Mastering Food Chains and Energy Pyramids Worksheet

In the study of ecology, understanding the flow of energy through an ecosystem is essential for students, researchers, and anyone interested in environmental science. Key concepts such as food chains and energy pyramids are foundational for this understanding. This blog post delves into how to master these concepts through focused worksheets, offering insights into how they work and their importance in the larger context of ecosystem dynamics.
Understanding Food Chains

At the heart of any ecosystem lies the food chain, a linear sequence showing how energy transfers from one organism to another. Here’s how to dissect and learn from a food chain worksheet:
- Identify the Trophic Levels: Each level in a food chain represents a trophic level, starting with primary producers like plants, which capture solar energy through photosynthesis.
- Trace Energy Flow: Energy moves up the food chain as consumers feed on lower trophic levels. Understanding this transfer helps in recognizing the energy pyramid concept later.
- Recognize Key Organisms: Distinguish between producers, primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers, as well as decomposers. Each plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
Components of a Food Chain

A typical food chain might look like this:
| Trophic Level | Example Organisms |
|---|---|
| Producers | Grasses, algae |
| Primary Consumers | Herbivores like rabbits, insects |
| Secondary Consumers | Carnivores, omnivores like birds, foxes |
| Tertiary Consumers | Top predators like wolves, eagles |
| Decomposers | Fungi, bacteria |
🍃 Note: Not all food chains have all these levels; some ecosystems might have fewer or more trophic levels.
Energy Pyramids

