5 Tips to Understand Global Wind Patterns Easily

Discover the Dynamics of Global Winds
Have you ever wondered what drives the consistent movement of air across the Earth? Wind patterns are fundamental to climate, weather, and even navigation at sea. Understanding these patterns is not only intriguing but also essential for various applications, from aviation to energy production. Here's a comprehensive guide to make the complex world of global wind patterns accessible and easy to grasp.
1. The Basics of Atmospheric Circulation

The Earth's atmosphere is in constant motion, driven by several factors:
- Solar Radiation: The sun heats the Earth unevenly, causing variations in air temperature and pressure.
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth's rotation deflects wind patterns to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Pressure Differences: Air moves from areas of high pressure to low pressure, creating wind.

2. Trade Winds and the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
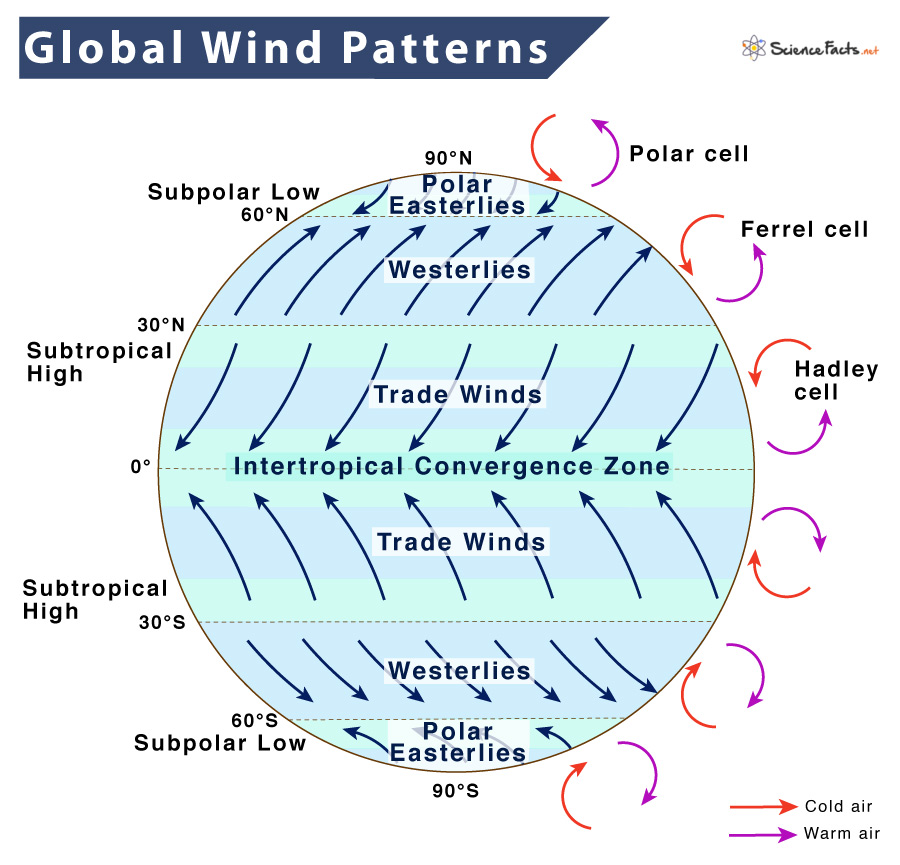
The ITCZ is where the trade winds from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres meet, often resulting in heavy rain and thunderstorms:
- Northeast Trade Winds in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Southeast Trade Winds in the Southern Hemisphere.
These winds are consistent and have been utilized by sailors for centuries for efficient navigation.
ITCZ Notes
🌍 Note: The ITCZ moves north and south with the seasons, following the sun’s zenith.
3. The Westerlies and Polar Easterlies

Beyond the tropics, we have the:
- Westerlies: Blow from the west in the mid-latitudes, impacting Western Europe with a milder climate than corresponding latitudes.
- Polar Easterlies: Cold, dry winds blowing out from the polar highs toward the west.

