Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction Rates: Worksheet Explained

The study of how quickly reactions take place is fundamental in chemistry, helping us understand the transformation of substances at the molecular level. Factors affecting chemical reaction rates include several key variables. In this post, we delve into the different elements influencing these rates, providing a clear explanation through a worksheet designed to enhance understanding.
Understanding Chemical Reaction Rates

The rate of a chemical reaction is essentially how fast or slow reactants convert into products. Several factors determine this speed:
- Temperature
- Concentration
- Pressure
- Catalysts
- Surface Area
- Nature of the Reactants
Each of these factors can either accelerate or decelerate the reaction process, and they often interact with each other in complex ways.
Factors Explained

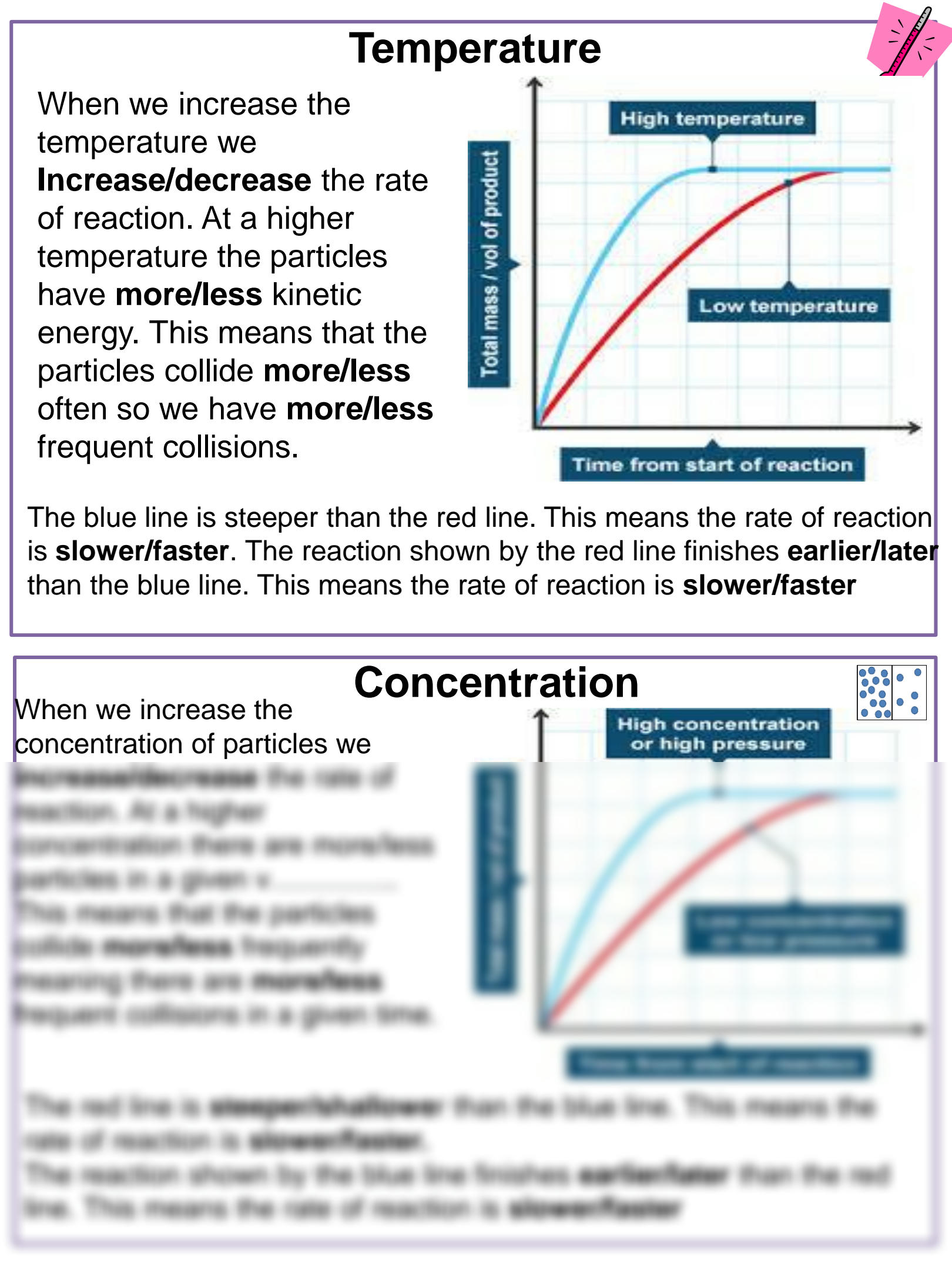
Temperature

Temperature directly influences the kinetic energy of particles, leading to:
- Increased collision frequency: More movement means more chances for molecules to collide and react.
- Higher energy collisions: At higher temperatures, particles have more energy, increasing the likelihood that collisions will result in a reaction.
- Overcoming activation energy: More particles possess energy above the activation energy threshold, making reactions easier.
🔥 Note: Remember that doubling the temperature does not mean doubling the reaction rate; it has a logarithmic relationship with the rate.
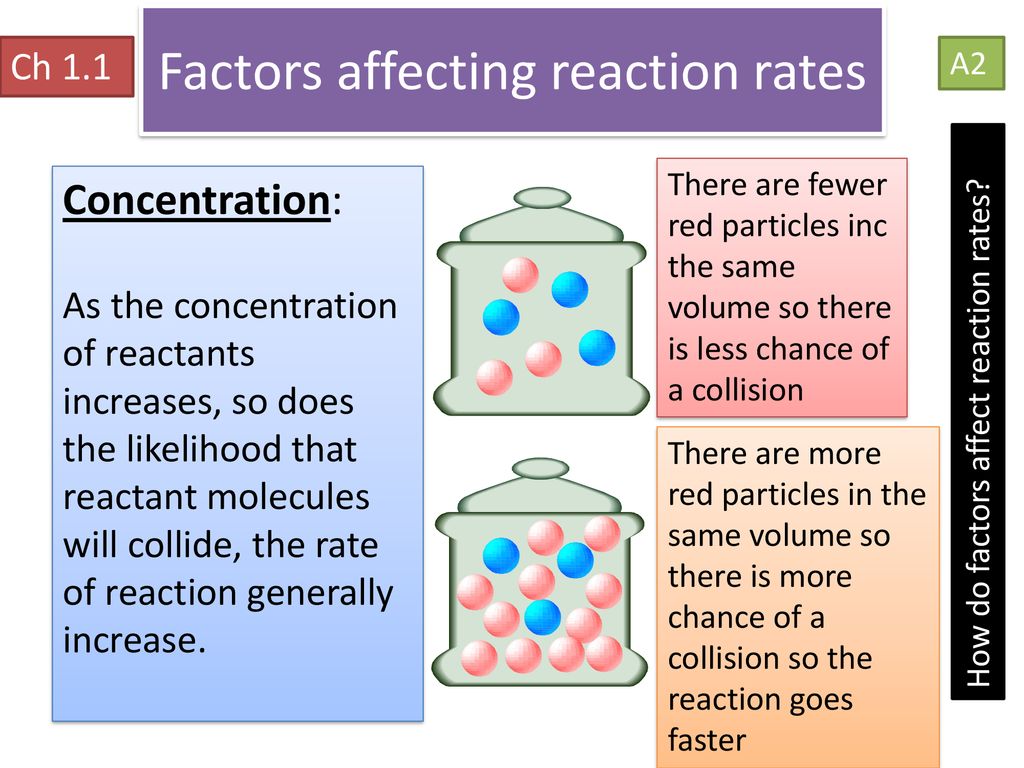
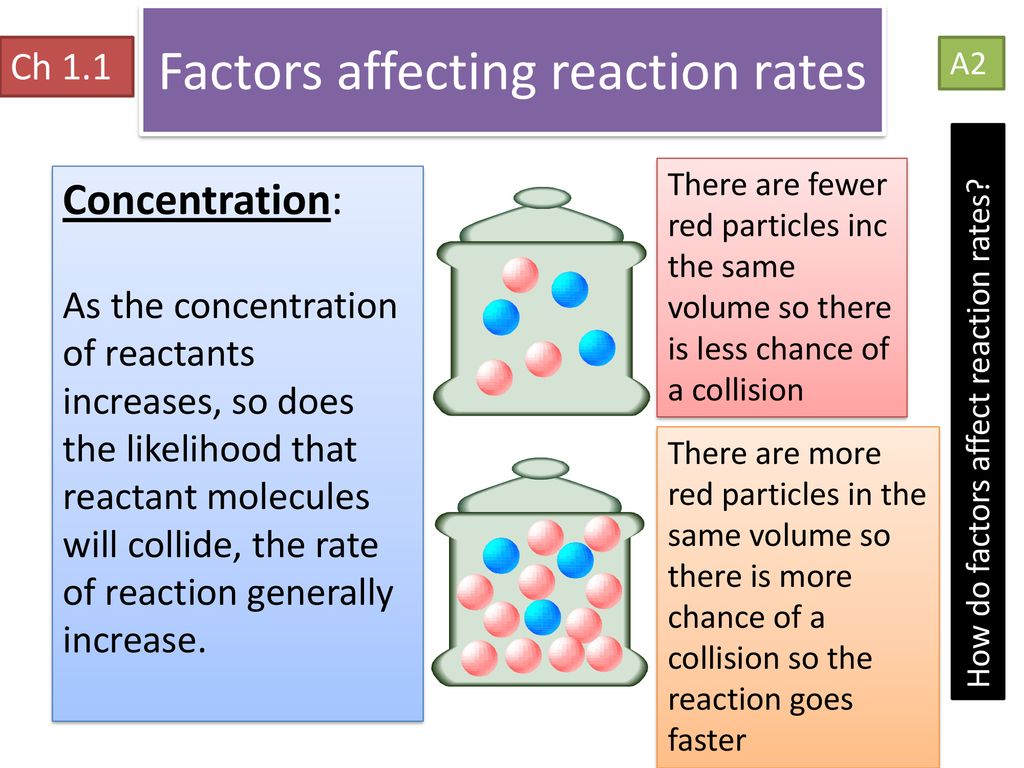
Concentration

