5 Essential Answers for Food Chains and Webs Worksheet

Understanding the dynamics of food chains and webs is crucial for comprehending how ecosystems function. For students and nature enthusiasts alike, food chains and webs provide a window into the intricate relationships between different organisms within a habitat. This article will guide you through five essential answers that you might encounter in a food chain and webs worksheet, enhancing your understanding of these ecological concepts.
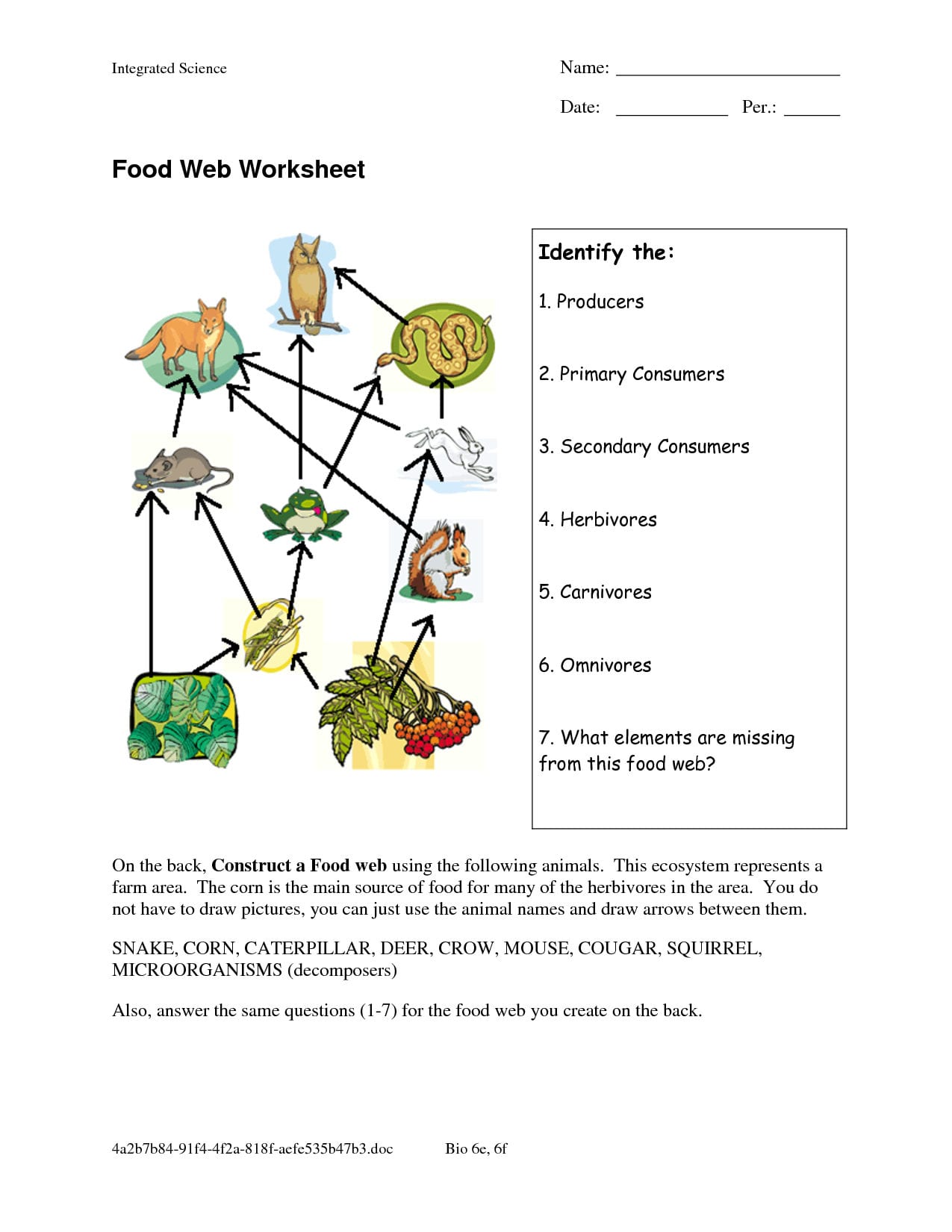
What are Food Chains and Food Webs?

Food chains represent the feeding relationships in an ecosystem. Each link in a food chain is made up of species that eat one another:
- Producers, like plants, are the first level. They convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers are herbivores, eating plants.
- Secondary Consumers eat the primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers are typically at the top of the chain, eating secondary consumers.
Food webs, on the other hand, offer a more complex view, illustrating the multiple interactions between different food chains in an ecosystem:
- It shows how species are interconnected through feeding relations, allowing for a more accurate depiction of natural food sources.
Why are Food Chains and Webs Important?

Food chains and webs are vital for several reasons:
- Ecosystem Stability: They show the balance of nature, where each species has a role in maintaining ecosystem health.
- Energy Transfer: They demonstrate how energy flows through trophic levels, with less energy available at each higher level due to inefficiencies in energy transfer.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Understanding these relationships helps in conservation efforts by highlighting the interdependence of species.

How to Create a Food Chain or Web?

Here are the steps to build a simple food chain or web:
- Identify the Organisms: Determine the key species in the ecosystem.
- Determine Feeding Relationships: Understand who eats whom.
- Construct the Chain: Arrange organisms in a linear sequence for a food chain, starting with producers.
- Add Complexity for a Web: Link multiple food chains together to form a web, showing overlap and connections.
What Happens if a Species Disappears?

If a species in a food chain or web becomes extinct or significantly declines:
- Ecosystem Imbalance: The loss of a species can lead to an overpopulation of its prey or starvation of its predators, causing cascading effects.
- Reduced Biodiversity: The loss of one species can lead to the decline of others, reducing biodiversity.
- Competition Changes: Remaining species might compete more intensely for the vacant ecological niche.
How do Humans Impact Food Chains and Webs?
Human activities have profound effects on food chains and webs:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture alter habitats, changing the dynamics of food sources.
- Pollution: Contaminants enter the food web, biomagnifying as they move up the chain, often with detrimental effects on top predators.
- Introduction of Non-native Species: Invasive species can disrupt existing relationships by competing with native species or preying on them.
- Climate Change: Altering temperatures and precipitation patterns impacts where species can live, feed, and breed, fundamentally changing food webs.
By exploring these essential answers, you gain a deeper insight into how food chains and webs work, their importance, and the significant impact humans have on these delicate systems. Understanding these concepts is not just academic; it's critical for ecological conservation and sustainable living, ensuring that the balance of nature is maintained for generations to come.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?

+
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each one is eaten by the next, starting with producers. A food web, however, is a network of many interconnected food chains, providing a more realistic representation of feeding relationships in an ecosystem.
Why is it important to understand food chains and webs?

+
Understanding food chains and webs helps us see the flow of energy, how species interactions maintain ecological balance, and informs conservation efforts to prevent biodiversity loss.
Can changes in one part of the food web affect the entire ecosystem?

+
Yes, changes in one species can have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem due to interconnected food relationships. This is known as a trophic cascade.
How can human activities disrupt food chains and webs?

+
Human activities like pollution, habitat destruction, climate change, and introduction of invasive species can significantly alter or destroy food chains and webs, often leading to ecosystem imbalance.
What role do humans play in food chains and webs?

+
Humans act as top predators in many food chains, but also as ecosystem engineers, influencing food webs through land use, agriculture, and other activities that alter natural environments.



