5 Insights from Food Inc: Movie Worksheet Guide

In "Food Inc.," filmmakers Robert Kenner and Eric Schlosser explore the untold truths of America's corporate food industry. This documentary reveals a world where food is mass-produced, often at the expense of health, safety, and ethical considerations. Here, we dive into five key insights from "Food Inc." to understand what's on your plate and why it matters.
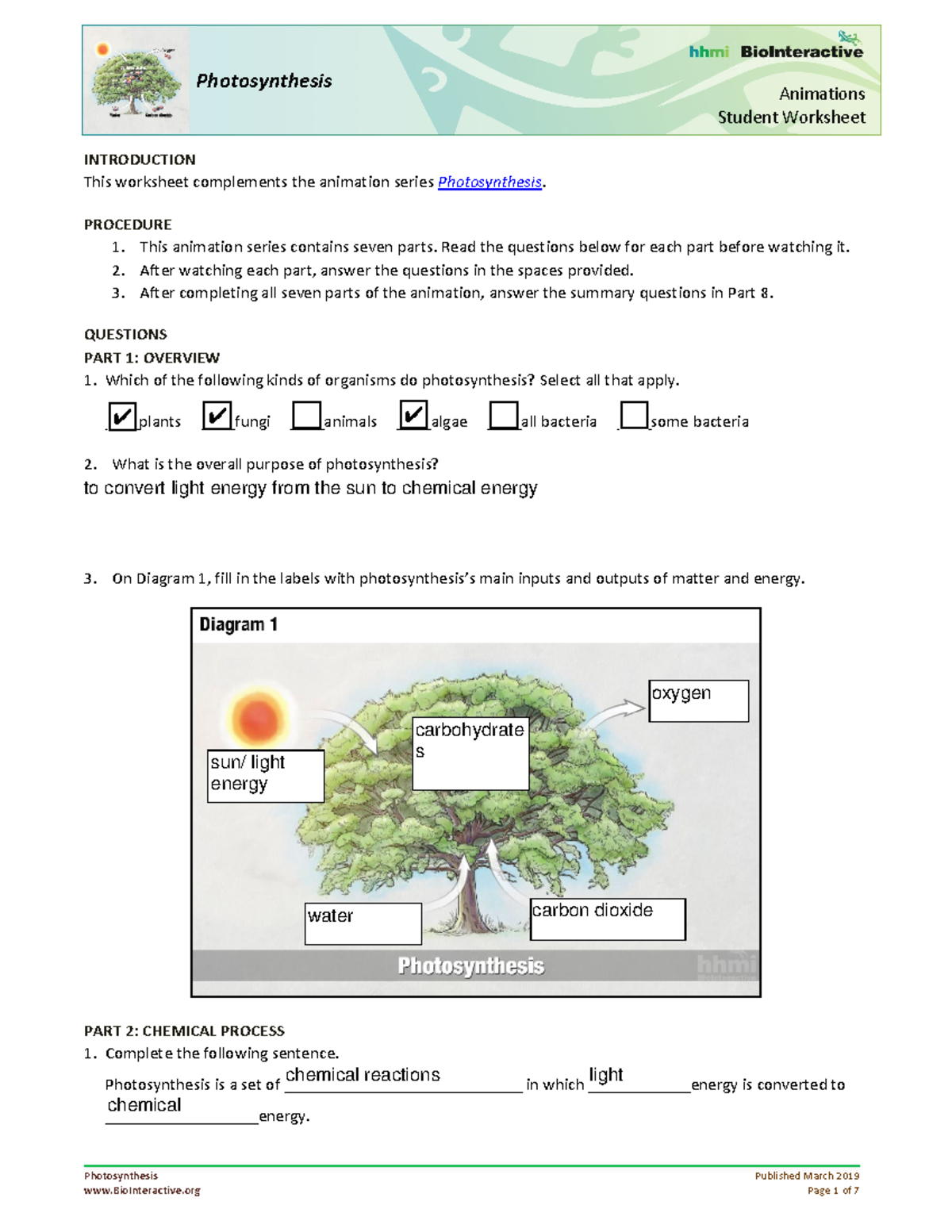
The Illusion of Choice

“Food Inc.” shatters the illusion of variety in supermarkets. What seems like a cornucopia of choices is often controlled by a handful of conglomerates:
- Brands Owned by Megacorporations: A single company might own numerous popular food brands, creating an appearance of diversity.
- Standardization: Products are similar in content regardless of brand, due to efficiency and cost considerations.
💡 Note: Next time you shop, look closely at the brands; you might discover they are owned by the same parent company.
Fast Food’s Influence on Agriculture

The documentary elucidates how fast-food chains like McDonald’s have significantly impacted agriculture:
- Demand for Cheap Ingredients: Fast food demands cheap, uniform ingredients, which forces farmers to adopt unsustainable practices.
- Monoculture: The need for scale leads to monocultures of corn, soy, and wheat, drastically reducing biodiversity.
| Farm Practice | Impact |
|---|---|
| Monoculture | Reduces biodiversity, soil health, and susceptibility to disease |
| CAFOs (Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations) | Increased antibiotic use, environmental pollution |

Worker Rights and Livestock Treatment

The treatment of both workers and livestock in the food industry is highlighted:
- Working Conditions: Workers often face unsafe working environments, low pay, and no job security.
- Livestock Treatment: Animals are raised in cramped, unhygienic conditions, often treated with hormones and antibiotics to hasten growth.
The Perils of Hidden Ingredients

“Food Inc.” addresses the issue of hidden or misleading ingredients:
- Sugar and High-Fructose Corn Syrup: These sweeteners are found in an array of products, contributing to health issues.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): The film explores the contentious debate around GMOs and their effects on our food system.
- Food Additives: Colorings, preservatives, and other chemical additives can make cheap food seem fresh and appealing.
📝 Note: Pay attention to the ingredients list on packaged foods to understand what you’re consuming.
The Power of Consumer Choice

“Food Inc.” concludes with a call to action, emphasizing how consumer power can drive change:
- Support Local and Organic: Choosing local and organic products supports sustainable farming practices.
- Advocate for Labeling: Knowing where your food comes from through better labeling helps in making informed choices.
- Policy Advocacy: Engaging in or supporting policies that promote ethical farming and food practices.
Ultimately, "Food Inc." sheds light on the intricacies of the food industry, exposing the consequences of a system driven by profit over people and the planet. From the illusion of choice to the hidden dangers in our food, this movie challenges us to reconsider our relationship with what we eat. It advocates for transparency, accountability, and a return to sustainable practices that can benefit our health, the environment, and the quality of life for all involved in the food production chain.
What is CAFO, and why is it controversial?

+
CAFO stands for Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation. It’s controversial because these facilities prioritize efficiency, leading to poor animal welfare, environmental pollution, and increased antibiotic use.
How can consumers find out if their food contains GMOs?

+
Consumers can look for the Non-GMO Project Verified seal or choose certified organic products, which by law cannot contain GMOs.
Why is local food important?

+
Local food reduces the carbon footprint of your food, supports local farmers, and often offers fresher, seasonal produce with traceability.
How can policy change help improve the food system?

+
Policy changes can mandate better labeling, regulate the use of antibiotics in farming, and support sustainable agricultural practices to address systemic issues highlighted in “Food Inc.”