5 Easy Steps to Master the Ideal Gas Law

Understanding the Ideal Gas Law

The ideal gas law is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of an ideal gas. It is a crucial concept to grasp for students and professionals in various fields, including chemistry, physics, engineering, and materials science. Mastering the ideal gas law requires a thorough understanding of its components and how they interact. In this article, we will break down the ideal gas law into manageable parts and provide a step-by-step guide to help you master it.
Step 1: Understanding the Components of the Ideal Gas Law

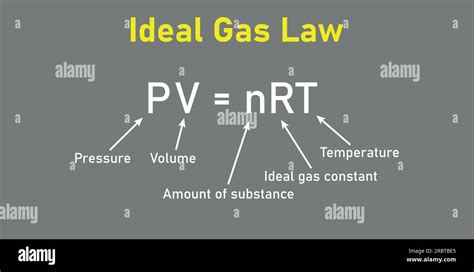
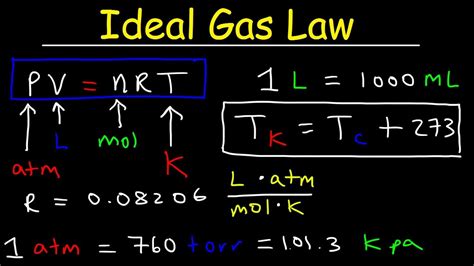
The ideal gas law is represented by the equation PV = nRT, where:
- P is the pressure of the gas
- V is the volume of the gas
- n is the number of moles of the gas
- R is the gas constant
- T is the temperature of the gas in Kelvin
It is essential to understand the units and definitions of each component:
- Pressure (P) is measured in units of pascals (Pa) or atmospheres (atm)
- Volume (V) is measured in units of cubic meters (m³) or liters (L)
- Number of moles (n) is a unitless quantity
- Gas constant ® is a constant that varies depending on the units used (8.3145 J/mol·K or 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)
- Temperature (T) is measured in units of Kelvin (K)
💡 Note: The gas constant (R) is not the same as the universal gas constant, which is a different value.
Step 2: Understanding the Relationships Between Components

The ideal gas law describes the relationships between the components:
- As the pressure (P) increases, the volume (V) decreases, and vice versa
- As the temperature (T) increases, the volume (V) increases, and vice versa
- As the number of moles (n) increases, the pressure (P) increases, and vice versa
These relationships can be visualized using a diagram or a graph:
| Pressure (P) | Volume (V) | Temperature (T) | Number of Moles (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
Step 3: Applying the Ideal Gas Law to Real-World Scenarios

The ideal gas law can be applied to various real-world scenarios, such as:
- Calculating the pressure of a gas in a container
- Determining the volume of a gas at a given temperature and pressure
- Finding the number of moles of a gas in a container
For example, if you know the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas, you can use the ideal gas law to calculate the number of moles:
n = PV / RT
Step 4: Solving Problems Using the Ideal Gas Law
To solve problems using the ideal gas law, follow these steps:
- Identify the given values and the unknown value
- Plug in the values into the ideal gas law equation
- Rearrange the equation to solve for the unknown value
- Check your units and ensure they are consistent
For example, if you are given the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas, and you need to find the number of moles, you can use the following steps:
- Given values: P = 2 atm, V = 10 L, T = 300 K
- Plug in values: n = (2 atm × 10 L) / (0.0821 L·atm/mol·K × 300 K)
- Rearrange equation: n = 0.8 mol
- Check units: n = 0.8 mol (consistent units)
Step 5: Practicing and Mastering the Ideal Gas Law

To master the ideal gas law, practice solving problems and applying it to real-world scenarios. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones. Use online resources, textbooks, and worksheets to practice.
Additionally, try to:
- Derive the ideal gas law from the kinetic theory of gases
- Use the ideal gas law to solve problems involving mixtures of gases
- Apply the ideal gas law to real-world scenarios, such as weather forecasting and industrial processes
By following these steps and practicing regularly, you will become proficient in applying the ideal gas law and be able to solve a wide range of problems.
In summary, mastering the ideal gas law requires a thorough understanding of its components, relationships, and applications. By breaking down the concept into manageable parts and practicing regularly, you can become proficient in applying the ideal gas law to real-world scenarios.
What is the ideal gas law?

+
The ideal gas law is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of an ideal gas.
What are the components of the ideal gas law?

+
The components of the ideal gas law are pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), gas constant ®, and temperature (T).
How do I apply the ideal gas law to real-world scenarios?
+
The ideal gas law can be applied to various real-world scenarios, such as calculating the pressure of a gas in a container, determining the volume of a gas at a given temperature and pressure, and finding the number of moles of a gas in a container.
Related Terms:
- Ideal gas Law Worksheet pdf
- ideal gas law word problems
- ideal gas law sample problems
- solving ideal gas law problems
- ideal gas law example problems
- ideal gas law practice problems