5 Ways to Distinguish Inherited from Acquired Traits

Have you ever found yourself marveling at how much you resemble your parents, only to realize that it might not be just a matter of looks but perhaps something deeper? Or maybe you've noticed how certain characteristics or habits you possess seem to defy your genetic lineage? The distinction between inherited traits and acquired traits is fundamental in understanding both human biology and behavior. This article will guide you through the intriguing world of genetics and biology, exploring how we can differentiate between what we are born with and what we've acquired through life's journey.
The Basics of Inheritance
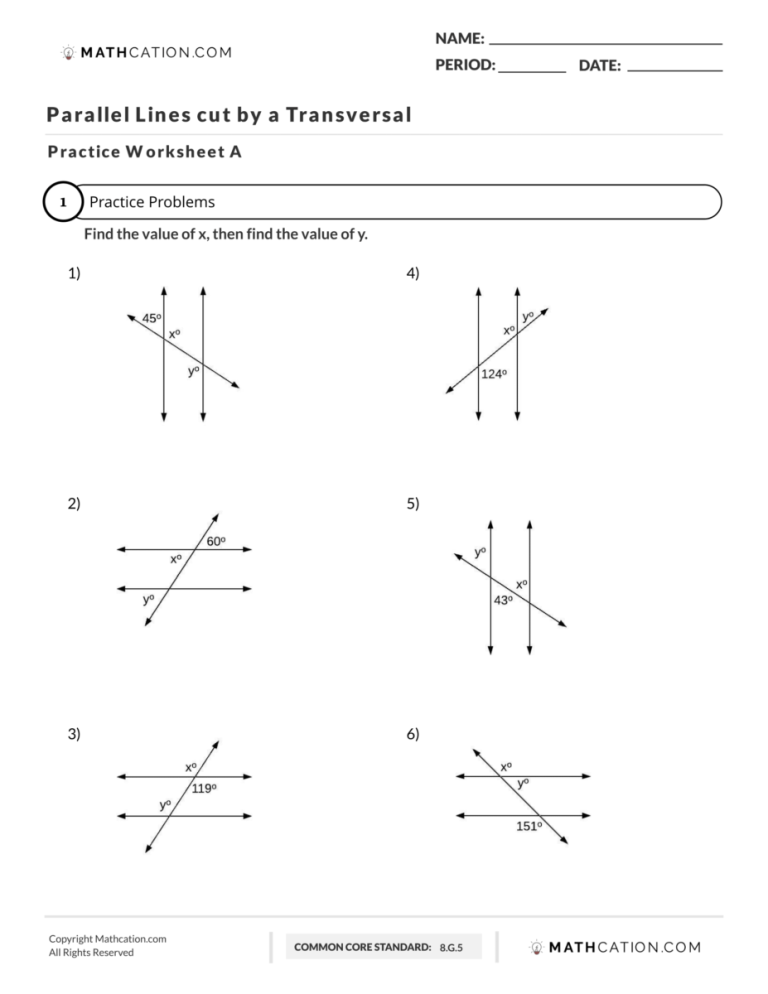
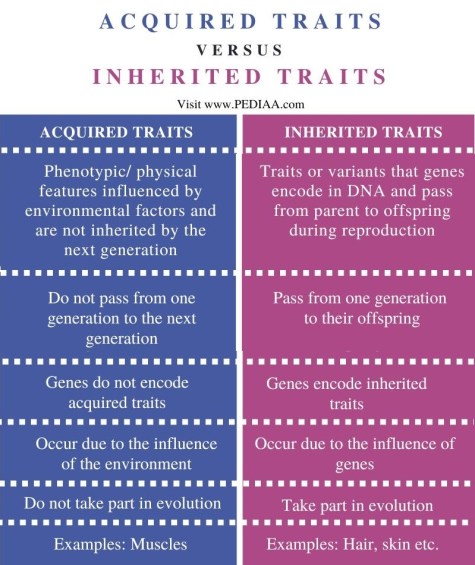
Before diving into the methods of distinguishing traits, let’s first understand what we mean by inherited traits. These traits are passed from one generation to the next through our genes. These genes, found in DNA, dictate physical appearances, metabolic processes, and even certain behaviors.
Inherited traits can be:
- Eye color
- Hair color and texture
- Height
- Blood type
- Skin pigmentation
- Genetic disorders (e.g., cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia)
The Nature of Acquired Traits

