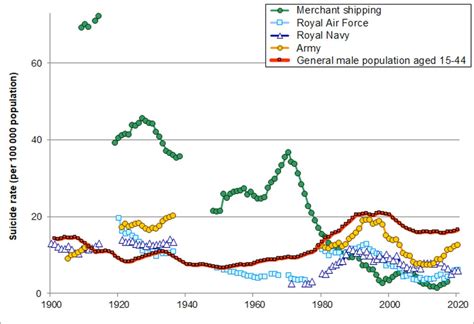
Military
Highest Occupation Suicide Rates Revealed
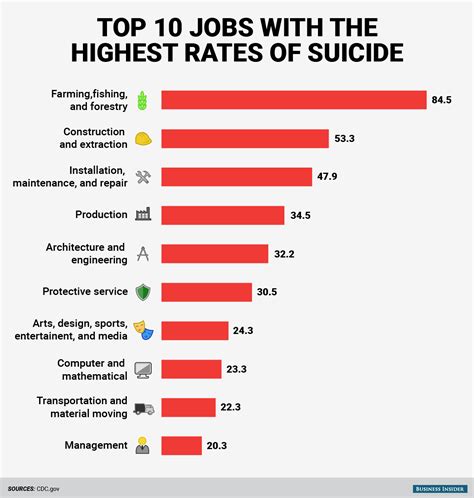
Introduction to Occupation and Suicide Rates

The relationship between occupation and suicide rates is a complex one, influenced by a myriad of factors including work-related stress, exposure to traumatic events, and access to means of suicide. Various studies have aimed to uncover which occupations have the highest suicide rates, providing insights into the mental health challenges faced by different professional groups. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing targeted interventions and support systems to mitigate the risk of suicide among workers in high-risk occupations.
Factors Influencing Suicide Rates in Occupations

Several factors contribute to the elevated suicide rates in certain occupations. These include: - Work-Related Stress: Jobs with high levels of stress, long working hours, and tight deadlines can contribute to mental health issues. - Exposure to Trauma: Professions that involve regular exposure to traumatic or disturbing events, such as healthcare workers dealing with COVID-19 patients or military personnel, can have a profound psychological impact. - Access to Means: Certain occupations provide easier access to means of suicide, such as firearms for military personnel or medications for healthcare workers. - Social Isolation: Jobs that require extensive travel or irregular schedules can lead to social isolation, further exacerbating mental health problems. - Stigma and Culture: The culture within some professions may discourage seeking help for mental health issues, perpetuating a stigma around discussing psychological struggles.
Occupations with High Suicide Rates
Research has identified several occupations with notably high suicide rates. These include: - Farmers and Agricultural Workers: The isolation, financial pressures, and access to lethal means contribute to high suicide rates in this group. - Veterinarians: The high stress of the job, combined with access to euthanasia drugs, places veterinarians at a higher risk. - Medical Doctors and Healthcare Professionals: The long hours, high stress, and exposure to traumatic situations can take a significant toll on mental health. - Military Personnel: The unique stresses of military life, including combat exposure and the culture of toughness, can increase the risk of suicide. - Construction and Extraction Workers: Jobs in this sector often involve high physical demands, stress, and sometimes, easy access to means of suicide.
🚨 Note: These occupations are not the only ones at risk, and suicide can affect anyone regardless of their profession. It's essential to approach the topic with sensitivity and understanding.
Support and Prevention Strategies

To address the high suicide rates in these occupations, several strategies can be employed: - Mental Health Training and Awareness: Educating workers about mental health issues, reducing stigma, and promoting a culture of support. - Access to Mental Health Services: Ensuring that workers have easy access to confidential mental health services and support. - Workplace Interventions: Implementing policies to reduce work-related stress, such as flexible working hours, workload management, and employee wellness programs. - Peer Support Programs: Establishing programs where workers can support each other, sharing experiences and advice. - Community and Family Support: Involving families and communities in support networks to provide a broader safety net.
Future Directions and Research

Continued research into the specific challenges faced by different occupations is crucial. This includes: - Occupation-Specific Studies: Conducting in-depth studies to understand the unique factors contributing to suicide risk in each profession. - Development of Targeted Interventions: Creating support programs tailored to the specific needs and challenges of different occupational groups. - Policy Changes: Advocating for policy changes that address work-related stress, access to means, and mental health support in high-risk occupations.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

The issue of high suicide rates among certain occupations is multifaceted and demands a comprehensive approach. By understanding the factors that contribute to these elevated rates and implementing targeted support and prevention strategies, we can work towards reducing the incidence of suicide among workers in high-risk professions. It’s a collective responsibility that requires the involvement of employers, policymakers, mental health professionals, and the community at large to create a supportive environment that prioritizes workers’ mental health and well-being.
What are the most common factors contributing to high suicide rates in occupations?

+
Work-related stress, exposure to traumatic events, access to means of suicide, social isolation, and the stigma around seeking mental health help are common factors.
Which occupations have been identified as having high suicide rates?

+
Farmers and agricultural workers, veterinarians, medical doctors and healthcare professionals, military personnel, and construction and extraction workers are among those identified.
What strategies can be employed to support and prevent suicide in high-risk occupations?
+
Mental health training and awareness, access to mental health services, workplace interventions, peer support programs, and community and family support are crucial strategies.



