Explore the Sun's Layers with Our Detailed Worksheet
The sun, our closest star, is more than just a ball of light; it's a complex structure with several layers, each playing a critical part in its overall function. In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive into the anatomy of the sun, exploring each layer through an interactive worksheet designed to deepen your understanding of solar physics. Whether you're an astronomy enthusiast, a student of science, or simply curious about the universe, this post will guide you through the layers of the sun, offering insights that will illuminate your knowledge like never before.
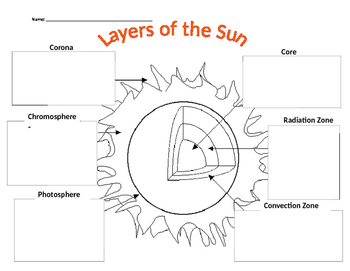
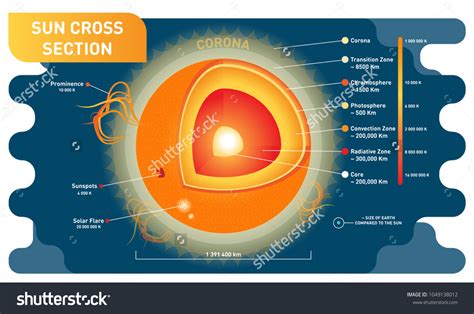
The Sun’s External Layers
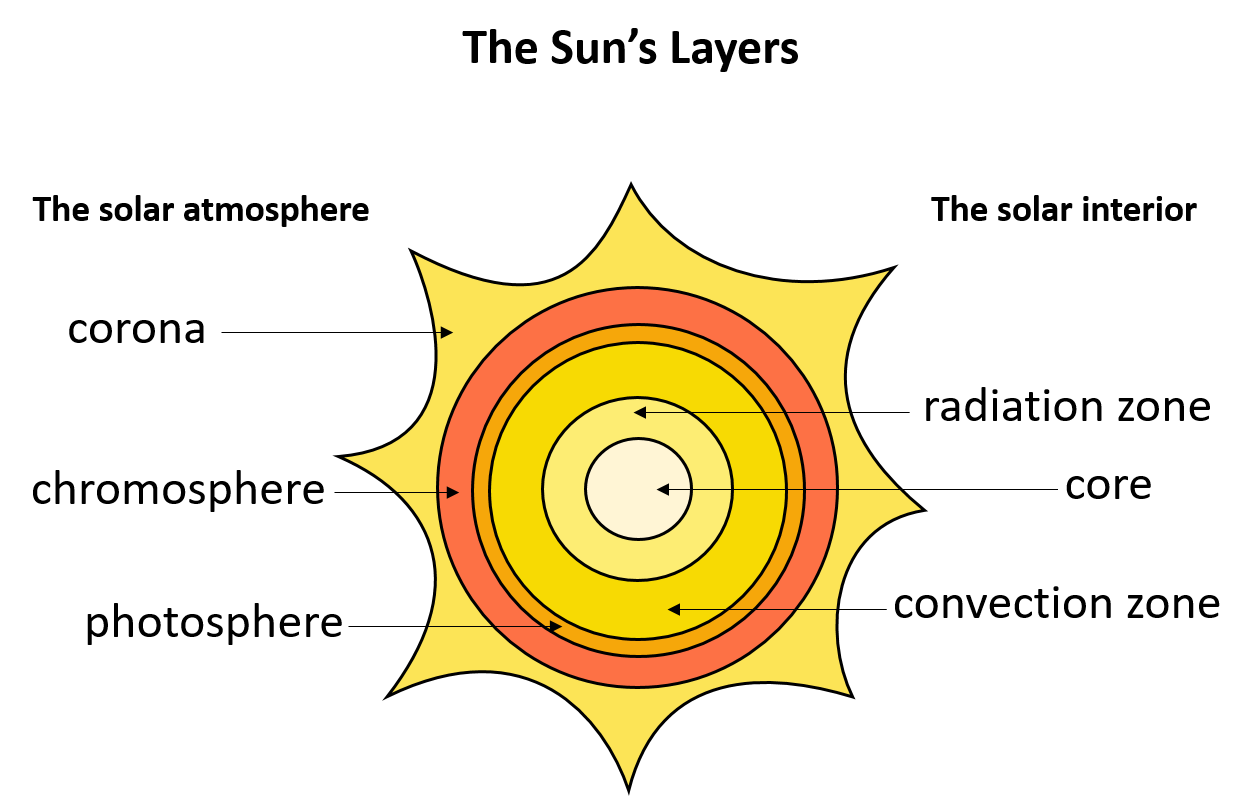
We’ll start our journey from the outside in. Here are the layers you can see with the naked eye or through a telescope:
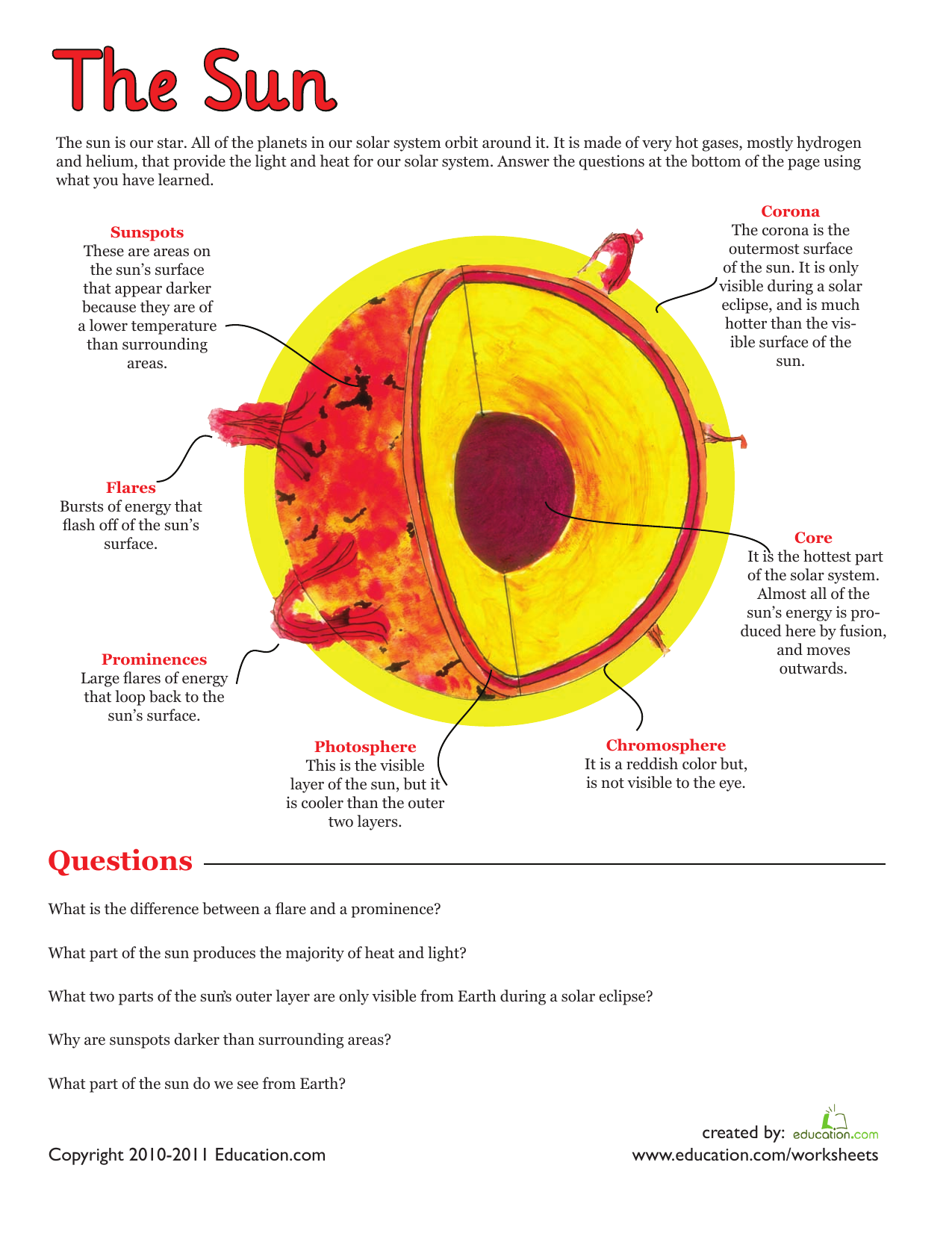
- The Corona - The outermost layer, visible during solar eclipses or through special filters, stretches millions of kilometers into space.
- The Chromosphere - Just beneath the corona, this layer is where solar flares and prominences occur.
- The Photosphere - This is the layer we observe directly as the sun’s surface, characterized by dark sunspots and solar granulation.