Contrasting with inherited traits are the traits we acquire over time due to environmental influences, personal choices, or unique experiences. Here's a list of some acquired traits:
- Language
- Skills (e.g., learning to play an instrument)
- Accents
- Dietary preferences
- Cultural behaviors
- Scars or tattoos
Method 1: Family History and Genealogy

One of the most straightforward ways to differentiate between inherited and acquired traits is by examining family history. Here's how:
- Review Family Trees: A family tree can visually represent the occurrence of traits through generations, helping identify which traits are familial.
- Conduct Interviews: Speak with older family members to uncover patterns of traits that have been consistently present in the family, thus distinguishing inherited traits from personal or environmental acquisitions.
📊 Note: Keep in mind that family history can be incomplete or inaccurate. Always cross-reference information with other methods to ensure accuracy.
Method 2: Genetic Testing
Advancements in genetics have made it easier to discern which traits are encoded in our DNA. Here are some genetic testing techniques:
- SNP Genotyping: This identifies single nucleotide polymorphisms, which can be linked to various traits.
- Sequencing: Full or targeted gene sequencing can reveal inherited mutations.
- Functional Tests: These might involve assays to measure the activity of enzymes or proteins produced by genes.
| Genetic Test | What it Reveals |
|---|---|
| SNP Genotyping | Variations in single nucleotides associated with traits |
| Whole Genome Sequencing | Comprehensive DNA analysis for all traits |
| Epigenetic Analysis | Changes in gene expression without changes to DNA sequence |
🔬 Note: Genetic testing is not a foolproof method. Some traits are influenced by multiple genes (polygenic), and environmental factors can affect gene expression.
Method 3: Twin Studies

Identical twins provide a natural experiment for distinguishing between inherited and acquired traits:
- Comparison: By comparing identical and fraternal twins, researchers can isolate genetic influence from environmental factors. If both twins share a trait, it’s likely inherited; if they differ, it might be acquired.
- Adoption: When identical twins are separated at birth, their acquired traits can differ significantly, offering insights into environmental influences.
Method 4: Phenotypic Variation

The study of how traits manifest in an organism’s appearance or behavior can also help in differentiation:
- Consistency: If a trait is consistent across different environments, it’s likely inherited.
- Variability: High variability in trait expression across different environments suggests an acquired trait.
- Twin and Sibling Studies: Siblings with similar genetics can show different trait expression due to environmental factors, indicating acquisition.
Method 5: Gene-Environment Interactions

Understanding how genes interact with the environment can provide profound insights:
- Epigenetics: DNA methylation and histone modification can silence or activate genes, influencing trait expression without altering the genetic code.
- Interaction Studies: By studying how environmental factors modify genetic expression, we can identify traits that are influenced by both genes and environment.
🔍 Note: Gene-environment interactions can be complex. For instance, some traits might be primarily inherited but can be significantly influenced by environmental conditions.
The journey to distinguish between inherited and acquired traits is both fascinating and enlightening, shedding light on the intricacies of human nature and biology. By employing a combination of family history analysis, genetic testing, twin studies, phenotypic observation, and gene-environment interaction research, we can begin to understand the complex tapestry of our traits. Whether it's the color of your eyes or your penchant for languages, understanding where these traits come from not only satisfies curiosity but also has implications for medicine, psychology, and personal identity.
Can an inherited trait be influenced by the environment?

+
Yes, traits that are genetically inherited can still be influenced by the environment through processes like epigenetics, where gene expression is modified without changing the DNA sequence.
How reliable are genetic tests in identifying traits?

+
Genetic tests are quite accurate for Mendelian traits that are controlled by single genes. However, for complex traits influenced by multiple genes and environment, they can provide only probabilistic predictions.
Why are identical twins important in trait studies?
+
Identical twins share nearly identical genetics, allowing researchers to control for genetic variables. By comparing them, especially if raised apart, we can determine the influence of environment on trait expression.
Are all physical traits inherited?

+
No, while many physical traits are genetically determined, environmental factors like diet, exercise, and exposure to sunlight can modify traits like body shape, muscle mass, and even skin pigmentation.