5 Essential Tips for Intermolecular Forces Worksheet Success

What are Intermolecular Forces?

Intermolecular forces (IMFs) are the attractive forces that exist between molecules. These forces are pivotal in determining various physical properties of substances, like their boiling points, melting points, and solubility. Understanding IMFs is crucial for students studying chemistry because these forces govern how molecules interact with each other in liquid and solid phases.

Tip 1: Understand the Different Types of Intermolecular Forces

To excel in your intermolecular forces worksheet, you need a solid understanding of the different types of IMFs. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- London Dispersion Forces: These are weak, temporary forces caused by the movement of electrons. They occur in all molecules but are the only significant forces in nonpolar molecules.
- Dipole-Dipole Forces: Found in polar molecules, these forces exist between the partial positive charge of one molecule and the partial negative charge of another. They are stronger than dispersion forces.
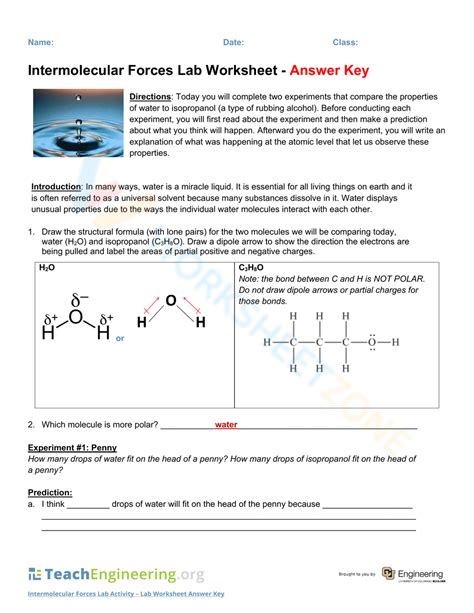
- Hydrogen Bonding: A special case of dipole-dipole interaction where hydrogen is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine. It significantly affects the properties of water and other biomolecules.
- Ion-Dipole Forces: These forces occur between an ion (like Na+) and the partial charges on a molecule (like H2O).
Tip 2: Relate Intermolecular Forces to Physical Properties
Recognizing how IMFs influence physical properties can simplify complex worksheet problems. Here’s what you should know:
- Boiling and Melting Points: Stronger IMFs generally lead to higher melting and boiling points because more energy is required to overcome the forces holding the molecules together.
- Solubility: “Like dissolves like.” Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes, and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes due to the intermolecular interactions.
- Viscosity: Substances with stronger IMFs often have higher viscosity due to the increased resistance to flow.
Tip 3: Use Comparative Analysis

Often, worksheets will ask you to compare different compounds. Here’s how:
- Compare the strength of different IMFs for a set of compounds. For example, which molecule, CH4 or H2O, would have a higher boiling point due to the presence of hydrogen bonding in water?
- Analyze how the molecular shape influences the IMFs. A linear molecule can have stronger dipole-dipole interactions than a bent one with the same composition.
- Evaluate the influence of molecular size and weight on dispersion forces.
Tip 4: Master the Calculations and Diagrams

Worksheets often include:
- Calculating the Strength of IMFs: You might need to estimate the force between two molecules. Use the equation: [ F_{IMF} = \frac{C \alpha_1 \alpha_2}{r^6} ] where C is a constant, α is the polarizability, and r is the distance.
- Drawing Potential Energy Diagrams: Illustrate the potential energy versus distance between molecules to show IMFs’ effect. These diagrams help visualize why molecules stay at certain distances from one another.
📌 Note: Remember that energy diagrams for dispersion forces will show a more gradual approach to the energy minimum than those for dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding due to the nature of these forces.
Tip 5: Practice, Practice, Practice

There’s no shortcut to mastery. Here are practical ways to improve:
- Previous Worksheets: Revisit old worksheets, even from peers, to gain more practice.
- Online Resources: Use educational websites, video tutorials, and quizzes to reinforce your knowledge.
- Group Study: Collaborate with others to solve problems, discussing different approaches to each question.
Wrapping up, understanding intermolecular forces not only helps in solving specific worksheet problems but also in grasping the bigger picture of chemical interactions. Remember, the key to success lies in a thorough understanding of the forces, their application to physical properties, comparative analysis, and practical problem-solving skills. Practice your understanding with a variety of examples and scenarios to master intermolecular forces worksheets effectively.
Why is understanding intermolecular forces important?

+
Intermolecular forces govern how molecules interact with each other, which affects a substance’s properties like boiling point, melting point, and solubility. Understanding these forces allows students to predict and explain various physical and chemical behaviors of substances.
How do intermolecular forces differ from intramolecular forces?

+
Intramolecular forces are the bonds that hold atoms together within a molecule (like covalent or ionic bonds). Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, are the attractions between different molecules, which are generally weaker than the intramolecular bonds.
Can you explain how to identify the presence of hydrogen bonding in a molecule?

+
Look for hydrogen atoms bonded directly to highly electronegative atoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine. If these conditions are met, there is a strong possibility of hydrogen bonding, which results in unique physical properties, such as unusually high boiling points and solubility in water.