The Sun’s Internal Layers

Beyond what we can see, the sun has layers deep within its core where energy is generated:
- The Convection Zone - Here, hot plasma rises to the surface, cools, and then sinks back down.
- The Radiative Zone - Energy from the core is transported through this region by radiation.
- The Core - The powerhouse of the sun, where nuclear fusion converts hydrogen into helium, releasing energy in the process.
Worksheet Activities to Understand the Sun’s Layers

To bring these theoretical concepts to life, let’s engage with some worksheet activities:
Activity 1: Layering the Sun
| Layer | Position | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Core | 1 (innermost) | The site of nuclear fusion, incredibly dense and hot. |
| Radiative Zone | 2 | Energy transfer occurs via radiation. |
| Convection Zone | 3 | Plasma convection occurs, heat rises. |
| Photosphere | 4 | The “surface” of the sun we see. |
| Chromosphere | 5 | Where solar activity like flares occurs. |
| Corona | 6 (outermost) | The outermost layer, extends far into space. |

🔍 Note: When listing the layers, it’s helpful to understand that their temperatures and physical properties vary significantly as you move outwards or inwards.
Activity 2: Solar Exploration

Imagine you’re traveling through each layer of the sun. Describe what you might see, feel, and experience at each point:
- In the core, the intense pressure and temperature would annihilate most things. It’s where fusion creates light and heat.
- Moving through the radiative zone, photons from the core would be moving incredibly slowly as they’re absorbed and re-emitted.
- The convection zone would be turbulent, with rising and sinking plasma currents that transport heat.
- The photosphere would dazzle with solar granulation, sunspots, and the presence of light.
- In the chromosphere, you’d see reddish light, solar flares, and prominences dancing into space.
- The corona would offer a cool, ethereal experience with solar wind and perhaps the sight of an eclipse.
Activity 3: Solar Phenomena

Investigate different solar phenomena and their relationships with the sun’s layers:
- Sunspots - Dark areas on the photosphere, cooler regions within larger magnetic fields.
- Solar Flares - Explosions in the chromosphere, often associated with sunspots.
- Coronal Mass Ejections - Huge eruptions of plasma and magnetic fields from the corona.
- Aurora - Caused by the interaction of solar particles with Earth’s atmosphere, originating from solar activity.
Having ventured through the sun's various layers and activities, we've crafted a vivid picture of this cosmic giant. The sun, a marvel of plasma and energy, shapes our existence with its light, heat, and solar activity. Our journey has shown that every layer of the sun has unique characteristics and roles in this stellar furnace, from the fusion-driven core to the expansive corona. Engaging with the sun through these activities has not only made the sun's processes tangible but also highlighted its constant influence on our world, from the warmth on our skin to the northern lights in the sky.
Why do we see the sun as a yellow-orange color?

+
The sun appears yellow-orange because of the way our atmosphere scatters sunlight. Short-wavelength blue light scatters more than longer-wavelength red light, allowing more of the orange-yellow spectrum to reach our eyes directly.
What is the temperature at the sun’s core?

+
The sun’s core can reach temperatures of approximately 15 million degrees Celsius. Here, nuclear fusion powers the sun, converting hydrogen into helium.
How long does it take for sunlight to reach Earth?

+
Light from the sun takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel the 93 million miles to Earth.
What are solar flares and how do they affect Earth?
+
Solar flares are sudden eruptions of electromagnetic radiation from the sun’s chromosphere. They can disrupt satellite communications, cause power outages, and when energetic particles reach Earth’s atmosphere, they can create auroras.