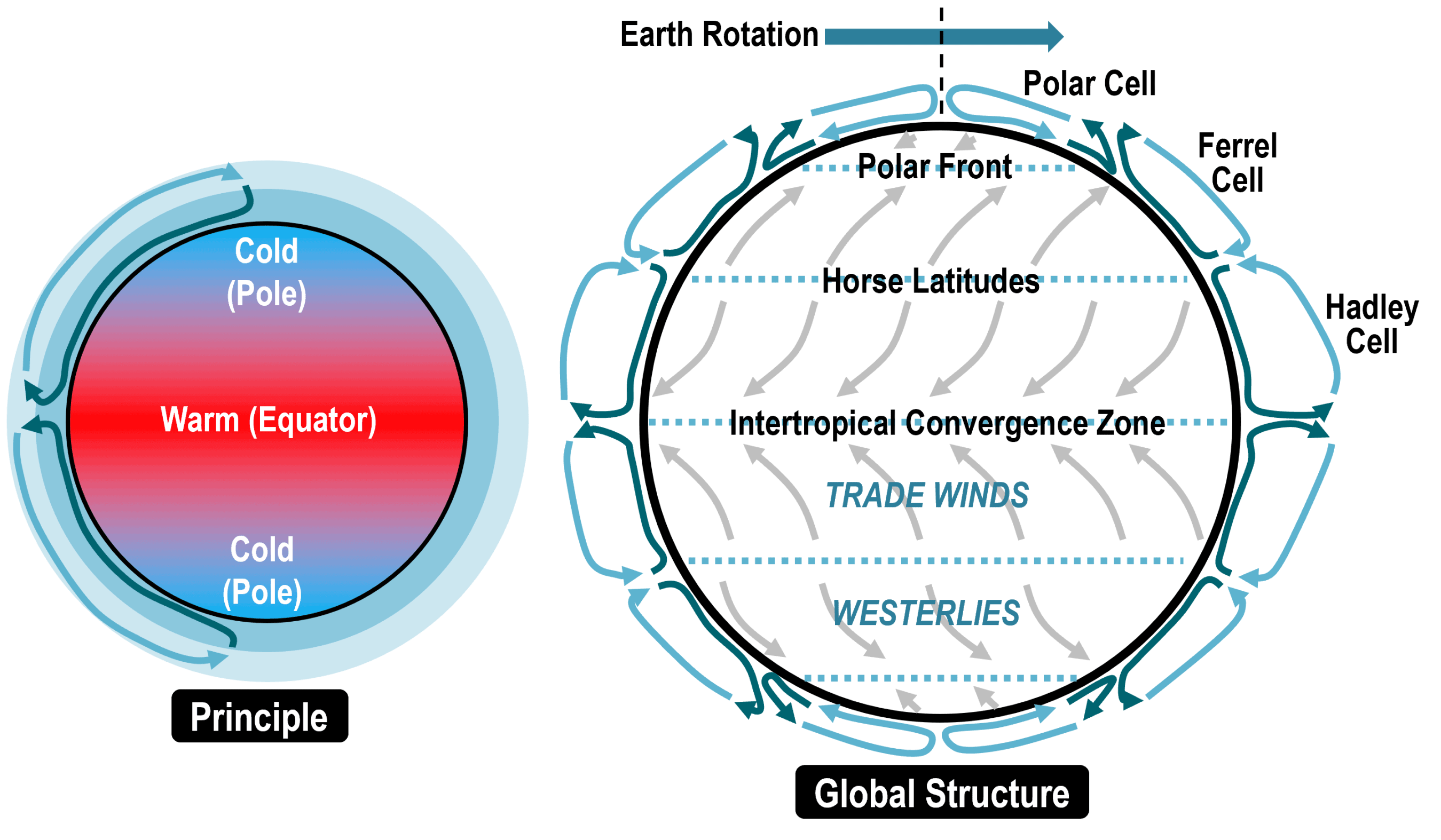
4. The Hadley, Ferrel, and Polar Cells

The Earth's atmosphere circulation is divided into three main cells in each hemisphere:
| Cell | Description |
|---|---|
| Hadley Cell | Heat rises at the equator, moves to about 30° latitude, and sinks back to the ground. |
| Ferrel Cell | Located between the Hadley and Polar Cells, this is where westerlies are created. |
| Polar Cell | At the poles, cold air sinks, moves to about 60° latitude, and ascends. |

