5 Ways to Master Cell Respiration in Biology Class
In the intricate world of biological processes, cell respiration stands as one of the most vital functions that allow life to thrive. It's the metabolic pathway that converts energy from food into a form that living cells can use, primarily ATP. For students of biology, mastering cell respiration can unlock a deeper understanding of cellular functions and energy dynamics. Here are five comprehensive strategies to help you excel in learning about cell respiration:
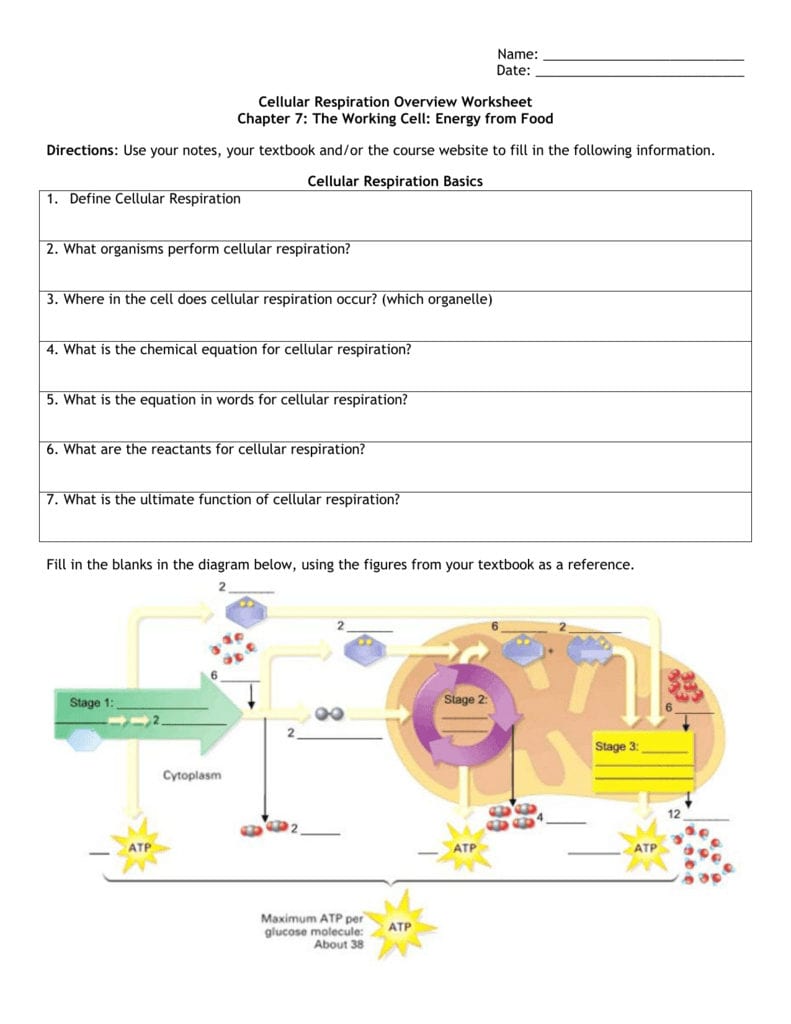
1. Understand the Basics of Cellular Respiration

Cell respiration is not just one process but a series of reactions that take place inside cells, primarily in mitochondria in eukaryotic organisms. Here's how to break it down:
- Glycolysis: Occurring in the cytoplasm, this process splits glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, generating a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH.
- The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Within the mitochondrial matrix, pyruvate is transformed into Acetyl-CoA, which then enters the cycle, producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis): This final step happens across the inner mitochondrial membrane, where electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along a chain, leading to ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis.
To grasp these stages, consider:
- Watching animated videos or interactive models that visually represent each step.
- Creating flashcards to memorize key molecules, enzymes, and reactions involved.
2. Visualize the Process

Visualization can be a powerful tool for learning complex processes like cellular respiration:
- Draw Diagrams: Sketching out the pathways helps in understanding the flow of electrons, the movement of molecules, and how energy is captured.
- Use 3D Models: Building or exploring 3D models of mitochondria can help visualize where and how each step occurs.
- Interactive Apps: There are several educational apps and websites that offer interactive simulations of cellular respiration.
🌟 Note: While visualizing is great, ensure that you understand the underlying chemical principles to make sense of why each step happens.
3. Make Connections

Biology is an interconnected web of processes. Understanding how cellular respiration fits into this network can enhance your grasp:
- Energy Flow: Understand how respiration connects with photosynthesis, forming the basis of life's energy cycle.
- Related Processes: Learn about fermentation, how it compares to aerobic respiration, and its role in cells when oxygen is not available.
- Organisms and Conditions: Study how different organisms (like anaerobes vs. aerobes) use respiration differently, and how environmental conditions affect cellular respiration.
4. Practice with Real-Life Scenarios

Relate cellular respiration to everyday life or biological phenomena:
- Exercise and Respiration: Explain why your breathing rate increases during physical activity.
- Alcohol Production: Describe how yeast uses anaerobic respiration (fermentation) to produce alcohol.
- Energy Efficiency: Compare how different foods (carbohydrates, fats, proteins) provide energy through cellular respiration.
This practical approach not only solidifies your understanding but also helps you see the relevance of cellular respiration in various biological contexts.
5. Participate in Active Learning

Active learning strategies can significantly improve retention:
- Study Groups: Discuss the process with peers, helping to clarify misunderstandings and learn from each other's insights.
- Quizzing: Regularly quiz yourself or have someone quiz you to reinforce the material.
- Teaching Others: One of the best ways to learn is by teaching. Explain cellular respiration to someone else.
📚 Note: Don't just memorize the steps; understanding the 'why' behind each stage will make your knowledge more robust and applicable.
As you delve into the world of cellular respiration, remember that mastery doesn't happen overnight. It requires consistent effort, curiosity, and a willingness to connect the dots between different biological processes. By understanding the basics, visualizing the processes, making connections with other biological concepts, applying knowledge to real-life scenarios, and engaging in active learning, you'll find that the complexities of cell respiration become less daunting. Over time, these strategies will not only help you in biology class but also enrich your understanding of life at its core level - the cellular level.
How does cellular respiration differ from photosynthesis?

+
While cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down organic molecules to produce ATP, photosynthesis is the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. Photosynthesis produces oxygen, which is used by organisms for respiration, and respiration produces carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, making these processes complementary.
What’s the importance of ATP in cellular respiration?

+
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is often called the energy currency of the cell. It’s produced during cellular respiration and provides the energy for most cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and biosynthesis.
Can cells survive without oxygen?

+
Yes, some cells can function under anaerobic conditions through fermentation, which produces ATP without oxygen. However, fermentation is less efficient than aerobic respiration. Most cells, especially those of multicellular organisms, require oxygen for prolonged survival because the ATP yield from aerobic respiration is much higher.