Genetics Basics Worksheet Answers Revealed: Master the Fundamentals

Understanding genetics can be both fascinating and challenging. For students diving into the world of molecular biology, mastering genetics basics is foundational to progress in biology and related fields. Today, we'll delve into some of the fundamental concepts through a common genetics worksheet, providing detailed answers and explanations to help you grasp these vital principles.
What are Genes?

Genes are segments of DNA that encode the blueprint for proteins, influencing traits from eye color to susceptibility to diseases. Here's a quick rundown:
- Genes: Made up of DNA, they carry genetic information.
- Alleles: Different versions of a gene, often responsible for variations in traits.
- Locus: The specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
Mendelian Inheritance

Gregor Mendel's pea plant experiments laid the groundwork for our understanding of inheritance. His key findings include:
- Principle of Segregation: Alleles segregate during gamete formation so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
- Principle of Independent Assortment: Genes for different traits segregate independently during gamete formation.
Worksheet Question:

What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous?
Answer:
- Homozygous: When an organism has two identical alleles for a particular gene, like AA or aa.
- Heterozygous: When an organism carries two different alleles for a gene, like Aa.
🔬 Note: Homozygous traits are often pure-breeding, while heterozygous traits can result in an organism that shows a dominant trait but can pass on a recessive trait.
Genetic Crossing and Punnett Squares
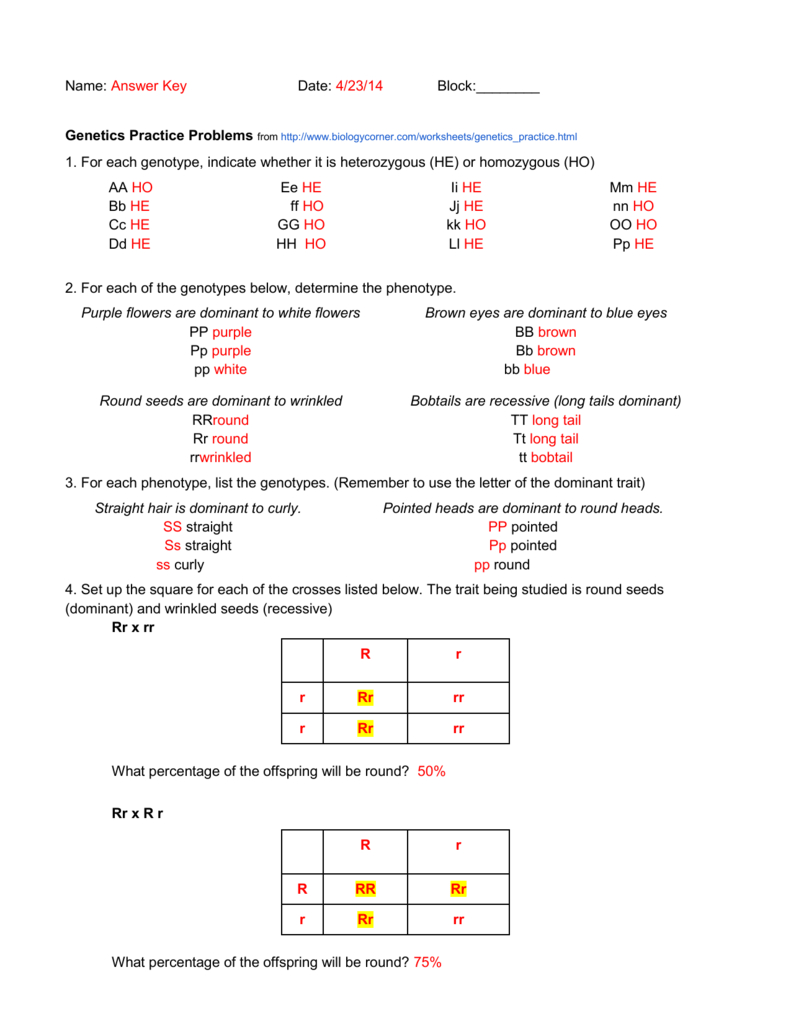
To predict the outcomes of genetic crosses, geneticists often use Punnett squares:
| Parent 1 | A | a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parent 2 | A | AA | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa |

Here's how to interpret this:
- If both parents are heterozygous (Aa), there's a 25% chance of each offspring being AA, Aa, or aa.
- This example shows a monohybrid cross, where a single trait is being considered.
Worksheet Question:

What are the probabilities of offspring phenotypes if both parents are heterozygous for a given trait?
Answer:
- 50% of the offspring will show the dominant phenotype (AA and Aa).
- 50% will have the recessive phenotype (aa).
Gene Linkage

Not all genes assort independently. When genes are linked, they tend to be inherited together because they are located on the same chromosome. Here's what you need to know:
- Linkage Groups: Genes that are physically close on a chromosome can travel together during meiosis.
- Recombination: Occasionally, linked genes can be separated due to crossing over, which increases genetic diversity.
🧬 Note: Recombination frequency is used to map the distance between genes on a chromosome.
Genetic Mutations

Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. They can be:
- Point Mutations: Substitution of a single base pair.
- Frameshift Mutations: Insertion or deletion altering the reading frame.
- Chromosomal Mutations: Changes in chromosome structure or number.
Worksheet Question:

Explain what a frameshift mutation is and its potential effects.
Answer: A frameshift mutation is when nucleotides are added or removed from a gene, shifting the reading frame from the point of the mutation. This can:
- Change every amino acid after the mutation in the resulting protein.
- Potentially lead to nonfunctional proteins or early termination signals, often resulting in genetic disorders or diseases.
Genotype and Phenotype

Your genotype is the set of genes you carry, while phenotype refers to the physical or biochemical characteristics you display:
- Genotype determines what alleles an organism has for a specific gene.
- Phenotype is influenced by genotype, environment, and gene expression.
Worksheet Question:

How does incomplete dominance differ from co-dominance?
Answer:
- Incomplete Dominance: The heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes, like blending.
- Co-dominance: Both alleles are expressed simultaneously without blending, like the AB blood type.
🔍 Note: Understanding these differences helps in predicting complex traits in offspring.
From genes to inheritance, mutations to gene expression, genetics is a multifaceted field that explains life at its core. By dissecting common genetics worksheets and answering fundamental questions, we've navigated through some of the crucial aspects of genetics. This journey is not just about mastering scientific principles; it's about unlocking the secrets of life, understanding heredity, and appreciating the diversity of life forms. The principles you've learned here are stepping stones towards more complex genetic topics, from genetic engineering to evolutionary biology. Keep exploring, and the world of genetics will continue to unveil its wonders to you.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?

+
A Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It allows one to determine the probabilities of producing different offspring genotypes given the genotypes of the parents.
How do linked genes influence inheritance patterns?

+
Linked genes are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together unless they are separated by crossing over. This means they do not follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment, and they influence inheritance patterns by causing traits to be inherited in groups rather than independently.
Why are genetic mutations important in biology?

+
Genetic mutations are crucial because they introduce variability into the gene pool. They can lead to evolutionary change, drive species adaptation, and are responsible for both genetic diversity and genetic disorders. Mutations can also play a role in cancer development when cells accumulate mutations that disrupt normal regulatory mechanisms.



