5 Ways Enzymes Act as Catalysts: Worksheet Answers
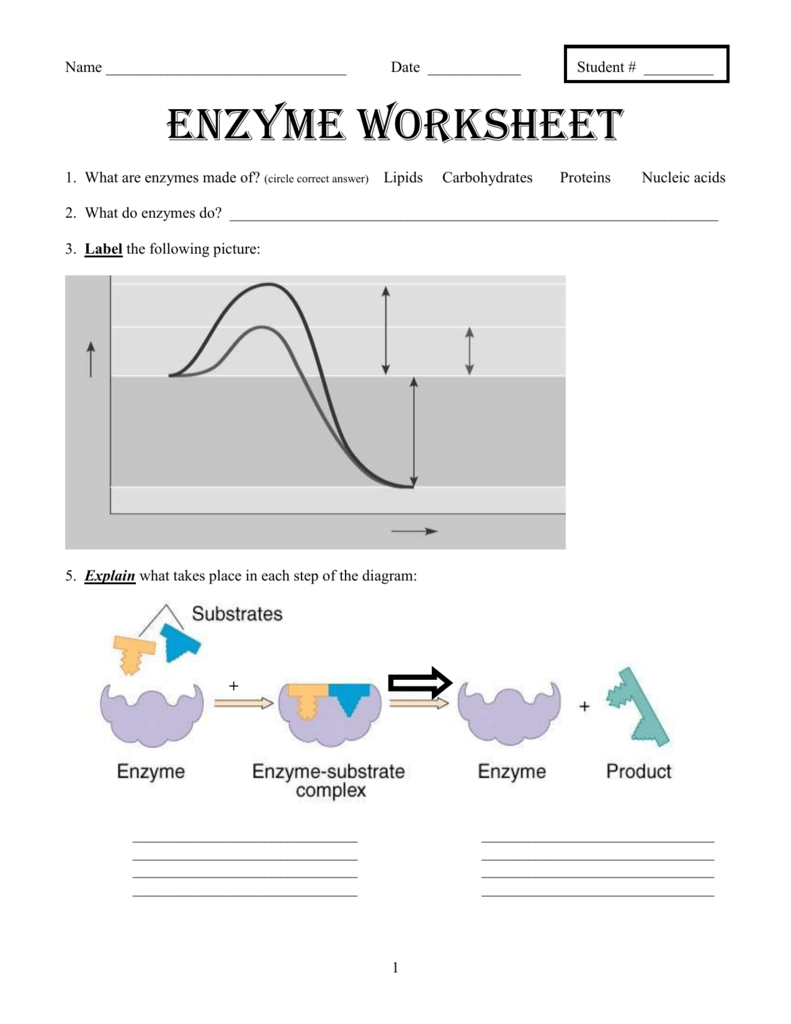
Enzymes are fascinating biological molecules that enhance the rate of numerous chemical reactions in the body without being consumed in the process. Known for their specificity and efficiency, enzymes are crucial in various metabolic pathways. Here, we delve into the five primary ways enzymes act as catalysts, providing detailed explanations and examples to enhance your understanding.
1. Lowering Activation Energy

One of the most significant roles of an enzyme is to lower the activation energy needed to start a reaction:
- The activation energy is the energy barrier that must be overcome for reactants to transform into products.
- Enzymes facilitate this by bringing reactants closer together or stabilizing the transition state, effectively reducing the energy requirement.
🧪 Note: Without enzymes, biological reactions would occur at a rate too slow to sustain life’s rapid processes.
2. Orienting Substrates Correctly

