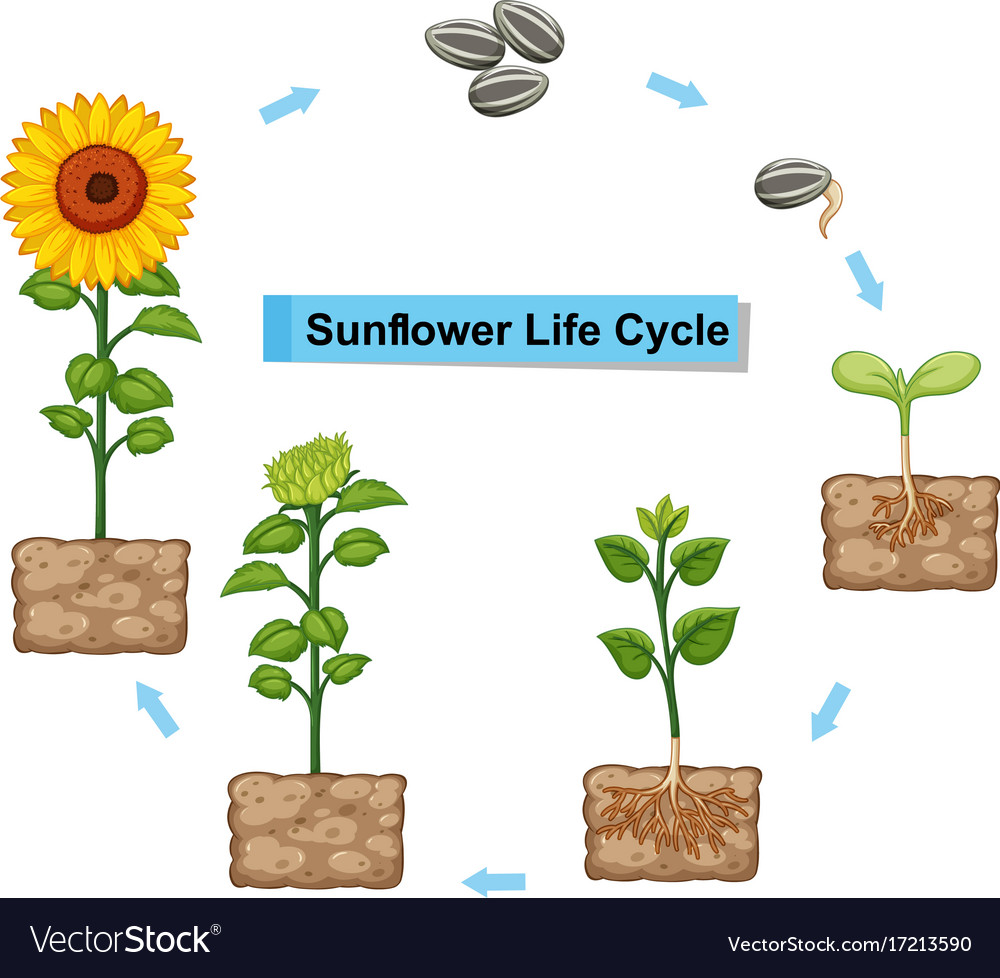
Stage 1: Seed Germination
Germination is the first step in the life of a sunflower. Here’s what happens during this stage:
- Water Absorption: Seeds absorb water which softens the seed coat.
- Enzyme Activation: The enzymes within the seed become active, preparing for growth.
- Root Emergence: The radicle, or primary root, breaks through the seed coat.
- Shoot Formation: Following the root, the shoot emerges, pushing the seed upwards.

🌱 Note: To encourage quick germination, maintain consistent moisture in the soil, but avoid overwatering which can lead to seed rot.
Stage 2: Emergence

After germination, the young sunflower plant begins its life above the soil:
- The cotyledons, or seed leaves, emerge from the soil to begin photosynthesis.
- The seedling grows quickly, developing its first set of true leaves.
📝 Note: This stage can vary in duration based on environmental conditions like temperature, light, and soil type.
Stage 3: Vegetative Growth
Now, the sunflower plant concentrates on growing taller and developing its root system:
- The plant focuses on leaf and stem growth, harnessing solar energy to fuel this process.
- The stem thickens, providing structural support as the plant grows taller.
| Weeks | Height (cm) | Number of Leaves |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | 10-15 | 4-6 |
| 3-4 | 30-40 | 8-10 |

