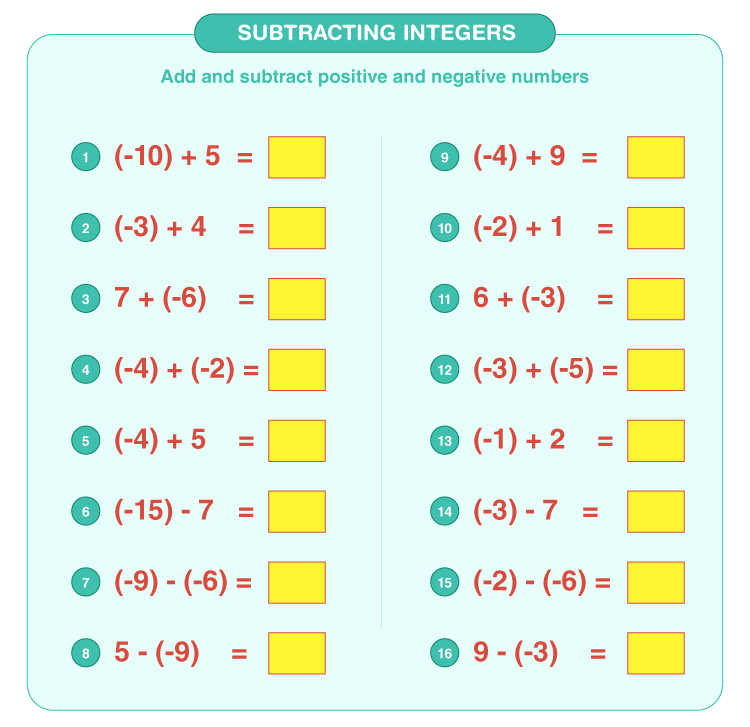
Ionic Bonding Practice Worksheet: Master Chemistry Easily
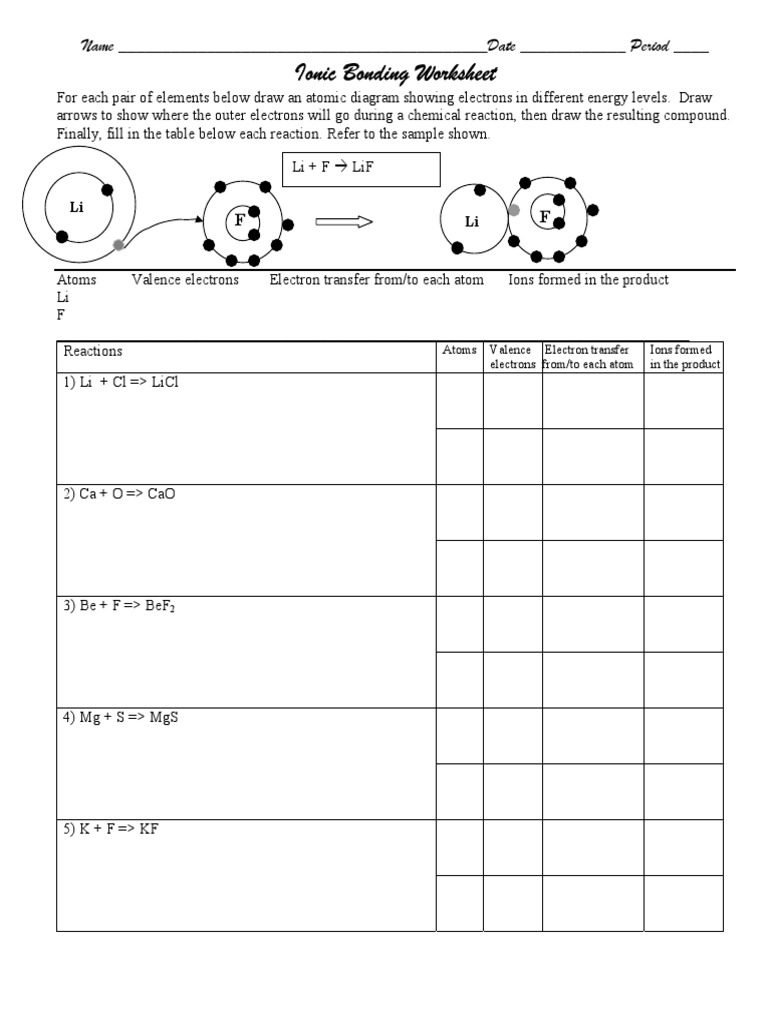
Mastering chemistry requires understanding various types of chemical bonding, with ionic bonding being one of the most fundamental concepts. Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, creating positive and negative ions that attract each other to form a compound. This blog post provides a comprehensive ionic bonding practice worksheet along with detailed explanations to help you strengthen your grasp on this essential topic.
Understanding Ionic Bonding


