Estimating Addition and Subtraction: Free Worksheet Guide
Whether you're a student seeking to enhance your mental arithmetic or a teacher looking for resources to use in the classroom, understanding how to estimate addition and subtraction can be incredibly beneficial. This guide provides a detailed overview of estimating techniques, accompanied by a free worksheet for practice. Let’s dive into the world of estimation to make calculations quicker and more efficient.
Why Estimation Matters

Estimation is not just about getting a ballpark figure; it’s about sharpening your mathematical intuition. Here are some key reasons why estimation skills are essential:
- Quick Decision Making: In real-life scenarios, exact calculations are often unnecessary. Estimation helps in making swift, informed decisions.
- Error Checking: It’s a useful tool for spotting errors in calculations, either your own or someone else’s.
- Understanding Number Sense: Estimation deepens one’s understanding of numbers and their relationships, which is crucial for advanced math.
Basic Techniques for Estimation

Before diving into specific strategies, here are some foundational techniques for estimating addition and subtraction:
- Rounding: The most common approach involves rounding numbers to a nearby, easier-to-work-with value, usually to the nearest ten, hundred, or thousand.
- Front-End Estimation: This method focuses on using the leading digits to estimate an answer, particularly useful for long numbers.
- Clustering: When numbers are close to each other, estimate by choosing a middle value and using it for all.
Estimation in Addition

Addition estimation can be simplified with the following steps:
- Round Each Addend: For example, if you’re adding 47 and 34, round 47 to 50 and 34 to 30. 50 + 30 = 80, which is a decent estimate.
- Front-End Estimation: Using the above example, focus on the leading digits: 4 + 3 = 7, then consider the trailing digits for a closer estimate.
- Compensation: If you round down one number, you might round up another to balance out your estimate. For instance, 47 rounded down to 40, but 34 rounded up to 40, giving 40 + 40 = 80.
Estimation in Subtraction

Subtraction estimation requires a slightly different approach:
- Rounding Both Numbers: Similar to addition, round both numbers, but be mindful of the direction. For example, if you’re subtracting 138 from 297, you might round 297 up to 300 and 138 down to 140, giving 300 - 140 = 160.
- Adjusting After Estimation: If the estimated difference is too far off, you can adjust. If your estimate was 160 and you find it too high, go down slightly, perhaps to 150 or 155.
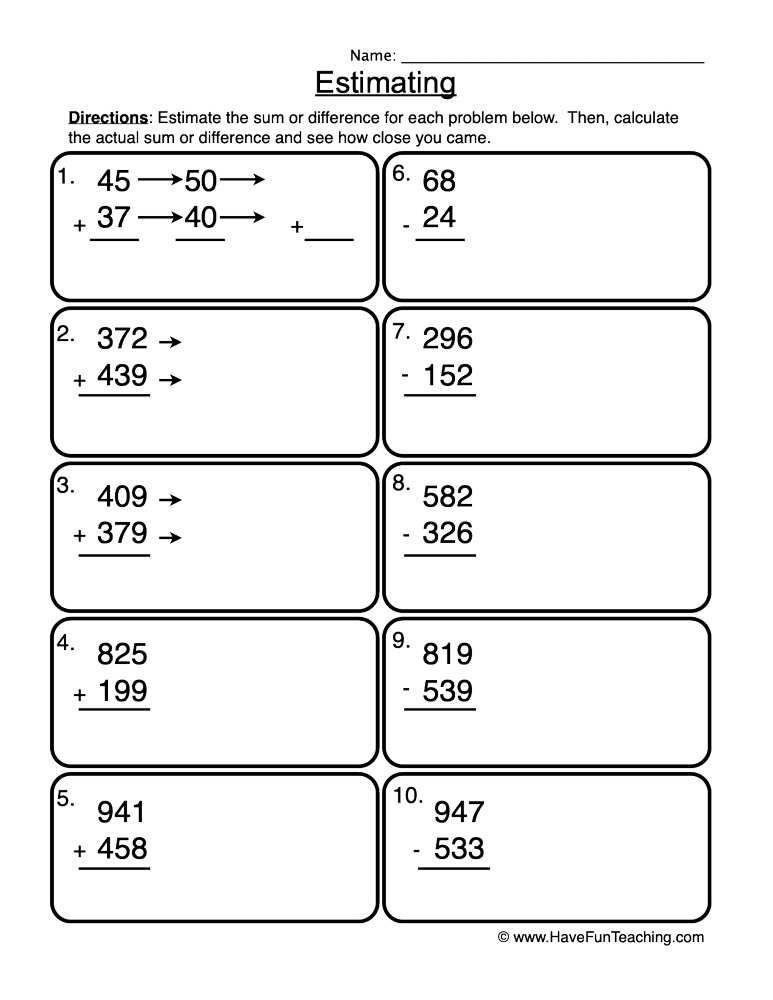
Using the Worksheet

We provide a free worksheet that includes various exercises to practice estimating addition and subtraction. Here’s how you can benefit from it:
- Practice Rounding: Several problems encourage students to round numbers before performing the operation.
- Front-End Estimation: Exercises guide students to focus on the leading digits for a quick estimate.
- Apply Compensation: Some problems require adjustment after rounding for more accuracy.
💡 Note: Estimation in math isn't just about simplification; it's also a tool for mental agility and precision in understanding numbers.
In summary, mastering the art of estimation allows for quicker mental calculations, error detection, and a better grasp of number sense. The free worksheet provided is an excellent starting point for practice, ensuring that both students and educators can engage with the material in a practical way. By integrating these techniques into everyday math problems, you'll not only speed up your calculations but also sharpen your overall mathematical proficiency.
Why is estimation important for students?

+
Estimation helps students in developing number sense, which is crucial for understanding more complex mathematical concepts, making quick decisions, and checking for calculation errors.
How can I make my child better at estimating?
+
Practice with worksheets like the one provided here, encourage daily real-life estimation exercises, and play math estimation games to make learning fun.
Can estimation be used in other subjects?

+
Yes! Estimation skills can be applied in science for measuring, in art for scaling, in social studies for time frames, and many other areas where quick, rough calculations are beneficial.