While food chains illustrate how energy moves through an ecosystem, energy pyramids provide a visual representation of this transfer in terms of energy content at each level:
- Biomass Pyramid: Reflects the mass of living material at each trophic level.
- Numbers Pyramid: Shows the number of organisms at each level.
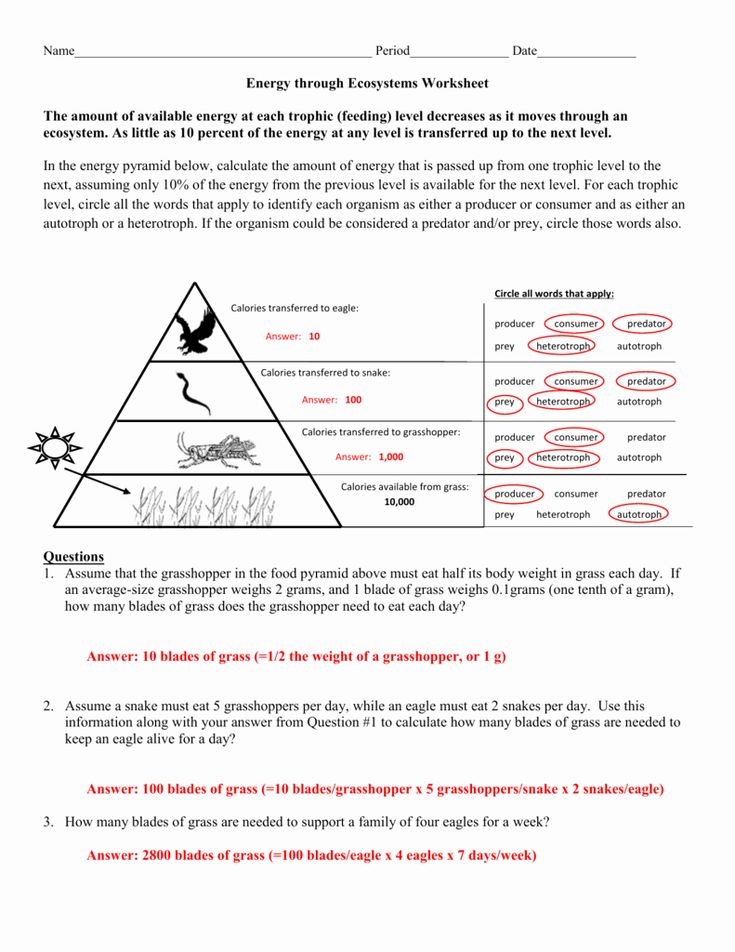
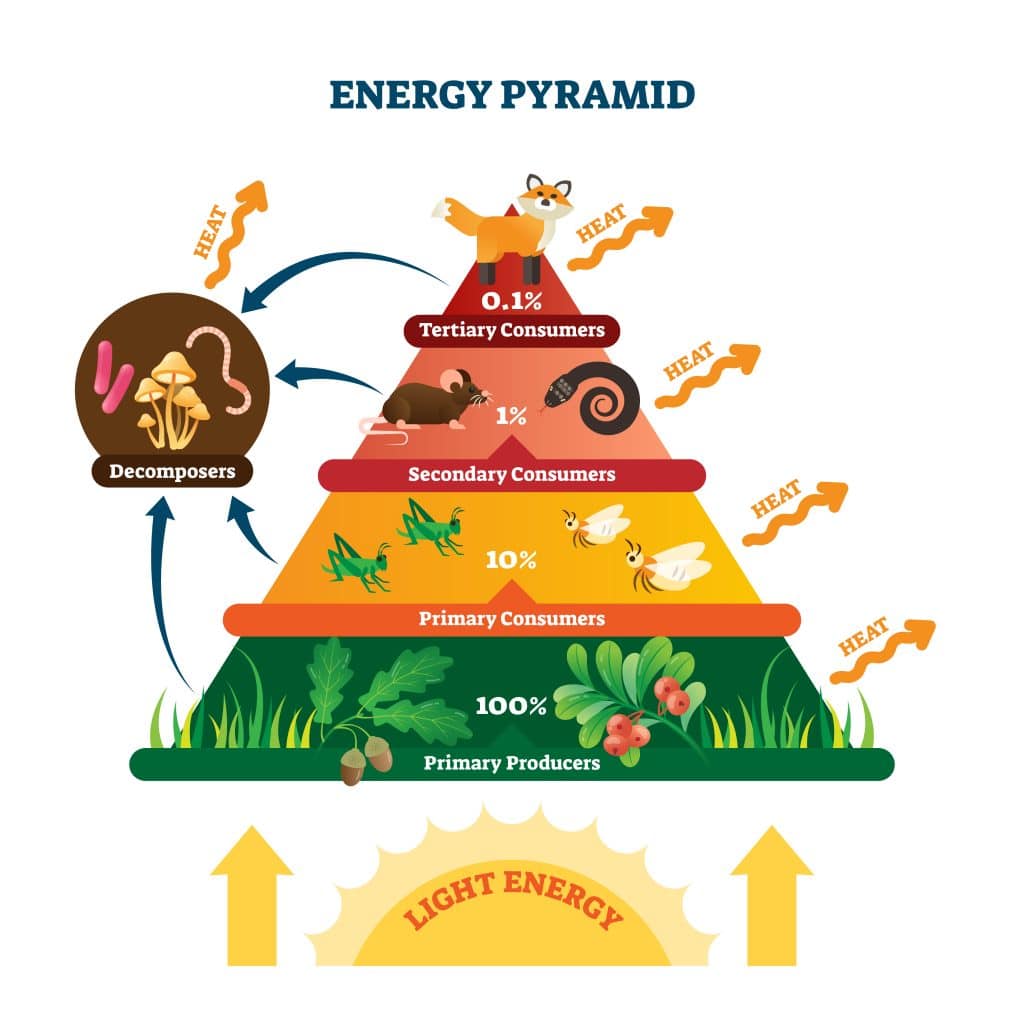
- Energy Pyramid: Depicts the amount of energy available at each trophic level, with a substantial reduction in energy from one level to the next due to the inefficiency of energy transfer (usually around 10%).
Here's what to focus on:
- Energy Loss: Only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is passed to the next, with the rest lost as heat, used in biological processes, or unconsumed.
- Prominence of Primary Producers: The base of the pyramid is always the widest, indicating that producers like plants are the most abundant in terms of numbers and biomass.
How to Work with Energy Pyramid Worksheets
Energy pyramid worksheets challenge students to:
- Calculate the energy transfer between levels.
- Analyze why some food chains are short and others longer based on energy limitations.
- Understand the ecological impact of removing or reducing a particular trophic level.
🌿 Note: Energy pyramids illustrate why ecosystems typically support fewer top predators than herbivores or plants; it’s a natural consequence of energy transfer inefficiency.
Interactive Learning with Food Chains and Energy Pyramids

Mastering these concepts can be enhanced through interactive and practical learning activities:
- Build Your Own Food Chain: Use actual organisms or images to create food chains, exploring different ecosystems.
- Energy Transfer Experiments: Conduct experiments or simulations to visualize the 10% rule and energy loss.
- Discussion and Debate: Hold discussions on how human activities affect food chains and pyramids, fostering critical thinking about conservation.
In summary, through worksheets dedicated to food chains and energy pyramids, students can visualize and quantify the energy flow in ecosystems. These tools not only help in understanding basic ecological principles but also encourage a deeper appreciation for the intricate balance of nature. By mastering these concepts, one can gain insights into ecological stability, the impact of species interactions, and how human activities might disrupt these natural systems.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?

+
A food chain is a simple, linear path showing how energy moves from one organism to the next. A food web, on the other hand, is more complex, consisting of multiple interconnected food chains, reflecting the reality of multiple feeding relationships in ecosystems.
Why do we have energy loss in energy pyramids?

+
Energy is lost at each trophic level due to metabolic processes like respiration, movement, and heat loss. Only about 10% of the energy is transferred to the next level because much of the energy is used by organisms for their own growth, reproduction, and survival.
How do invasive species affect food chains and energy pyramids?

+
Invasive species can disrupt existing food chains by consuming prey species or competing with native species for resources. This can alter energy pyramids by changing the biomass at different trophic levels, potentially leading to ecosystem imbalances or collapse of certain trophic levels.