Ionic bonding occurs when one atom loses an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions. Here’s how it typically happens:
- Metals, which tend to lose electrons, form positive ions (cations).
- Non-metals, which tend to gain electrons, form negative ions (anions).
- The attraction between these oppositely charged ions is what we refer to as an ionic bond.
Key Characteristics of Ionic Compounds

Before diving into practice problems, let’s review the characteristics of ionic compounds:
- High melting and boiling points due to strong ionic bonds.
- Electrical conductivity when dissolved in water or melted.
- Formation of crystal lattice structures which often have a cubic shape.
Ionic Bonding Practice Worksheet

To help you master ionic bonding, here are some practice questions. Remember, understanding why an ionic bond forms is as important as knowing how to write out the formula correctly.
Problem 1: Determine the Ions

| Element | Ionic Charge |
|---|---|
| Na | +1 |
| O | -2 |

⚠️ Note: Remember that elements in the same group usually form ions with the same charge due to having the same number of valence electrons.
Problem 2: Write Ionic Formulas

Write the formula for the ionic compound formed between:
- Calcium (Ca) and Chlorine (Cl)
- Aluminum (Al) and Oxygen (O)
Problem 3: Lewis Structures for Ionic Compounds

Draw the Lewis structures for:
- Potassium Chloride (KCl)
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Problem 4: Predicting Ionic Compounds

Given the ions, predict the formula of the compound:
- Al3+ + O2-
- Na+ + S2-
Tips for Solving Ionic Bonding Problems

- Determine ionic charges based on group numbers or common charges.
- Ensure the charges balance to form a neutral compound.
- Use Lewis structures to visualize electron transfer.
- Understand that metals generally form cations and non-metals form anions.
As we conclude, mastering ionic bonding is essential for a deep understanding of chemistry. Through practice, you not only learn how to write formulas and predict properties but also develop an intuitive sense of how atoms interact to form stable compounds. This practice worksheet provides the foundation for understanding not just ionic compounds but the broader landscape of chemical reactions and properties. Remember, the key to mastering chemistry lies in consistent practice, understanding, and applying fundamental principles.
What are the main differences between ionic and covalent bonding?

+
Ionic bonding involves the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions that attract each other. In contrast, covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms to form stable structures. Ionic bonds typically occur between metals and non-metals, while covalent bonds are found between non-metals.
How do you determine the charge of an ion?

+
The charge of an ion can often be determined by looking at its position in the periodic table. Elements in the same group (column) usually form ions with the same charge because they have the same number of valence electrons. For example, Group 1 elements form +1 ions, while Group 17 (halogens) form -1 ions.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?

+
Ionic compounds have high melting points because the ionic bonds between the oppositely charged ions are very strong. It requires a significant amount of energy to break these bonds, leading to high melting and boiling points.
How can I check if an ionic formula is correct?

+
To ensure an ionic formula is correct, check if the total positive charges of the cations balance with the total negative charges of the anions, resulting in a neutral compound. Also, verify if the ions used are common and appropriate for the elements involved.
Is there a difference in how ionic bonds are formed in different compounds?

+
Yes, while the basic mechanism of ionic bonding remains the same (transfer of electrons), different elements can form varying numbers of bonds due to their electron configurations. Additionally, the stability and properties of the resulting compounds can differ significantly based on the nature of the ions involved.