Stage 4: Flower Bud Development

At this stage, the sunflower begins to form its most iconic feature:
- Bud Formation: A small bud appears at the top of the stalk.
- Bud Growth: The bud grows bigger, eventually showing the characteristic yellow of sunflower petals.
Stage 5: Blooming
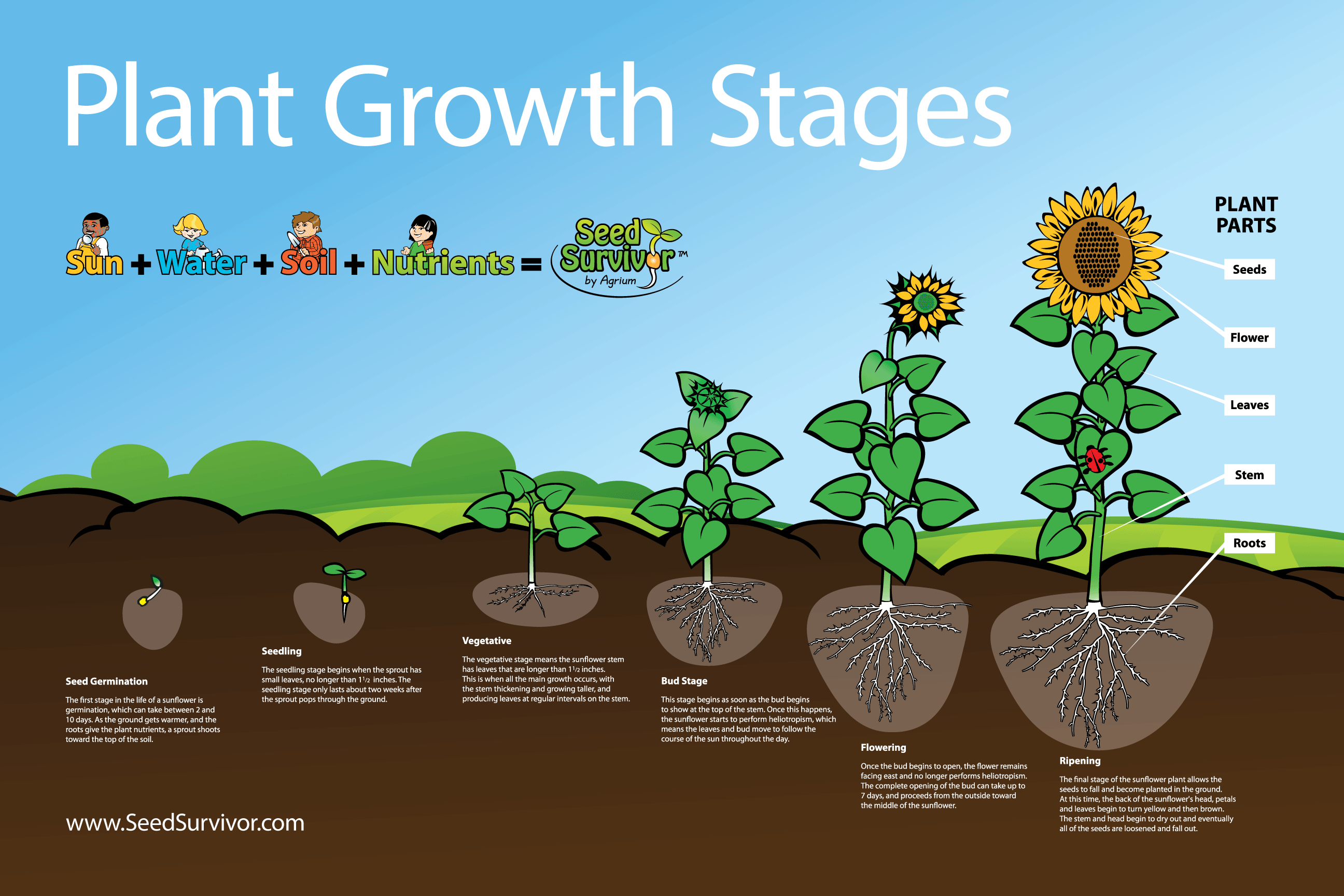
The blooming phase is perhaps the most celebrated part of a sunflower’s life:
- The bud opens up to reveal bright yellow petals arranged around a disc filled with seeds.
- The flower faces the sun, a phenomenon known as heliotropism.
🐝 Note: This is when pollinators like bees are attracted to the sunflower, aiding in cross-pollination.
Stage 6: Pollination and Seed Formation

After blooming, the sunflower shifts its focus to seed production:
- Once pollinated, seeds start to form within the flower head.
- The petals may wilt, and the center becomes filled with seeds, ready for dispersal.
Stage 7: Maturation

