How Airspeed Indicators Work in Aviation
Understanding the Basics of Airspeed Indicators

Airspeed indicators are a crucial component of an aircraft’s instrument panel, providing pilots with vital information about the aircraft’s speed. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of airspeed indicators, exploring their history, functionality, and importance in aviation.
A Brief History of Airspeed Indicators

The concept of airspeed indicators dates back to the early days of aviation. In the 1900s, pilots relied on primitive instruments, such as anemometers, to estimate their airspeed. However, these early instruments were inaccurate and unreliable. It wasn’t until the 1920s that the first airspeed indicators were developed, using a pitot-static system to measure airspeed.
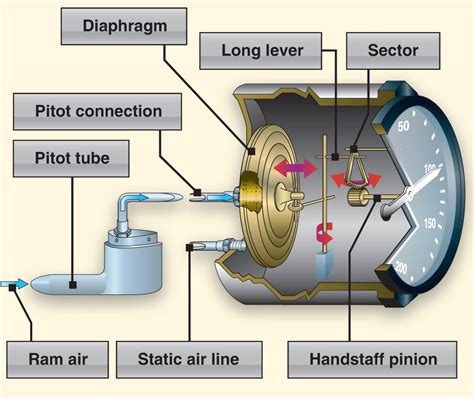
How Airspeed Indicators Work

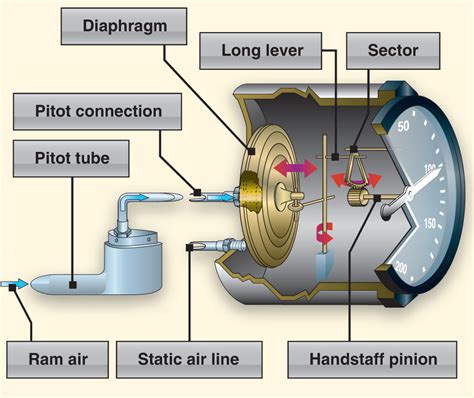
Airspeed indicators measure the difference in air pressure between the pitot tube and the static ports. The pitot tube, located on the wing or fuselage, faces into the oncoming airflow and measures the total air pressure. The static ports, usually located on the side of the fuselage, measure the static air pressure.
The airspeed indicator uses this pressure difference to calculate the aircraft’s airspeed. The indicator is typically connected to a mechanical or electronic system that converts the pressure readings into a visual display of airspeed.
Components of an Airspeed Indicator

A typical airspeed indicator consists of the following components:
- Pitot tube: Measures the total air pressure
- Static ports: Measures the static air pressure
- Airspeed indicator: Displays the calculated airspeed
- Mechanical or electronic system: Converts pressure readings into a visual display
Types of Airspeed Indicators

There are two primary types of airspeed indicators:
- Mechanical airspeed indicators: Use a mechanical system to convert pressure readings into a visual display
- Electronic airspeed indicators: Use electronic sensors and computers to calculate and display airspeed
Importance of Airspeed Indicators in Aviation
Airspeed indicators play a critical role in aviation, providing pilots with essential information about their aircraft’s speed. This information is used to:
- Maintain safe flight speeds: Avoiding stalls, spins, and other hazardous flight regimes
- Optimize aircraft performance: Achieving efficient climb and cruise speeds
- Ensure safe landing: Maintaining a stable approach speed
💡 Note: Airspeed indicators are not the same as ground speed indicators. Airspeed indicators measure the aircraft's speed relative to the air, while ground speed indicators measure the aircraft's speed relative to the ground.
Common Issues with Airspeed Indicators
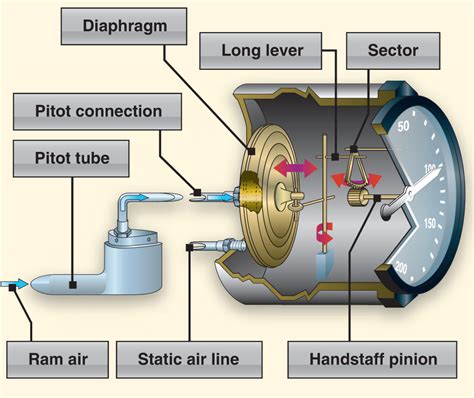
Airspeed indicators can be prone to errors and malfunctions, which can have serious consequences. Some common issues include:
- Pitot tube blockage: Debris or ice can block the pitot tube, causing inaccurate readings
- Static port blockage: Debris or ice can block the static ports, causing inaccurate readings
- Instrument failure: Mechanical or electronic failures can cause the airspeed indicator to malfunction
🚨 Note: Regular maintenance and inspection of airspeed indicators are crucial to ensure accurate readings and safe flight operations.
Modern Developments in Airspeed Indicators

Advances in technology have led to the development of more accurate and reliable airspeed indicators. Some modern developments include:
- Digital airspeed indicators: Using electronic sensors and computers to calculate and display airspeed
- GPS-based airspeed indicators: Using GPS data to calculate airspeed
- Angle of attack indicators: Providing pilots with information about the aircraft’s angle of attack
Conclusion
Airspeed indicators are a vital component of an aircraft’s instrument panel, providing pilots with essential information about their aircraft’s speed. Understanding how airspeed indicators work and their importance in aviation is crucial for safe and efficient flight operations. By recognizing common issues and staying up-to-date with modern developments, pilots can ensure accurate and reliable airspeed readings.
What is the difference between airspeed and ground speed?

+
Airspeed is the speed of the aircraft relative to the air, while ground speed is the speed of the aircraft relative to the ground.
How do airspeed indicators measure airspeed?

+
Airspeed indicators measure the difference in air pressure between the pitot tube and the static ports to calculate airspeed.
What are some common issues with airspeed indicators?

+
Common issues include pitot tube blockage, static port blockage, and instrument failure.
Related Terms:
- Air speed indicator in aircraft
- Vertical speed Indicator
- Airspeed indicator Limitations
- How to read airspeed indicator
- Airspeed indicator possible errors
- How does the VSI work