Higher concentrations increase the probability of molecular collisions, as there are more reactant particles per unit volume:
- Increased collision frequency: With more particles in a given space, the likelihood of collisions increases.
- Higher effective collisions: More particles means a higher chance of particles colliding in the correct orientation for reaction.
Changing the concentration of a reactant can significantly alter the reaction rate, as depicted below:
| Concentration | Reaction Rate |
|---|---|
| Low | Slow |
| Medium | Moderate |
| High | Fast |

Pressure
Pressure affects reactions involving gases:
- Increased pressure increases density: Forcing gases closer together increases the number of collisions.
- However, the effect is not always significant: Only for reactions where volume changes occur during the reaction.
Catalysts

Catalysts speed up reactions by:
- Lowering activation energy: Catalysts provide an alternative pathway for the reaction with lower energy requirements.
- Increasing effective collisions: They may orient molecules correctly or temporarily bond to reactants, facilitating the reaction.
🧪 Note: Catalysts are not used up in the reaction, but they can be poisoned or deactivated by impurities in the reaction mixture.
Surface Area
The larger the surface area of the reactant:
- More exposed area for reaction: This principle is key in reactions involving solids. For example, powdering or crushing substances increases the rate of reaction by providing more surface area for reactants to interact with.
💡 Note: This is why reactions involving powders or finely ground substances proceed much faster than those with large, solid chunks.
Nature of the Reactants
The intrinsic properties of substances involved in a reaction can also influence the rate:
- Chemical bonding: Stronger bonds require more energy to break, slowing the reaction.
- Structure and phase: Reactants in gas or liquid phases react faster due to higher mobility than solids.
- Electronegativity and ionicity: More electronegative or ionic compounds often have different reactivity patterns.
Worksheet Analysis

The provided worksheet typically includes questions or scenarios that ask you to explain how these factors would impact specific reactions. Here’s an example question:
Question: Why does an increase in temperature generally increase the rate of a chemical reaction?
The answer involves discussing how increased temperature increases both the frequency and the energy of collisions, making reactions more likely to occur.
👩🔬 Note: Practical applications often use these principles to control or optimize reaction rates, like in industrial processes or pharmaceuticals.
Recap

Through this analysis, we’ve explored how temperature, concentration, pressure, catalysts, surface area, and the nature of reactants play critical roles in determining the rate of chemical reactions. By understanding these elements, chemists can predict, manipulate, and control reactions to meet their needs in industrial, environmental, or biological settings.
How does temperature affect reaction rates?

+
Temperature increases the rate of chemical reactions by enhancing the kinetic energy of the reactants, leading to more frequent and higher energy collisions, which are more likely to result in a reaction.
What role do catalysts play in reactions?
+
Catalysts accelerate reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, making it easier for reactants to turn into products without being consumed in the process.
Can concentration affect reaction rates?

+
Yes, higher concentrations mean more reactant particles in a given volume, increasing collision frequency and thus the rate of reactions. However, once a certain concentration is reached, the increase in rate slows down as the system reaches a saturation point.