The final stage of a sunflower’s growth is about ripening the seeds:
- The back of the flower head turns brown, signaling the seeds are maturing.
- The seeds can be harvested once the flower head dries out and the seeds are fully developed.
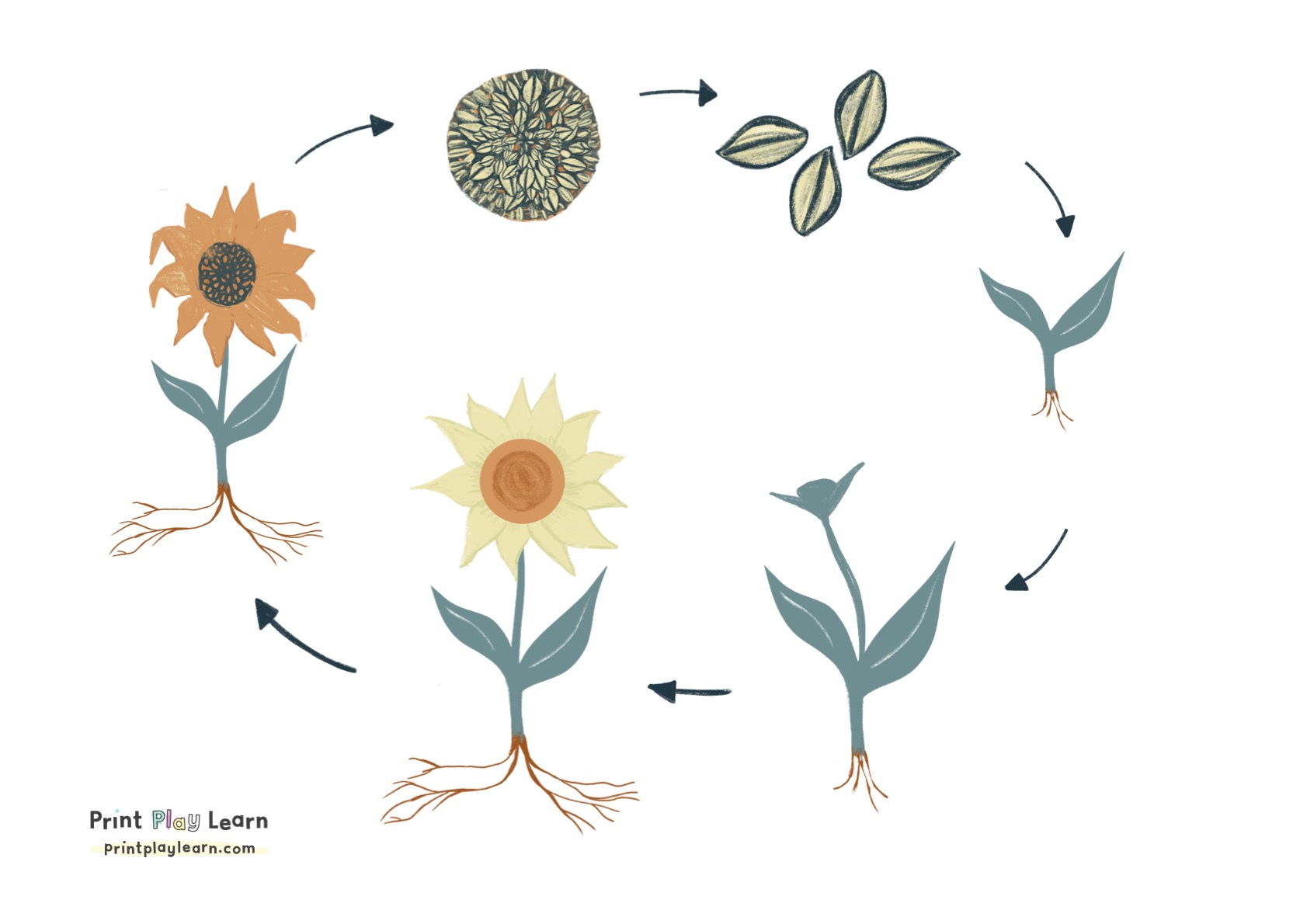
The life cycle of a sunflower is a magnificent example of nature's resilience and beauty. From a tiny seed, it grows to display vibrant petals that capture the essence of summer. By understanding these 7 Stages of Sunflower Growth, you gain an appreciation for the complexities of plant life and the care it requires. Using our free worksheet, you can observe and document each phase of this journey, whether you're a student, an enthusiast, or just someone curious about how these garden giants come to life.
How long does it take for a sunflower to complete its growth cycle?
+
The duration varies, but a sunflower typically completes its growth cycle in about 90-120 days, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
Can sunflowers be grown indoors?
+
Yes, sunflowers can be grown indoors if they receive sufficient light and are transplanted outdoors or into larger pots once they outgrow their initial containers.
What should I do if my sunflower plants are not growing tall?

+
If your sunflowers are not growing as expected, ensure they have enough sunlight, nutrients from the soil, and adequate water. Consider using a fertilizer formulated for flowering plants.
How do I harvest sunflower seeds?

+
Wait until the back of the flower head turns brown and the petals have fallen. Then, cut the head off the plant, remove the seeds, and let them dry before storing or eating.
Can sunflowers grow in cold climates?

+
Sunflowers prefer warm weather but can be grown in cooler climates with careful timing and possibly using greenhouse conditions for the initial stages.