🔹 Note: The interactions between these cells produce jet streams, which are narrow, fast-flowing currents of wind that significantly influence weather patterns.
5. The Role of Terrain and Oceans

Mountains, coastlines, and ocean currents also affect wind patterns:
- Mountain Ranges: They can block wind flows, leading to regions like rain shadows with less precipitation.
- Ocean Currents: Warm currents can bring moist air leading to precipitation, while cold currents might stabilize air masses.
Here’s a quick summary of how these elements shape wind patterns:
| Feature | Effect on Wind |
|---|---|
| Mountains | Create orographic lift or barriers to wind |
| Oceans | Modify air temperatures and moisture content |
🌊 Note: Ocean currents are especially influential in areas where they interact with jet streams, often resulting in major weather events.
By simplifying these complex wind patterns, we've covered the essentials that can help you better comprehend global atmospheric dynamics. From understanding how trade winds facilitate sailing to recognizing the impact of ocean currents on local weather, this guide provides a foundation for anyone interested in meteorology or related fields.
The intricate dance of winds around the Earth not only shapes our climate but also plays a critical role in numerous ecological, industrial, and cultural aspects of life. With this understanding, you'll be better equipped to interpret weather reports, navigate ocean voyages, or even harness wind for energy.
Remember that while these patterns have general predictability, local variations and anomalies can still occur due to numerous factors, making each weather event unique. Whether for professional purposes or pure curiosity, delving into wind patterns will enrich your appreciation for the natural world and its complex systems.
What causes wind to blow?

+
Wind is caused by pressure differences within the atmosphere due to uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. Air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
How does the Coriolis effect influence wind patterns?
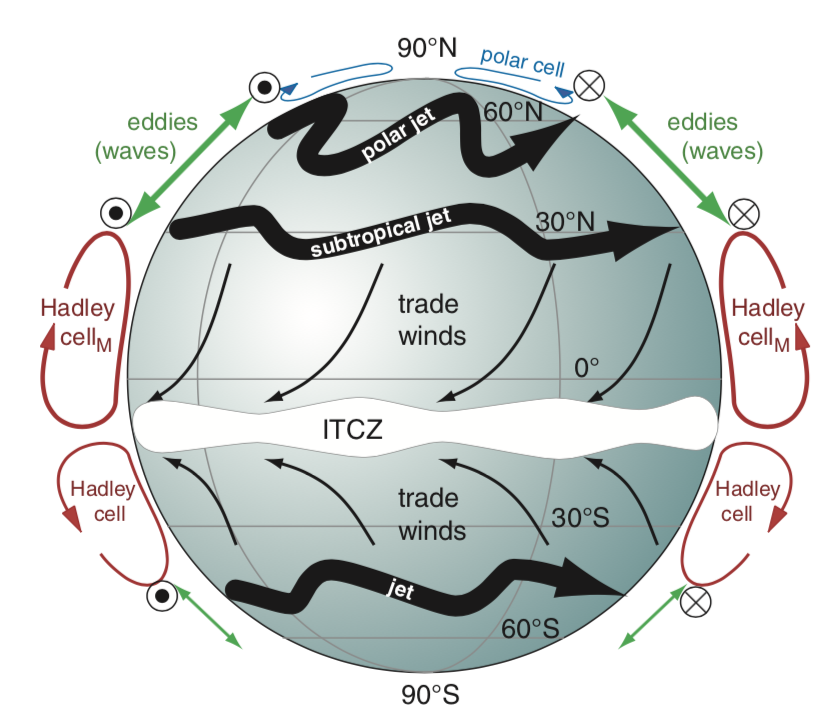
+
The Coriolis effect is due to the Earth’s rotation, which deflects moving objects (like wind) to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere, shaping global wind patterns.
Why are trade winds important for sailing?
+
Trade winds are consistent and blow from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere. These predictable winds have historically facilitated long-distance sailing and navigation.