Enzymes ensure that reactions occur by:
- Orienting substrates (reactants) in a precise spatial arrangement.
- This orientation aligns the reactive parts of molecules to maximize collision efficiency.
Example: The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose. It orients glucose and ATP in a way that their phosphate groups are close together, allowing the transfer of the phosphate group with minimal energy expenditure.
3. Induced Fit Mechanism
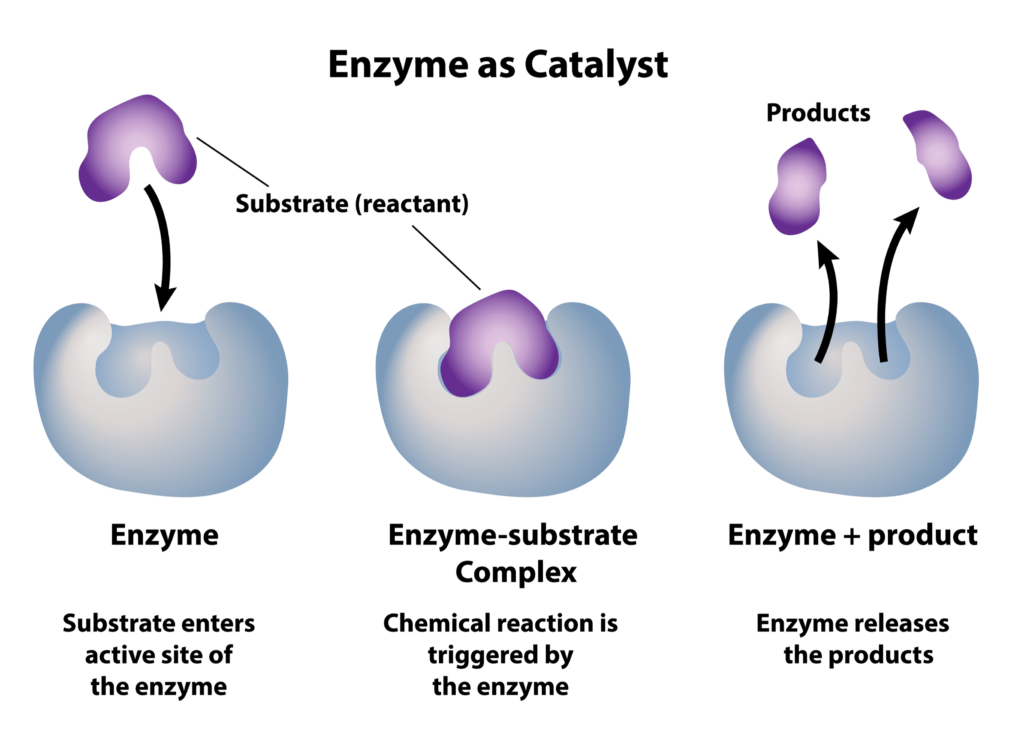
The concept of induced fit further explains enzyme functionality:
- Upon substrate binding, the enzyme’s shape changes slightly to fit the substrate more perfectly.
- This conformational change stresses the bonds in the substrate, promoting the reaction.
This model provides a dynamic view of how enzymes actively participate in catalysis, beyond the once-popular lock-and-key model.
4. Stabilizing Transition States

Enzymes can:
- Stabilize the transition state, which is a high-energy intermediate state of the reaction.
- This stabilization lowers the energy needed to reach this state, speeding up the reaction.
Enzyme-substrate interaction often involves forming temporary covalent bonds or other interactions that make the transition state more stable.
5. Providing Microenvironments

Enzymes can create:
- Unique microenvironments where the reaction conditions are more favorable.
- For example, some enzymes may contain cavities with specific pH or ion concentrations that are optimal for the reaction.
Such microenvironments ensure that the chemical reaction occurs under conditions that are not generally available in the cell’s cytoplasm.
Enzymes are not just passive entities but active participants in biochemical reactions. Their ability to decrease activation energy, orient substrates, induce fit changes, stabilize transition states, and create specific reaction environments makes them indispensable to life. By understanding these mechanisms, we gain insight into the complexity and efficiency of biological systems.
Enzyme Catalysis in Daily Life

Understanding how enzymes work can have practical implications in daily life:
- From enhancing digestion processes to industrial applications in cleaning products or fermentation, the principles of enzyme catalysis are ubiquitous.
- Biotechnological advancements use engineered enzymes to produce pharmaceuticals or degrade pollutants, showing the direct application of these concepts.
Enzyme catalysis is not just a topic for the biochemistry classroom; it permeates our daily existence, making our biological processes efficient and sustainable. The intricacies of how enzymes lower the energy barriers, manipulate substrate orientation, and provide optimal conditions for reactions are what make life possible at its core. This knowledge not only helps in understanding human physiology but also in innovating solutions for various industries.
What is the lock-and-key model of enzyme action?

+
The lock-and-key model suggests that the enzyme’s active site has a specific shape into which the substrate fits perfectly, like a key into a lock. This model, while simplistic, helped in understanding the specificity of enzymes.
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
+
Competitive inhibitors compete with the substrate for the enzyme’s active site, reducing the enzyme’s efficiency by blocking substrate binding. This inhibition can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration.
Why are enzymes specific to certain reactions?

+
Enzyme specificity arises from the unique three-dimensional structure of the enzyme’s active site, which matches only specific substrates due to the shape, charge, and hydrophobic interactions.
Can enzymes be reused after catalyzing a reaction?

+
Yes, enzymes are not consumed during reactions. After the reaction, the enzyme returns to its original shape, ready to bind another substrate molecule, ensuring it can participate in multiple reactions.
What happens to enzyme activity at extremely high or low temperatures?
+
At high temperatures, enzymes can denature, losing their structure and functionality. At very low temperatures, enzyme activity slows down significantly due to reduced molecular motion, although the structure remains intact.



